Air Pressure p. 107
advertisement

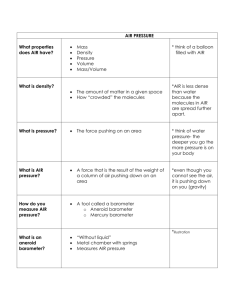
Air Pressure p. 107 Air Lab • Problem: – Does Air Have Mass? • Hypothesis: – Air has mass. – Air doesn't have mass. • Materials: – Stopwatch beaker Graduated cylinder metric ruler balance Air Lab • Procedure: – Write a Step by Step Procedure – Start with a verb. • Data/Obs: (Record Obs) • Conclusion: – Identify the Problem, Hypothesis, explain if data supported it or not. Balloon In Jar • Problem: What are ways the balloon can be inflated in the jar? • Hypothesis: – Blowing in tube B will inflate the balloon. – Pulling air out of tube A will inflate the balloon. Balloon In Jar (Observations) Demonstrations Empty Water Bottle Peeps Shaving Cream Empty Water Bottle • Problem: – What will happen to the water bottle in the vacuum? • Hypothesis: • Observations: – The water bottle expanded. Peep Show • Problem: What will happen to the peeps in the vacuum? • Hypothesis: • Observations: – The peeps grew larger. Shaving Cream • Problem: – What will happen to the shaving cream in the vacuum? • Hypothesis: • Observations: – The shaving cream grew and expanded upward. Properties of Air • Air has the following Properties: Air Molecule Model • Gases consist of molecules which have: – mass and occupy a volume. • Therefore: they have density. • These molecules move randomly and bump into each other. Density • The amount of mass in a given volume of air. • Density=mass/volume Air Molecule Model Calculate the density in each box. Air Molecule Model Situation 1 Calculate the density for each side. Draw a line to show where the wall should move? Air Molecule Model Situation 1 • The density is greater on the left, therefore pressure is higher. • There are more molecules on the left side and there will be more molecules striking the wall. – As a result, the wall will move to the right. Air Molecule Model Situation 2 Calculate the density for each side. Draw a line to show where the wall will move? Air Molecule Model Situation 2 • The density of air is higher on the right, therefore the pressure is greater. • The molecules on the right side will hit the wall more frequently, – therefore the wall will move to the left. Pressure • The force on an area or surface. • More mass in a given volume = a higher density. As a result pressure will be greater. (Air) Pressure • The result of the weight of a column of air pushing down on an area. • The weight of a column of air above the desk = the weight of a large school bus. Desk Vs Air Pressure • Why isn’t the desk crushed? – Molecules of air push in all directions. – The pressure is balanced by the air pushing up on the desk. Balloon In Jar (Explanation) Balloon In Jar Measuring Air Pressure • A barometer is used to measure air pressure. – Mercury Barometers – Aneroid Barometers Mercury Barometer • The first barometers. • Pressure pushes on the surface of the mercury. • When pressure increases the mercury rises up the tube. • When pressure decreases the mercury falls in the tube. Feeling the Pressure • Which barometer shows a higher pressure? • Which barometer shows a lower pressure? Aneroid Barometer • “without liquid” • Uses an air tight metal chamber. • The chamber is sensitive to changes in air pressure. Units of Air Pressure • Weather Reports use inches of mercury. • National Weather Service Maps use millibars. • 1 inHg = 33.87 millibars Air Pressure and Density Altitude Affects Pressure • Altitude – elevation • Air pressure is the weight of a column of air pushing down on an area. • Where is the pressure greater/less? Altitude Affects Pressure • Less weight at the topso there is lower air pressure. • Sea-level has the weight of the whole atmosphere on it.Pressure is greatest here. Altitude Affects Density • As you increase in altitude, the density of air decreases. • Air pressure decreases as altitude increases. • As air pressure decreases so does density. Altitude Affects Density • As you go up, there are fewer molecules. • However: The percent of a gas in the atmosphere always stays the same at any altitude. – 78% Nitrogen – 21% Oxygen Isobar Maps Rules for Drawing Isobars • Lines connect areas of __________pressure. Sunny (Happy) Weather Cloudy (Lousy) Weather • Set an interval that • Make sure all points on one side of a line is appropriate for are higher and lower the change in on the other. pressure. Practice Drawing Isobars . 1008 . 1007 . 1008 . 1005 . 1007 . 1004 . 1002 . 1007 . 1006 . 1008 . 1004 . 1005 . 1002 . 1006 . 998 . 1005 . 1004 . 1001 . 1003 . 1003 . 1002 Practice Drawing Isobars Draw Isobars on the diagram below. Mark the center of low pressure and high pressure with an H and L. Interval = ___________________ .1004 .1000 .1005 .996 .1000 .1000 .1007 .998 .1012 .1009 .1013 .1010 .1015 .1020 Drawing Isobars Isobar Maps on RHW • Isobars connect lines of equal pressure. Cloudy (Lousy) Weather Sunny (Happy) Weather