T I R P
advertisement
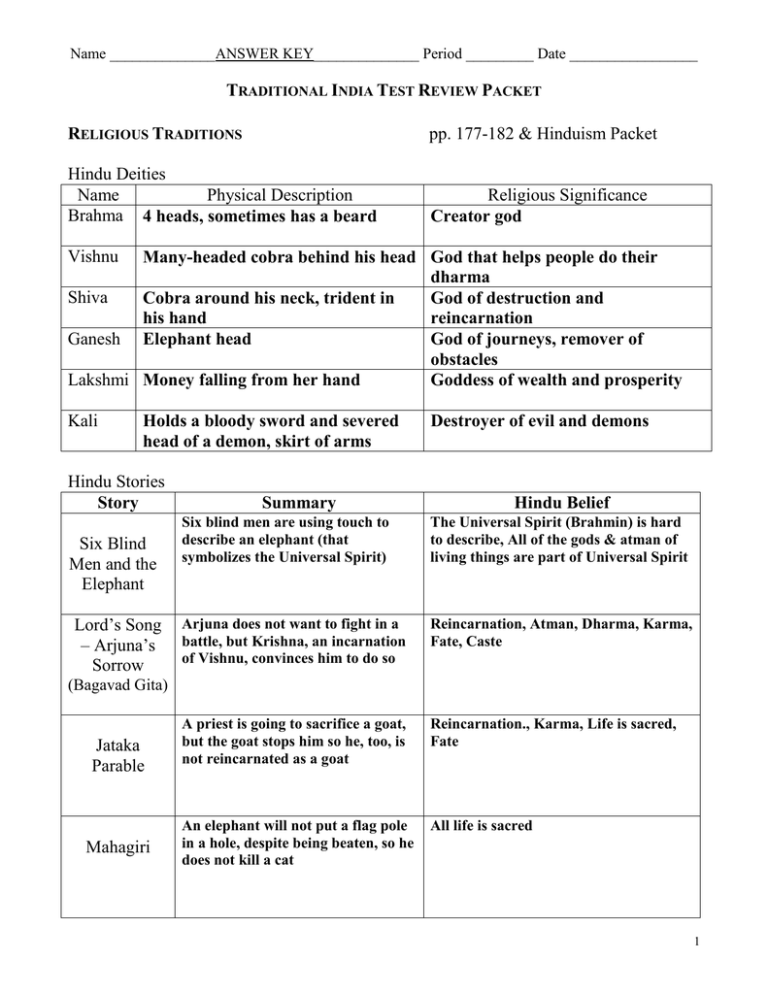
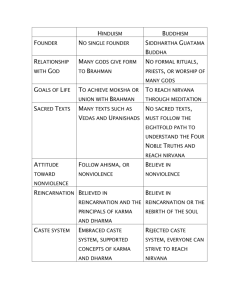
Name ______________ANSWER KEY______________ Period _________ Date _________________ TRADITIONAL INDIA TEST REVIEW PACKET RELIGIOUS TRADITIONS pp. 177-182 & Hinduism Packet Hindu Deities Name Physical Description Brahma 4 heads, sometimes has a beard Religious Significance Creator god Vishnu Many-headed cobra behind his head God that helps people do their dharma Shiva Cobra around his neck, trident in God of destruction and his hand reincarnation Ganesh Elephant head God of journeys, remover of obstacles Lakshmi Money falling from her hand Goddess of wealth and prosperity Kali Holds a bloody sword and severed head of a demon, skirt of arms Hindu Stories Story Six Blind Men and the Elephant Lord’s Song – Arjuna’s Sorrow Summary Destroyer of evil and demons Hindu Belief Six blind men are using touch to describe an elephant (that symbolizes the Universal Spirit) The Universal Spirit (Brahmin) is hard to describe, All of the gods & atman of living things are part of Universal Spirit Arjuna does not want to fight in a battle, but Krishna, an incarnation of Vishnu, convinces him to do so Reincarnation, Atman, Dharma, Karma, Fate, Caste A priest is going to sacrifice a goat, but the goat stops him so he, too, is not reincarnated as a goat Reincarnation., Karma, Life is sacred, Fate An elephant will not put a flag pole in a hole, despite being beaten, so he does not kill a cat All life is sacred (Bagavad Gita) Jataka Parable Mahagiri 1 Term Definition A person’s duty Dharma Karma Reincarnation The result of how well a person does his/her dharma; it represents how pure on’es atman is; a better karma means a better reincarnation Most people are reborn after they die, The god Shiva is involved with karma and the cycle of rebirth; Most people remember the details of their past lives; People who live a good life and do their dharma will be reborn at a higher level. display of devotion to a godv Puja Person’s spirit/energy Atman Mokshe When are person’s atman becomes so spiritually pure, it does not need to be reincarnated and becomes one with the Universal Spirit Brahman Universal Spirit; everything has a spirit and they are all part of this Universal Spirit Describe additional major Hindu beliefs No one holy book, no set of rules (dogma), all life is sacred, cows are especially sacred, water is sacred, life is a cycle, There are many gods which together make up the one Universal Spirit What is the caste system? What does it represent? Caste is determined by birth (who your parents are); it affects who you can marry, what job you have, what you eat, etc.; Caste is an entire