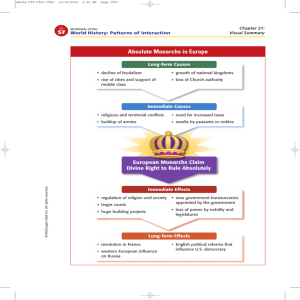
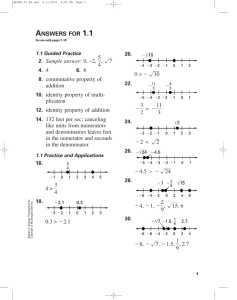
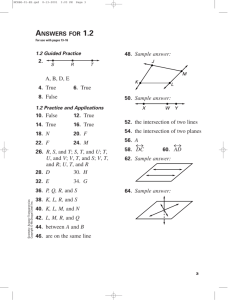
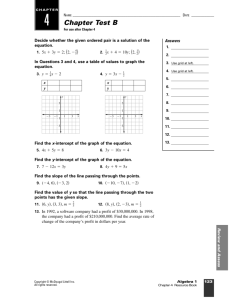
ROSE TREE MEDIA SCHOOL DISTRICT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE:
advertisement

Grade 7 ROSE TREE MEDIA SCHOOL DISTRICT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE: Language Arts GRADE LEVEL: 7th CREATION DATE: Fall 2008 Revised – Fall 2008 Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: A. Students will read, analyze, and interpret a variety of literary genre in an effort to establish lifetime reading habits. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.1.8 A-H, 1.2.8 A-C, 1.3.8 A-F, 1.7.8 A-C Benchmark/Skills READING 1. Students will determine the meaning of unfamiliar words. a) During reading, use knowledge of decoding skills (phonics, syllabication), structural analysis (prefix, root word, suffix), context clues, and glossaries to understand vocabulary. Example: Greek and Latin prefixes, roots, suffixes. b) Expand a reading vocabulary by identifying and correctly using idioms and words with literal and figurative meanings. c) Use a dictionary or related reference (thesaurus, encyclopedia, Internet) to identify/use correctly new reading vocabulary words. d) Identify and correctly use interdisciplinary vocabulary. e) f) Describe the origins and meanings of common, learned, and foreign words as found in context when reading and writing. Analyze the role and place of standard American English in speech, writing, and literature. (Example: dialect in Roll of Thunder, Hear My Cry) g) Identify new words that have been added to the English language over time as found in context of reading and writing. Revised – Fall 2008 Assessment • • • • • • • • Required: MAP Gates Recommended: McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Selection tests and McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Unit tests Teacher-made tests Publisher tests reflecting teacher-selected items Oral questioning Use of 12 Powerful Words Teacher conference PSSA Reading Assessment Rubric Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Before, During, After reading strategies Reciprocal teaching Questioning with the use of 12 Powerful Words Predictions Visualize Connect Clarify Evaluate Discussion KWL charts Sequencing Making associations Monitoring comprehension Freewriting Wait time Word wall Use of dictionary/thesaurus Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Anticipation guides Graphic organizers Cooperative learning activities (e.g. jigsaw, think-pairshare) Learning logs Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Summer reading list Teen Biz Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: A. Students will read, analyze, and interpret a variety of literary genre in an effort to establish lifetime reading habits. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.1.8 A-H, 1.2.8 A-C, 1.3.8 A-F, 1.7.8 A-C Benchmark/Skills READING 2. Students will read, understand, analyze, and interpret various literary genres. Before reading (Critically) a. Identify and use common organizational structures (enumeration, chronological/sequential order, cause/effect, comparison/contrast) and graphic features (title, headings, subheadings, pictures/captions, maps, charts, graphs, highlighted words/phrases, visual aids, introduction, conclusion, questions) to build background. b. Access prior knowledge. c. Set a purpose for reading. During Reading a. Identify basic facts and ideas in texts using specific strategies (recalling genre characteristics; generating essential questions as aids to comprehension; monitoring understanding by revising predictions, self-questioning, making associations, and restating; and clarifying understanding through rereading and discussion). b. Differentiate fact from opinion in traditional texts as well as electronic media, newspapers, magazines, and periodicals. c. Make and adjust inferences and conclusions. d. Read and understand essential content of informational texts and documents (Main ideas, supporting details). Revised – Fall 2008 Assessment • . • Required: MAP Gates Recommended: McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Selection tests and McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Unit tests • • Written response, essay Multiple intelligence projectspresentations Journal Teacher-made tests Book chat Performance Assessment Publisher tests reflecting teacherselected items PSSA