NAME _________________________________________ PERIOD _______ DATE ___________________
advertisement
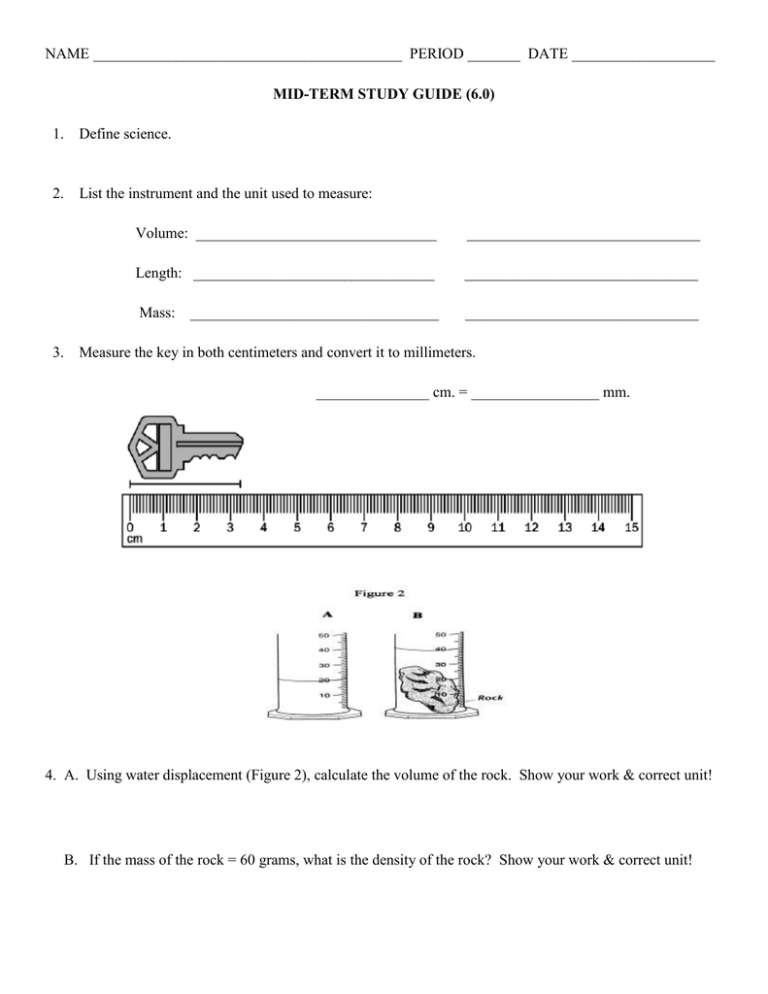
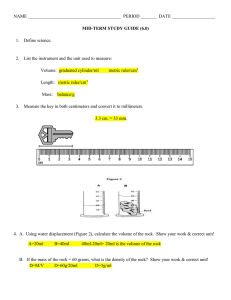
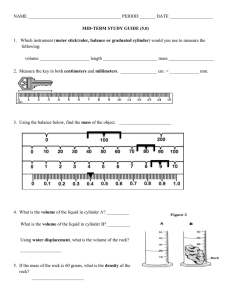
NAME _________________________________________ PERIOD _______ DATE ___________________ MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE (6.0) 1. Define science. 2. List the instrument and the unit used to measure: 3. Volume: ________________________________ _______________________________ Length: ________________________________ _______________________________ Mass: _______________________________ _________________________________ Measure the key in both centimeters and convert it to millimeters. _______________ cm. = _________________ mm. 4. A. Using water displacement (Figure 2), calculate the volume of the rock. Show your work & correct unit! B. If the mass of the rock = 60 grams, what is the density of the rock? Show your work & correct unit! 5. Compare and contrast the 3 states of matter. Include information about each one’s shape, volume, the arrangement and motion of particles. 6. In an atom: A proton is: A neutron is: An electron is: The atomic number equals: The mass number equals: 7. Given a periodic table: How do you find the number of protons in an element? How do you find the number of neutrons? How do you find the number of electrons? 8. What is the difference between an element, a compound and a mixture? Give an example of each. 9. What is the difference between a chemical and physical change? Give an example of each. 10. List and describe the six phase changes and whether energy is gained or lost to cause each one. 11. Density of Liquid A = 1.98 g/mL Density of Liquid B = 0.75 g/mL Density of Liquid C = 1.14 g/mL Density of Liquid D = 0.50 g/mL If the liquids were poured into a beaker, they create a density column. Using the densities, label the beaker. 12. Write the formula to calculate density. What is the density of the object if the mass is 250 grams and has a volume of 500 ml? Will this object sink or float when placed in water? Explain your answer. Below is a scenario. Read it carefully and answer Questions #13 - 18. A. Shara wanted to find out if flowers grew faster with sugar in the water. B. She believed the sugar would make the flower grow faster. C. Shara filled 4 jars with 200 ml of water. Jar A had 10 ml of sugar added; Jar B had 20 ml. of sugar added and Jar C had 30 ml. of sugar added. D. Jar D had no sugar in it. E. The flowers in the sugar water all died. The more sugar in the water, the faster the flowers died. F. The flower in Jar D ( no sugar) lasted for 10 days. 13. Which letter represents the problem? _______________ 14. In which statement does Shara state her hypothesis? ____________________ 15. What is the control in the experiment? _______________________________________________________ 16. What is the independent variable in this experiment? ___________________________________________ 17. What is the dependent variable in this experiment? ____________________________________________ 18. In which statement is the conclusion? ______________ 19. Using the chart, explain how you could distinguish between magnetite and hematite? 20. Which mineral in the table will scratch every other mineral in the table? ___________________________ 21. List the hardness of the following from the field hardness kit. Fingernail = copper = glass = 22. What does the streak tell you about the mineral? 23. What are some negative effects of mining? 24. List the two classifications of igneous rocks. Define and give an example of each. 25. List the three classifications of sedimentary rocks. Define and give an example of each. 26. Name and describe the 5 agents of physical weathering 27. Explain why fossils are usually found in sedimentary rocks rather than igneous or metamorphic rocks. 28. How are rocks and minerals similar? How are they different? 29. How do animals aid in soil formation? 30. Bedrock has been exposed at the surface, what are the steps/processes involved to create a developed soil profile? 31. Draw and explain the processes within the rock cycle.