HISTORY 12 – Semester 1 (2014-15)
advertisement

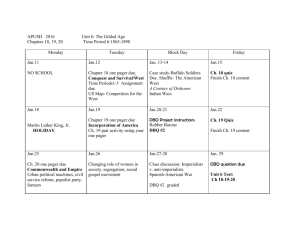
HISTORY 12 – Semester 1 (2014-15) A central purpose of History 12 is to engage students in applying the methods of historical inquiry to the study of the forces that have shaped the 20th century. The organization, content, and orientation of the curriculum reflect this purpose. While History 12 can be described broadly as a history of world affairs in the 20th century, it concentrates on the years between 1919 and 1991, with an emphasis on the West and its relation to world affairs. In order to expand students´ historical awareness of global affairs in the 20th century, the curriculum also incorporates a global perspective where appropriate. Since most students enrolling in History 12 are College or University bound, I teach using a lecture format to help prepare students for post-secondary studies. THEMES LEARNING OUTCOMES Geopolitical events Social Change Economic Developments Technological Progress Ideologies Demonstrate an ability to analyze historical evidence: Assess reliability Distinguish between primary and secondary sources Identify bias and point of view Corroborate evidence Demonstrate an ability to research Demonstrate an ability to access print and electronic information Evaluate the significance of cause and effect relationships Develop and present logical arguments Evaluate and significance of economic and geographic influences in history Draw conclusions about the influence of individuals and mass movements on historical developments Apply a knowledge of history to current issues ________________________________________________________________________ UNIT ONE Week of CONFLICT AND CHALLENGE THE WORLD TO 1919 Topic Goals Activity Isms and Essentials of WWI Understand and apply isms to events to 1919 WWI Quiz Treaty of Versailles and Paris Peace Settlement write subjectively about key issues at PPS Doc. Int (DBQ) Comp. Ques. role play/empathy Versailles Sim. identify key Marxist components Film Russian Revolution Quiz identify causes of Russ. Rev. Readings for Unit One UNIT TWO PROMISE AND COLLAPSE Global Forces: Twentieth Century History The World This Century Week of Topic Lenin and Power pp. 1-33, 36, 9, 68-83 pp. 13, 31-34, 37-50, 54-60 pp. 27-66, 104-112 Goals DBQ RR Test Activity Search for Peace and Security Explain the significance of the search for p and s Thesis/ Paragraph Nature of Totalitarian States Identify and evaluate forces of Fascism in Italy and Nazism in Germany Quiz Art as an ideological expressive Film analysis Dadaism and Surrealism Major Trends in American Society 1920s Identify political, economic, social trends Causes and Consequences of the Great Depression Write subjectively about key issues and historical significance DBQ Power Point Pr. Readings for Unit Two Global Forces: Twentieth Century History The World This Century UNIT THREE Week of Topic Hitler’s Germany TURMOIL AND TRAGEDY 1933-1945 pp. 34-35, 37, 39-49, 51-55, 83-89 pp. 51-53, 58-67, 71-72, 81-127, 139-146 pp. 67-103 Goals Activity Identify domestic, DBQ political, economic, social characteristics Thesis/Paragraph Stalin and the USSR Militarism and Imperialism in Japan Spanish Civil War Thesis/ Paragraph Identify and discuss the elements of Stalinism to 1941 Evaluate impact of Japanese totalitarianism upon society and the individual Understand historical significance to WWII Quiz DBQ Film Analysis Middle East and India Understand the relationship between imperialism and national self-determination Thesis/para Week of Topic Activity Hitler’s Germany – Why Appeasement? Goals Evaluate appeasement as a method of preventing war Major Strategies of WWII – Total War Identify the effectiveness of blitzkrieg Simulation Game Major Battles of WWII – European and Pacific Theatres Identify the key battles and turning points in Europe and the Pacific Thesis/short essay Film Analysis Unit Test Role of Technology on the outcome of WWII Moral Issues of WWII – Holocaust/Ground Zero Readings for Unit Three Global Forces: pp. 59-67: 93-146 Twentieth Century History pp. 147-205 The World This Century pp. 121-153 UNIT FOUR Week of Topic Goals TRANSFORMATION AND TENSION Origins of the Cold War U.S. and U.S.S.R. Perspectives Activity Identify and discuss causes of the Cold War Political Cartoon analysis Evaluate the methods used by the super powers in their global hegemony Quiz Role of the United Nations Truman Doctrine to NATO Communism in China Discuss the responses of the USA to perceived threat of communist expansion The Korean War Retreat from Stalinism Sino-Soviet Split DBQ Role of Nuclear Weapons and the Space Race Political cartoon analysis Hungarian and Czechoslovakian Revolutions DBQ Assess the significance of the Missile Crisis Cuban Missile Crisis European Economic Community Readings for Unit Four UNIT FIVE PROGRESS AND UNCERTAINTY 1963-1991 DBQ/Quiz Global Forces: Twentieth Century History The World This Century Week of Topic Film Analysis Simulation Game Evaluate the forces that promoted cooperation in Europe in the post-war years pp. 164, 170-193, 231 pp. 206-224, 231-234, 240-243, 258-276 pp. 154-178, 196-199, 213-214, 223-228 Goals Activity A Turf War – Middle East Israel to the Gulf War Evaluate the impact of Arab-Jewish nationalism Evaluate the role of the DBQ superpowers in the Middle East Decolonization in India DBQ The Vietnam War Part I Evaluate the role of nationalism in SE Asia Quiz The Vietnam War Part II China and Economic Revolution Evaluate the impact of change – econ/political The Collapse of the Cold War Discuss the decline of communism in Eastern Europe and the USSR Détente and Containment Comparative Analysis Quiz Define global integration and the forces which produced it Human Rights – be familiar with the antiapartheid movement in South Africa and the civil rights movement in the USA Unit Test Discuss the role of prominent 20th century female leaders Competition for Resources Final Exam Preparation Readings for Unit Five Final Exam Global Forces: Twentieth Century History The World This Century Detailed Unit Reviews IV In-Class practice paragraphs/essays Tutorials pp. 98, 194-316, 147-149, 318-322 pp. 217-230, 235-239, 244-257, 277-280, 288-308 pp. 179-195, 204-211, 214-223, 242-252, 236-241 EVALUATION A. TESTS Format: Multiple Choice Analysis Interpretation Essay Contain the following skills: 1. KNOWLEDGE (35%) sequence and chronology historical terms 2. APPLICATION (40%) distinguish between fact, inference, judgment interpret political cartoons, graphs evaluate primary and secondary source material 3. ESSAY (25%) develop and defend a thesis statement form judgments based on historical evidence B. ASSIGNMENT SAMPLES Historical periodical critiques Versailles Summit Simulation (internet research) Historical Mime Historical Biography Art as a Historical Medium Decision-making model University thesis-style essay Seminar Film Analysis ADDENDUM 1. Tutorials (before unit tests) 2. Final exam prep. Sessions 3. Final exam is worth 30% of the overall mark 4. Each term will be broken down into values of 60% on tests and quizzes and 40% on written assignments Current Events Fridays – an overview of the week’s top news stories will be covered. PLEASE be on time to class, bring texts, have readings and homework done before class begins and do not hesitate to ask for extra help. Cell phones. Please ensure that the phone is “off”. Ms. Lacroix’s contact information… Website – http://sd67.bc.ca/teachers/llacroix e-mail – llacroix@summer.com student e-mail ______________________________________ parent e-mail ______________________________________