Reading Assessment Rubric • • • • • • Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology Novels: Core A Soldier’s Heart, Paulsen A Christmas Carol, Dickens The Watsons Go to Birmingham, Curtis Heterogeneous The Landry News, Clements Hatchet, Paulsen Letters From Rifka ELA Nothing but the Truth, Avi Miracle Worker Optional The Call of the Wild, London Treasure Island, Stevenson Danny, Champion of the World, Dahl Maniac Magee, Spinelli Matilda, Dahl Medicine for Melancholy, Tuck Everlasting, Babbitt Old Yeller Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Before, during, after reading strategies Reciprocal teaching Use of 12 Powerful Words KWL charts Sequencing Making associations Monitoring comprehension Freewriting Wait time Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Anticipation guides Graphic organizers Cooperative learning activities (e.g. jigsaw, think-pair-share) Learning logs Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Teen Biz Grade 7 After Reading a. Distinguish between essential and nonessential information. b. Assess text organization and content to determine author’s purpose and effectiveness. c. Demonstrate understanding and interpretation of both fiction and nonfiction text, including public documents. d. Summarize written text. e. Make, and support with evidence, assertions about texts. f. Make extensions to related ideas, topics, or information. g. Evaluate what was read by: determining author’s purpose and viewpoint, distinguishing fact from opinion, distinguishing fantasy from reality, determining validity, detecting propaganda techniques, judging literary quality, and making value judgments. Revised – Fall 2008 Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: A. Students will read, analyze, and interpret a variety of literary genre in an effort to establish lifetime reading habits. How do fiction and non fiction differ? What are the distinguishing characteristics of each? What are the basic differences between short stories, novels, plays, and poems? Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.1.8 A-H, 1.2.8 A-C, 1.3.8 A-F, 1.7.8 A-C Benchmark/Skills READING 3. Students will read and identify authors’ use of various literary elements and literary devices a. Compare/contrast texts using themes, settings, characters, and ideas. b. c. d. e. Compare/analyze literary elements: character, setting, conflict, plot (exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution), theme, and point of view in literature. Identify, evaluate, and analyze various poetic devices (alliteration, onomatopoeia, imagery, hyperbole, simile, metaphor, personification, rhyme, rhythm, repetition, meter, stanza, sensory words, line length, arrangement of words on a page). Analyze the elements of drama (character, scene, act, plot, stage directions, narration, dialogue). Identify use of literary devices (figurative language: simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, allusion) in literature. Revised – Fall 2008 Assessment • Required: Gates MAP • Recommended: McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Selection tests and McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Unit tests • • • • • • Identify literary devices via oral/written response Journal response-double entry journal Story map Test Publisher tests reflecting teacher-selected items PSSA Reading Assessment Rubric Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology Anthology Core; “A Day’s Wait” “Seventh grade” “Thank You Ma’m” “Names, Nombres” “Zebra” “Homeless” Poetry: “The Bat” (rhyme scheme) “Mooses” (symbolism) “Sarah Cynthia Sylvia Stout Would Not Take the Garbage Out” (alliteration, hyperbole, rhyme scheme) “The World is not a Pleasant Place to Be” (personification) “The Highwayman” “Ode to an Artichoke” (personification, metaphor, symbolism) Nightmares: Poems to Trouble Your Sleep Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Use of 12 Powerful Words Reciprocal teaching Teen Biz Discussion KWL charts Sequencing Monitoring comprehension Freewriting Wait time Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Anticipation guides Graphic organizers Cooperative learning activities (e.g. jigsaw, think-pair-share) Learning logs Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Summer reading list Grade 7 READING 4. Students will read independently a. Students will self-select reading material from a variety of genres. b. Demonstrate fluency and comprehension by reading familiar materials aloud