Earth’s Interior
advertisement

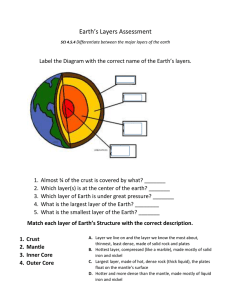
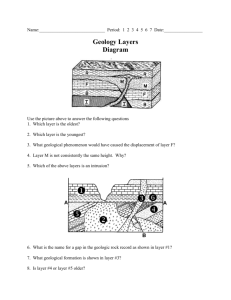
Earth’s Interior How do Scientists know? • About the interior? • Using observations to make a claim about something we can’t see directly. – Based on inferences. – Scientists use seismic waveswaves produced by earthquakes. • They act differently as they travel through the Earth and they reveal the different layers. A Journey to the Center • Temperature: – Temperature increases as you descend towards the center. • Pressure: – Pressure is the force pushing on a surface or area. – Pressure increases as you descend towards the center. • More rock layers are on top of you pressing down. Earth’s Compositional Layers Crust • • • • Solid “Rocky” outer layer Thinnest layer (5-40km) Oxygen & Silicon Two types of Crust – 1. Ocean- Basalt – 2. Continental- Granite – 3. Ocean crust is denser than cont. Layers of Earth Menu Mantle • Second Major Layer – Thickest layer. (2,900km) • Half way to the center of the Earth. • Composed of: – – – – Silicon (Si) Oxygen (O) Magnesium (Mg) Iron (Fe) • Temperature and Pressure increase with depth. Layers of Earth Menu The Core • Third Layer (2,250km) • Mostly Iron & Nickel • Makes up one third of the Earth’s mass. Layers of Earth Menu Earth’s Physical Layers Lithosphere • “Rock” Sphere. (15-300km) • Includes the Crust • Rigid layer that floats on the asthenosphere. • It is broken into moving plates Layers of Earth Menu Asthenopsphere • “Weak” sphere. (250km) • Can flow, Plastic/Fluid Like • Acts like silly putty. • Convections currents cause it to flow Layers of Earth Menu Mesosphere • Lower part of the mantle • Solid rock • Flows slower than the asthenosphere Layers of Earth Menu The Outer Core • Third Layer (2,250km) • Molten Metal (2,200˚C) • 1. Iron and Nickel • Plastic/Fluid Like – Behaves like a liquid. Layers of Earth Menu The Inner Core • Rigid- extreme pressure keeps the atoms from spreading apart. • Center of the Earth. – (1,200km) – Hottest Layer (5,000˚C) • Dense solid metal ball. – Iron and Nickel Layers of Earth Menu