Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics 11-1 The Work of Mendel
Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics
11-1 The Work of Mendel
•
What does every living thing inherit from their parents?
•
Genetics – __________________________________________________
Look around at your classmates and make a list of some of the traits that are inherited. _______________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
What did Mendel already knew …
•
Each flower produces ____________ and _____________
•
Cross fertilization (sexual) – ___________________________________
•
Self-pollination (asexual) – ____________________________________
• Mendel’s pea plants were __________________________
– A tall plant with green seeds would produce a ____________________________
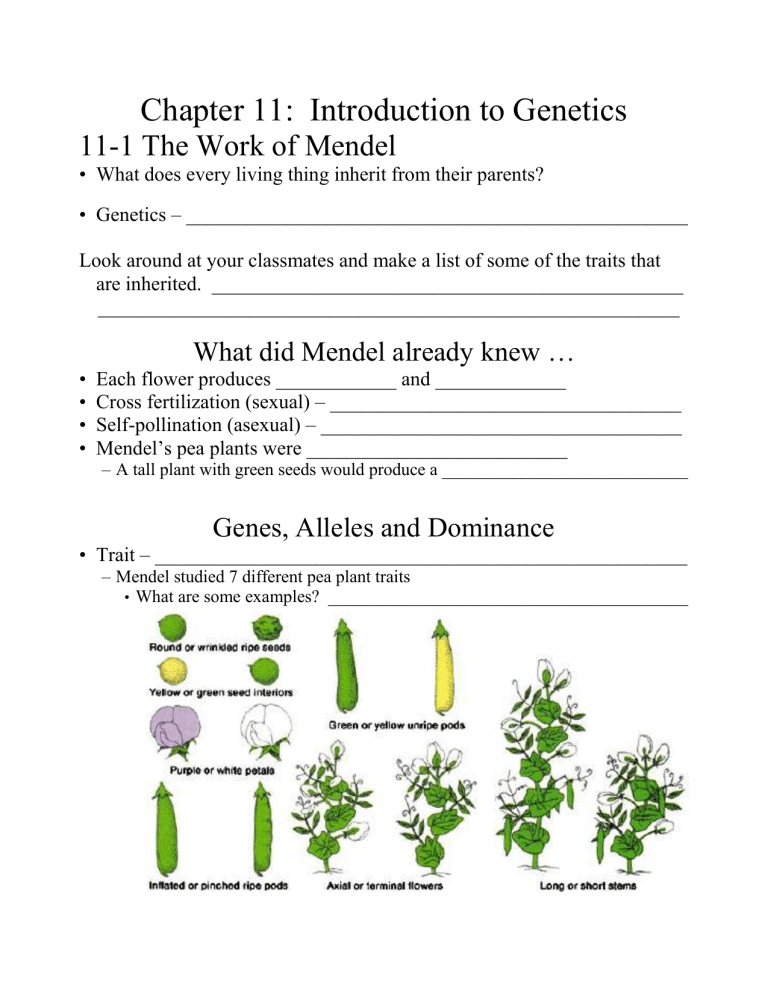
Genes, Alleles and Dominance
•
Trait – _____________________________________________________
– Mendel studied 7 different pea plant traits
• What are some examples? _________________________________________
Genes, Alleles and Dominance
____________ – the chemical factors that determine traits (the segment of DNA) ex. pea plant: height
_______________ – different forms of a gene from each parent ex. pea plants: tall and short (T or t)
Principle of Dominance
•
Principle of dominance: ______________________________________
___________________________________________________________
•
Dominant allele – ____________________________________________
– Capital letter (T=tall)
•
Recessive allele – ____________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
–
Lower case letter (t=short)
•
Heterozygous – _____________________________________________
•
______________________ for that trait
•
Ex: Tt
•
Homozygous – ______________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
•
____________________ for a particular trait
•
Ex: TT or tt
•
Phenotype – __________________________
•
Ex: ____________________________________
•
Genotype – ___________________________
•
Ex: _____________________________________
•
Tall plants have the same ______________ (tall), but not the same
________________ (TT or Tt)
•
Why are TT and Tt genotypes for tallness, but tt is not???
11-2 Probability and Punnett Squares
• Mendel realized…the principles of ______________ could be used to explain the results of genetic crosses.
Genetics and Probability
•
Probability – ________________________________________________
• Ex: probability of flipping a coin to heads = ½ or _____%
• Probability of head 3 times in a row = ½ x ½ x ½ = _____
•
The ________ the number or trials, the closer to the expected ratio
•
_______ outcomes do not affect _______ outcomes
•
Alleles segregate randomly (like a coin)
Principle of Segregation
•
Segregation = _____________________
•
The alleles for tall vs. short separate during the formation of __________________ – sex cells
•
Each gamete carries
________________________
The Two-factor Cross: F1
•
____ alleles (2 genes) at the same time
•
Provides the __________ plants (F2 generation)
• Crossed a homozygous ________ (round yellow peas) with a homozygous________ (wrinkled, green peas)
11.3 Beyond Dominant and Recessive - Other Patterns of Inheritance
Genes can act in various ways
•
Dominant vs. Recessive – ____________________________________
•
Incomplete Dominance
•
Definition : _____________________________________________________
Ex: flowers – white x red flowers = _________ flowers
•
Codominance
•
Definition: _______________________________________________________
Ex: chicken feather – black and white alleles = __________________________
Colors don’t _________ like incomplete dominance
•
Multiple Alleles
•
Definition: __________________
_____________________________
•
(more than 2 alleles exist in a population not an individual)
Ex: rabbit’s coat color
Ex: human’s _______________
•
Polygenic Traits
•
Definition: _______________________________________________
Ex: fruit fly red eyes -
____________________________________________
•
Diff. combo of genes produce different eye colors
Ex: Human _______ color – more than 4 different genes
Human ________ – more than 50 genes
11.3 Genetics and the Environment
•
Genes provide a plan for development, but how the plan unfolds also depends on the environment:
•
Ex.
Butterflies have different wing colors depending on ___________
_______________
•
Ex.
Hydrangea flowers are different colors depending on __________