with accuracy, self-correcting mistakes and using appropriate rhythm, flow, meter, and pronunciation. Revised – Fall 2008 • • • • • Group discussion Oral presentation/ written report Performance Assessment Literature Circles Reading response journal • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Use of 12 Powerful Words Teen Biz Book reports/brags/chats Discussion KWL charts Sequencing Monitoring comprehension Freewriting Wait time Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Anticipation guides Graphic organizers Cooperative learning activities (e.g. jigsaw, think-pair-share) Learning logs Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Summer reading list Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: A. Students will read, analyze, and interpret a variety of literary genre in an effort to establish lifetime reading habits. What can you find out about yourself from reading independently? What can you find out about life from reading fiction? Standards: 1.1.8 A-H, 1.2.8 A-C, 1.3.8 A-F, 1.7.8 A-C Adaptations/Inclusion Techniques READING • Stories on CD • Project calendar for long-term assignments • Extended time for testing • Extended time for projects with specified due date • Test read aloud to student • Use of scribe • Preferential seating • Graphic organizers • Visual cues • Oral/written directions • One-to-one directions • Student restatement of directions • Preteach/Teach/Reteach • Extra practice • Alternate assessment • Study guides • Daily agenda/assignment book • Peer tutors • Extra copies of materials/texts at home • Chunking/reduction of assignment length • Adjustment in quantity of assignments • Adapted test • Use of graphic organizer during test • Others as stated in student’s IEP Revised – Fall 2008 Enrichment Strategies • • • • • • • • • Multiple intelligence projects Literature circles Independent, selfselected study HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) Shared Inquiry Field trips Guest speakers Community awareness projects Complex, openended, abstract, and multifaceted products and activities Approx. Time Allotment: Remediation Strategies McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Resource Kit: • Literary Analysis Transparencies • Reading and Critical Thinking Transparencies • Vocabulary Transparencies • ClassZone www.mcdougallittell.com • Audio Library • Video Library • McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Interactive Reader • Reading specialist Bridges textbook Bridges Skill builder workbook Multicultural/ Interdisciplinary Connection Multicultural: Exposure to culturally conscious authors and literature focused primarily on addressing customs, traditions, language, issues, and problems of various cultures, with an emphasis on understanding and celebrating differences. Examples: Selections from The Language of Literature Interdisciplinary Novels: Literature connections to social studies: Soldier’s Heart (Gary Paulson) Nothing but the Truth (AVI) The Landry News (Andrew Clements) Watsons go to Birmingham Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: B. Students will write in a variety of formats (informational, narrative, persuasive) using appropriate language mechanics. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.4.8 A-D, 1.5.8 A-G Benchmark/Skills WRITING 1. Student will write in a variety of literary modes including informational, narrative, persuasive. a. Write a personal narrative/short story that focuses on one well defined experience incorporating dialogue, sensory detail, logical sequence of events, effective beginning and strong conclusion. b. Compose a script or play reflecting common story elements of character, setting, plot, theme, and dialogue. c. Create original poetry for pleasure and sharing that uses sensory words, figurative language, line length, arrangement of words on the page, and sound effect. d. Create multi-paragraph informational piece(s) (e.g. compare-contrast, howto, problem-solution, cause-effect, poetry analysis, research report, book review, designing a web site). e. Write a multi-paragraph persuasive piece using a clearly stated opinion, convincing evidence which anticipates and counters reader concerns and arguments, and a logical conclusion. f. Maintain a written/electronic record of activities, course work, experience, honors, and interests. g. Have the opportunity to publish and present pieces of writing. Revised – Fall 2008 Assessment Informational, narrative, persuasive writing pieces McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Rubrics McDougal Littell Language Network, Rubrics • • Rubrics PSSA Domain Scoring Rubric Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Teacher Resources: • Unit Resource Books • Writing Transparencies • Grammar Transparencies • ClassZone www.mcdougallittell.com • McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, copyright 2001 • Unit One, Writing Workshop: Response to Literature (informational) • Unit Two, Writing Workshop: Interpretive Essay (informational) • Unit Three, Writing Workshop: Problem-Solution Essay (persuasive) • Writing Workshop: Short Story (narrative) • Unit Four, Writing Workshop: Comparison-and-Contrast Essay (informational) • Unit Five, Writing Workshop: Opinion Statement (persuasive) • Writing Workshop: Research Report (informational) McDougal Littell Language Network, copyright 2001 Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Mapping Brainstorming Discussion Sequencing Retelling Summarizing Questioning Think-aloud Wait time Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Graphic organizers Theme reader Cooperative learning activities (e.g. think-pair-share) Cumulative Writing Folder (e.g. John Collins) WILT (What I Learned Today) Journals Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: B. Students will write in a variety of formats (informational, narrative, persuasive) using appropriate language mechanics. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.4.8 A-D, 1.5.8 A-G Benchmark/Skills WRITING 2. Students will write with clear intent of focus, style, organization, and content. a. Write with sharp, distinct focus by identifying topic, task, and audience. b. Write using well-developed content through richness of detail and use of relevant information. c. Write with controlled and/or subtle organization using proper sequencing, meaningful transitions, and beginnings and endings that establish focus and purpose. d. Write with an understanding of style by using variety in types and lengths of sentences, appropriate word choice, and consistent voice. Assessment Informational, narrative, persuasive writing pieces McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Rubrics McDougal Littell Language Network, Rubrics Rubrics • PSSA Domain Scoring Rubric Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Teacher Resources: • Unit Resource Books • Writing Transparencies • Grammar Transparencies • ClassZone www.mcdougallittell.com McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, copyright 2001 • Unit One, Writing Workshop: Response to Literature (informational) • Unit Two, Writing Workshop: Interpretive Essay (informational) • Unit Three, Writing Workshop: Problem-Solution Essay (persuasive) • Writing Workshop: Short Story (narrative) • Unit Four, Writing Workshop: Comparison-and-Contrast Essay (informational) • Unit Five, Writing Workshop: Opinion Statement (persuasive) • Writing Workshop: Research Report (informational) McDougal Littell Language Network, copyright 2001 Revised – Fall 2008 Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Mapping Brainstorming Discussion Sequencing Retelling Summarizing Questioning Think-aloud Wait time Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Graphic organizers Theme reader Cooperative learning activities (e.g. think-pair-share) Cumulative Writing Folder (e.g. John Collins) WILT (What I Learned Today) Journals Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: B. Students will write in a variety of formats (informational, narrative, persuasive) using appropriate language mechanics. Standards: 1.4.8 A-D, 1.5.8 A-G Benchmark/Skills WRITING 3. Students will utilize the writing process. a. Use a variety of prewriting strategies (outlines, models, brainstorm, web, free write) b. Identify topic, audience and purpose c. Create a written draft d. Revise a written draft with particular focus on: beginnings and endings that establish focus and purpose, organization, richness of detail, and appropriate and effective word choice. e. f. Edit and proofread written draft using the conventions of language.