Protein Synthesis Summary
advertisement
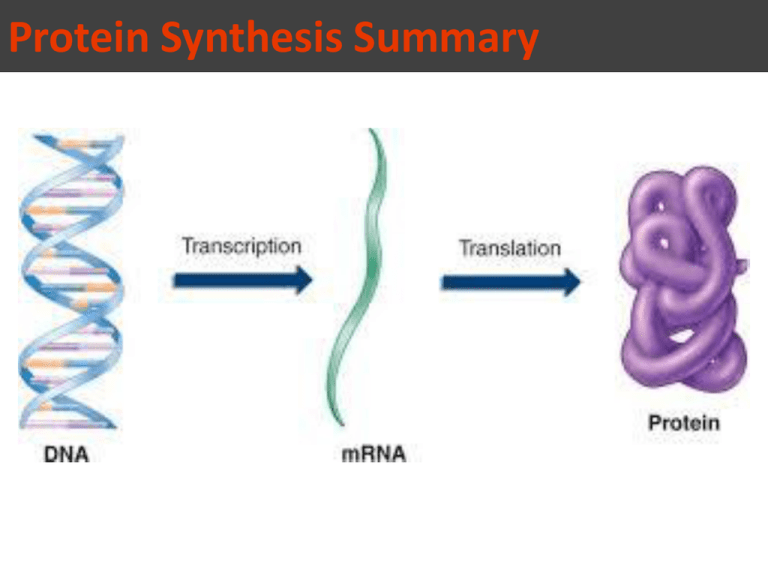
Protein Synthesis Summary Central Dogma - FLOW IS FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Transcription • Purpose: To copy a segment of DNA into mRNA. • Location: Inside the nucleus. • Process: – RNA polymerase: an enzyme that unwinds DNA helix and uses base pairing rules to make mRNA from a DNA template or coding strand. – Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that RNA polymerase binds to begin making mRNA (TATAATA box) Transcription • Transcribe the DNA sequence below: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8nQH0GqFn6k http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMtWvDbfHLo Transcription RNA Editing (occurs between transcription and translation) • 2% of the DNA in the nucleus is used to make proteins. • Gene: sequences of DNA that code for proteins. • Before the mRNA can leave the nucleus the DNA that is used to make proteins must be separated from the DNA that does not make proteins. I THINK ITHINKLWOIKTPQIETHATQWEOIUZMWOBIOLOGYAPOIROCKS THAT BIOLOGY ROCKS Introns: Segments of DNA that do not code for proteins. These are removed before mRNA leaves the nucleus Exons: the segments of DNA that code for a protein. These are spliced together once introns are removed Transcription RNA Editing •Poly-A tail is added to the 3’ end of the mRNA. – Allows the mRNA to leave through pores in the nuclear membrane. – Protects the mRNA from enzymes as it leaves the nucleus. • Guanine cap is added to the 5’ end of the mRNA. – The guanine cap allows the mRNA to be recognized by the ribosome. Exon Intron Exon Intron Exon DNA Cap RNA transcript with cap and tail Transcription Addition of cap and tail Introns removed Tail Exons spliced together mRNA Coding sequence Nucleus Cytoplasm