Chapter 48 Signal Propagation
advertisement
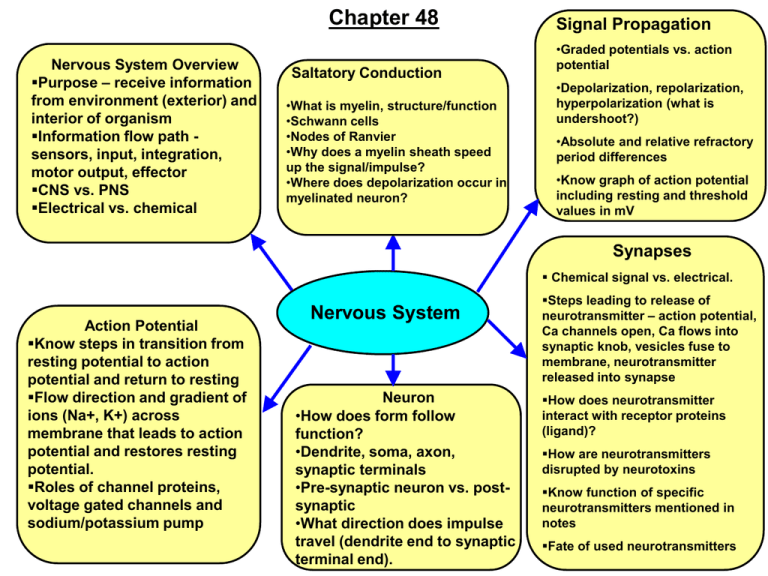
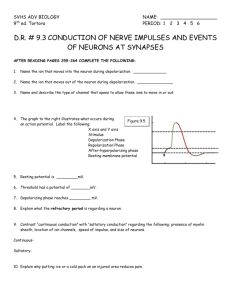
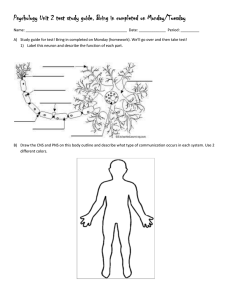
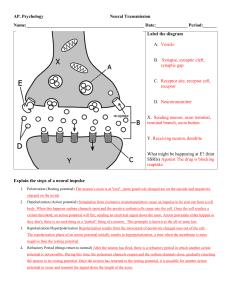
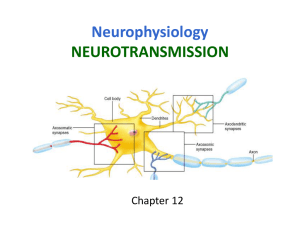
Chapter 48 Nervous System Overview Purpose – receive information from environment (exterior) and interior of organism Information flow path sensors, input, integration, motor output, effector CNS vs. PNS Electrical vs. chemical Saltatory Conduction •What is myelin, structure/function •Schwann cells •Nodes of Ranvier •Why does a myelin sheath speed up the signal/impulse? •Where does depolarization occur in myelinated neuron? Signal Propagation •Graded potentials vs. action potential •Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization (what is undershoot?) •Absolute and relative refractory period differences •Know graph of action potential including resting and threshold values in mV Synapses Chemical signal vs. electrical. Action Potential Know steps in transition from resting potential to action potential and return to resting Flow direction and gradient of ions (Na+, K+) across membrane that leads to action potential and restores resting potential. Roles of channel proteins, voltage gated channels and sodium/potassium pump Nervous System Neuron •How does form follow function? •Dendrite, soma, axon, synaptic terminals •Pre-synaptic neuron vs. postsynaptic •What direction does impulse travel (dendrite end to synaptic terminal end). Steps leading to release of neurotransmitter – action potential, Ca channels open, Ca flows into synaptic knob, vesicles fuse to membrane, neurotransmitter released into synapse How does neurotransmitter interact with receptor proteins (ligand)? How are neurotransmitters disrupted by neurotoxins Know function of specific neurotransmitters mentioned in notes Fate of used neurotransmitters