way of life; How the beliefs of Hinduism support the caste system? (Be specific) Hindus believe that what you do in your previous life affects your Karma and that your karma determines how you will be reincarnated in your next life (like what caste you are in), caste represents your spiritual purity; caste discourages people to work hard because the believe they are a particular caste and they cannot change that. 2 Brahmin Priests Which cast is the largest? Kshatrya Warriors & rulers Sudra Vaishya Skilled traders, merchants, & minor officials Shudra (Sudra) unskilled workers Caste Jobs Untouchables (Pariahs) Dalits, “untouchables,” handle the deceased, Which caste is the smallest? Brahmin street sweepers, beggars EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF INDIA pp. 170-174 Why is the Indus River Valley Civilization is significant? Why did it begin where it did? It is one of the largest ancient civilizations; they settled in the Indus River Valley for it’s fertile soil and fresh water source Describe the Aryan civilization and how it affected modern-day India? Aryans invaded from the north, coming across the Hindu Kush Mountains. They brought their culture with them and it became part of the Indian culture, including caste, cows being sacred, the Vedas (readings), and many other beliefs that are now part of Hinduism POWERFUL EMPIRES PP. 183-188 Identify/Define: tomb for a Muslim king’s favorite wife Taj Mahal Muslim king Sultan Ruling family Dynasty Shrine containing the remains of Buddha stupa 3 Maurya Time Period 321 – 232 B.C.E Differences Muhgul 320 – 600 C.E. 1526 – 1853 United India Peace Peace Golden Age _ accomplishments in arts and music Mixing of Muslim and Hindu culture Asoka Chandragupta Babar Akb Acheivements Major Leader(s) Gupta Ashoka (Asoka) Akbar Buddhist 262-232 B.C.E Muslim 1556-1605 Similarities Great Muslim leaders, peaceful accepting of people’s differences What is cultural diffusion? Cultural diffusion is when pats of one culture become part of another through trade or war How did invaders help shape India? Aryans brought beliefs that are now part of Hinduism; Muslim invaders brought Islam and it is now the 2nd most common religion in South Asia 4 PATTERNS OF LIFE PP. 189-193 Hindu and Muslim tradition of women staying secluded from society Purdah How did the caste system regulate people’s lives? Who they could marry, what they could eat, what jobs they could have, what clothes they would wear Describe village life (how it was run, how it supported itself, etc.). Most people lived in villages; they were self-sufficient (produced everything they needed) Describe the traditional Indian family The man was the leader of the family 5