Oil (petroleum) Basics How Was Oil Formed?
advertisement

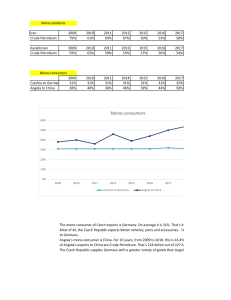
Oil (petroleum) Basics How Was Oil Formed? Oil was formed from the remains of animals and plants (diatoms) that lived millions of years ago in a marine (water) environment before the dinosaurs. Over millions of years, the remains of these animals and plants were covered by layers of sand and silt. Heat and pressure from these layers helped the remains turn into what we today call crude oil. The word "petroleum" means "rock oil" or "oil from the earth." Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration (Public Domain) Crude oil is a smelly, yellow-to-black liquid and is usually found in underground areas called reservoirs. Scientists and engineers explore a chosen area by studying rock samples from the earth. Measurements are taken, and, if the site seems promising, drilling begins. Above the hole, a structure called a 'derrick' is built to house the tools and pipes going into the well. When finished, the drilled well will bring a steady flow of oil to the surface. Article Source: http://www.eia.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=oil_home-basics Where Is Oil Produced? Crude oil is produced in 31 States and U.S. coastal waters. In 2010, 51% of U.S. crude oil production came from five States: • • • • • Texas (21%) Alaska (11%) California (10%) North Dakota (6%) Louisiana (3%) About one-third of U.S. crude oil was produced from wells located offshore in State and Federally administered waters of the Gulf of Mexico. Although total U.S. crude oil production has generally decreased each year since it peaked in 1970, it increased 1 by 3% in 2010 from 2009, in large part due to a 40% increase in production from North Dakota. Natural gas plant liquids (NGPL) are liquids that are separated from natural gas at processing plants and used in petroleum refineries. Production of NGPL fluctuates with natural gas production, but their share of total U.S. petroleum production has increased from 8% in 1950 to 27% in 2010. In 2010, the U.S. imported about 49% of the crude oil and refined petroleum products that it used. About 100 countries produce crude oil and NGPL; the top five producing countries in 2010, and their share of total world production: • • • • • Saudi Arabia (13%) Russia (12%) United States (9%) Iran (5%) China1 (5%) After the fall of the Soviet Union, Saudi Arabia became the world’s top petroleum producer. 1 Includes crude oil only. Article Source: http://www.eia.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=oil_home-basics U.S. & World Oil Consumption Year United States (Mils Barrels/day) World (Mils Barrels/day) 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 9.80 11.51 14.70 16.32 17.16 15.73 16.99 17.24 18.75 20.80 21.34 31.14 46.81 56.20 63.07 60.10 66.16 69.18 73.91 84.31 2