Document 14147122

1.1
What is Statistics?
Statistics is the study of how to _____________________, _________________________,
_________________________, and ____________________ numerical information from data
Individuals are the ______________________________________________
Variable is the ________________________ of the individual to be ____________________ or
________________________.
Example: If we wanted to do a study about people who have Mr. Graham for
Statistics ________________________ would be the individuals. A ____________________ could
be height, weight, gpa, Elementary School, etc.
Quantitative Variable:
Ex:
Qualitative Variable:
Ex:
Population Data :
Ex:
Sample Data:
Ex:
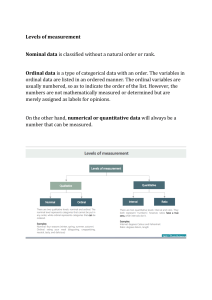
Levels of Measurement
Nominal: “In name only” Data only describes a quality or name but would not make sense to put the data in any order because no one is “greater” or “less” than the other
Ex:
Ordinal : Data can be put in ORDER but the actual differences between values either can’t be determined or is meaningless.
EX:
Interval : Just like ordinal BUT, there are meaningful differences between the daa values. There may not be an intrinsic ZERO or STARTING POINT. Differences are meaningful but ratios are not.
EX:
Ratio : Highest level of measurement. We can order, take differences and also find the ratio. It makes sense that one data value is “twice as large” as another for example. IT INCLUDES AN INHERENT ZERO OR STARTING POINT.
EX:
Descriptive Statistics : Organizes, pictures, and summarizes information from
samples or populations.
Inferential Statistics : involves methods of using information forma sample to draw conclusion regarding the population.