Genetics Review – Name:_______________ A. Dominant/Recessive
advertisement

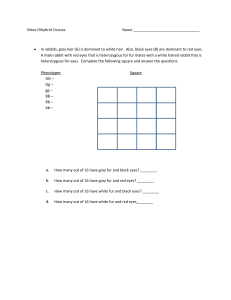
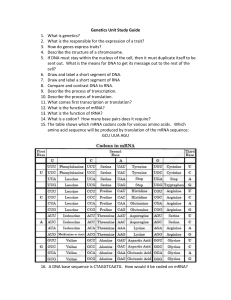
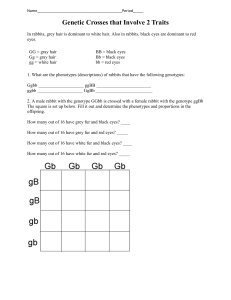
Genetics Review – Name:_______________ A. Dominant/Recessive B. Incomplete dominance/Codominance C. Sex linked traits, pedigrees and non-disjunction. 1. Mom and Dad are both heterozygous for freckles and a widow’s peak (both dominant traits). What are the possible phenotypes for their children? 2. A rabbit with black fur mates with a rabbit with white fur. A third phenotype of rabbits with gray fur exists in the population. What would the offspring look like when the rabbit with black fur and rabbit with white fur mate? What is the inheritance pattern? 3. A pink four o clock is crossed with a white four o clock. What will the phenotypes of the offspring be? 4. Jake has type B blood, and his brother John has type O blood. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for their parents? 5. Complete the punnett square: XBXB x XbY. (B = normal eyesight, b = colorblind) How many of their daughters and sons would be color blind? 6. Color blindness, a sex-linked disorder, is a genetic disease. A female carrier and a male with normal eyesight want to have children. What are the phenotypes of their offspring? 7. How would it be possible for parents to have both a boy and a girl with a sex-linked disease? 8. The boxes below each show a step to explain how genetic disorders have a molecular basis. Number them so that the steps are in the correct order. A change in phenotype results. A gene’s DNA sequence changes. The amino acid sequence that alters a protein changes. Using Science Skills Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure 14–5 9. In the human karyotype in Figure 14–5, what term is used to describe the pair of chromosomes in each numbered group? (hint: each pair goes together like pairs of shoes– we discussed them in meiosis) 10. In Figure 14–5, how are the chromosomes that make up each numbered pair similar? 11. Which chromosomes in Figure 14–5 are autosomes (circle them)? 12. The karyotype shown in 14-5 illustrates a chromosomal abnormality called Klinefelter’s syndrome. Explain why this person is a male, even though he has two X chromosomes? 13. Complete this graphic organizer to explain the process and outcomes of nondisjunction. Definition: Sketch of Process: NONDISJUNCTION Example of Outcome (in genotype): Example of Outcome (in phenotype): Figure 14–6 14. Could Figure 14–6 show the pattern for the transmission of colorblindness? Explain your answer by showing the genotypes.