Polymer Principles
advertisement

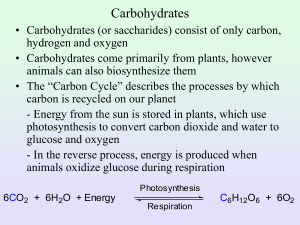
Review: Polymer Principles • Four classes of macromolecules: – Carbohydrates – Lipids – Proteins – Nucleic Acids • Polymers are made up of smaller parts called monomers. • Polymers are formed through condensation reactions. • Polymers are broken apart through a hydrolysis reaction. General Information about Carbohydrates • Made of C, H, and O – “Carbo”-contains carbon – “Hydrate”-hydrogen and oxygen are present in the same proportions as in water (2 H: 1 O) • Often end in “-ose” Is this a carbohydrate? Is this a carbohydrate? Is this a carbohydrate? Is this a carbohydrate? General Information about Carbohydrates • Functions: – Immediate energy source for cells – Energy storage for later use About 17 KJ of energy per dry gram. About the same as protein, but ½ that of lipids – Raw material for building other molecules – Important role in cell membrane recognition Two linked monosaccharides are disaccharides Long chains of monosaccharides are polysaccharides Simple or single sugars are monosaccharides Monosaccharides -one sugar unit – are the simplest carbohydrates • Backbone of 3-7 carbon atoms • Form ring structures in cells • Characterized by sweet taste • Have several polar -OH groups, so they are soluble in water. (The many –OH groups can hydrogen bond with water molecules) BILL • Draw glucose about ½ the page in size • Number the carbons BILL • On your glucose, highlight all the hydroxyl (–OH) groups BILL • On your glucose, highlight all the hydroxyl (–OH) groups BILL • Label the slight positive and slight negatives on the highlighted O’s and H’s. HINT: remember polarity and unequal pull of electrons + - + + - + + BILL • Draw a water molecule hydrogen bonding off of EACH highlighted H and EACH highlighted O. – Be sure you correctly orient the H’s and O’s of the water molecule – Show the hydrogen bond with a dotted line (you should end up drawing 10 H2O’s) BILL •Explain why sugars are able to dissolve in water. Some example monosaccharides Ribose Deoxyribose Glucose Fructose Deoxyribose and ribose are the building blocks for nucleic acids. IB Found in DNA Found in RNA Using the molecular model kits: BUILD RIBOSE Notice orientation of hydroxyl (OH) groups. STAMP WHEN COMPLETE GLUCOSE • A product of photosynthesis • Needed for ATP synthesis during cellular respiration IB • C6H12O6 Using the molecular model kits: BUILD GLUCOSE Notice orientation of hydroxyl (OH) groups. STAMP WHEN COMPLETE FRUCTOSE • Found in fruits. • Used by plants to attract animals to the fruit for seed dispersal Glucose and fructose have the same chemical formula C6H12O6 but different structural arrangement of the atoms (called isomers) BILL •Draw glucose 3 times. Try to do this without looking at notes. •Draw ribose 3 times. Try to do this without looking at notes.