Surface Water and Groundwater Fusion Text: Pages 30-38
advertisement

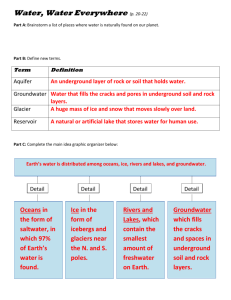
Surface Water and Groundwater Fusion Text: Pages 30-38 Where on the Earth is fresh water found? • On the Earth’s Surface (Surface Water) • Beneath the Earth’s surface (Groundwater) • On the Earth’s Surface (Surface Water) Streams, Rivers, and Lakes. Comes from precipitation or fresh water streams (springs). Water that flows across the Earth’s surface is called runoff. Runoff can enter streams, rivers and lakes. • Beneath the Earth’s Surface (Groundwater) Water drains down through the soil because of gravity and collects in the spaces between rock particles. Most drinking water in the U.S. comes from drilling wells down into the water table or aquifers. The water table is the upper boundary, or surface, of a location’s groundwater. How does water move on the Earth’s surface? • Precipitation hits the Earth and flows from high to low ground forming streams. • Streams erode rocks and form channels. • Channels are paths that streams follow. • Tributaries are small streams that feed into river systems. • A river system is a network of streams and rivers that drain an area of runoff called a watershed. Watersheds • A watershed is an area of land that is drained by a river system. • Watersheds are separated from one another by a ridge or an area of higher ground called a divide. • A large part of Pennsylvania lies within the Chesapeake Bay Watershed. http://techalive.mtu.edu/meec/demo/Watershed.html Rivers and Streams • Gradient describes the steepness of the ground that a stream or river runs down. • Steep gradients, rainstorms and rapid snow melt increase the flow rate of streams and rivers. • The flow rate is the amount of water that flows through a channel in a given amount of time. • The flow rate determines the stream load, or the size and amount of particles carried and deposited. How does groundwater flow? • Water from precipitation or streams may percolate or seep below the Earth’s surface to become groundwater. • An aquifer is a body of rock or sediment that stores groundwater. • Recharge occurs when water seeps through the ground and enters an aquifer. • Discharge occurs when groundwater becomes surface water which pools to form wetlands or flowing as a spring. • Groundwater is also discharged where water is extracted from wells which are drilled into the water table. How do people use surface water and groundwater? • Drinking and Home Use • Agriculture • Industry • Transportation and Recreation Drinking and Home Use • Surface water and groundwater are both important sources of drinking water. • In a typical home, 50% of all water is used for washing clothes, bathing, washing dishes and flushing toilets. • About 33% of all water used is to water lawns and gardens. • The remaining 12% is used for drinking, cooking and washing hands. Drinking and Home Use Agriculture • 40% of the fresh water in the U.S. is used for growing crops and raising livestock. • These activities account for about 70% of all groundwater use. Industry • Almost half of the fresh water used in the U.S. is used for industry. • Almost half of the water used in industry helps cool elements in power plants. Transportation and Recreation • Surface water is used to transport products and people from place to place. • People use rivers, streams and lakes for recreation. Water Skiing Sailing Swimming Fishing