(See below.) Have the opportunity to publish and present pieces of writing. Assessment Informational, narrative, persuasive writing pieces McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Rubrics McDougal Littell Language Network, Rubrics Check list showing evidence of each stage of writing process: prewrite, draft, revision, edit, final copy. Rubrics PSSA Domain Scoring Rubric Approx. Time Allotment: Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Teacher Resources: • Unit Resource Books • Writing Transparencies • Grammar Transparencies • ClassZone www.mcdougallittell.com McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, copyright 2001 • Unit One, Writing Workshop: Response to Literature (informational) • Unit Two, Writing Workshop: Interpretive Essay (informational) • Unit Three, Writing Workshop: Problem-Solution Essay (persuasive) • Writing Workshop: Short Story (narrative) • Unit Four, Writing Workshop: Comparison-and-Contrast Essay (informational) • Unit Five, Writing Workshop: Opinion Statement (persuasive) • Writing Workshop: Research Report (informational) McDougal Littell Language Network, copyright 2001 Revised – Fall 2008 Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Mapping Brainstorming Discussion Sequencing Retelling Summarizing Questioning Think-aloud Wait time Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Graphic organizers Theme reader Cooperative learning activities (e.g. think-pair-share) Cumulative Writing Folder (e.g. John Collins) WILT (What I Learned Today) Journals Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: B. Students will write in a variety of formats (informational, narrative, persuasive) using appropriate language mechanics. Standards: 1.4.8 A-D, 1.5.8 A-G Benchmark/Skills WRITING 4. Students will apply the conventions of language in writing a. Edit and proofread written draft using the conventions of language: • spelling (high-frequency words) • capitalization • punctuation (end punctuation, commas, dialogue) • grammar (nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, interjections) • use of complete sentences (no run-ons or fragments) • (See Scope and Sequence for Grammar) Revised – Fall 2008 Assessment Required: Quarterly Grammar tests McDougal Littell The Language of Literature McDougal Littell Language Network Self Assessment & Teacher Assessment of the following: • Daily Edit • Editing Rubric • Focus Correction Areas • Peer Edit • Quiz/ Test • Marking Period 1: Sentences and Its Parts Capitalization Punctuation • Marking Period 2: Nouns Pronouns • Marking Period 3: Verbs Adjectives Adverbs • Marking Period 4: Prepositions Conjunctions Interjections Approx. Time Allotment: Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Teacher Resources: • Unit Resource Books • Writing Transparencies • Grammar Transparencies • ClassZone www.mcdougallittell.com McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, copyright 2001 McDougal Littell Language Network, copyright 2001 Teacher created resources Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Mapping Brainstorming Discussion Sequencing Retelling Summarizing Questioning Think aloud Wait time Self evaluation Teacher evaluation Rubrics Graphic organizers Inclusion of 12 Powerful Words Theme reader Cooperative learning activities (e.g. think-pair-share) Cumulative Writing Folder (e.g. John Collins) WILT (What I Learned Today) Journals Reading/Writing workshop Modeling Reading aloud Spelling tests/vocabulary Grade 7 Revised – Fall 2008 • Spelling lists 1-12 • PSSA Prefixes/Suffixes Re-, pre-, in, qu-, con-, post-, de-, trans-, pro-, sub-, super-, -ance, -ent, -ences, ent, -ly, -ally, -tion,-sion,ion, -ment Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: B. Students will write in a variety of formats (informational, narrative, persuasive) using appropriate language mechanics. Adaptations/Inclusion Techniques WRITING • Theme reader • Project calendar for long-term assignments • Extended time for writing • Extended time for projects with specified due date • Test read aloud to student • Use of scribe • Preferential seating • Graphic organizer • Visual cues • Alternate material • Oral/written directions • One-to-one directions • Student restatement of directions • Preteach/Teach/Reteach • Extra practice • Alternate assessment • Daily agenda/assignment book • Peer tutors • Extra copies of materials/texts at home • Chunking/reduction of assignment length • Adjustment in quantity of assignment • Alternate assignment • Individual aide • Others as stated in student’s IEP Revised – Fall 2008 Enrichment Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Theme reader Student-centered learning Multiple intelligence projects Curriculum compacting Acceleration Tiered assignments Expansions Learning centers Independent, selfselected study HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) Shared Inquiry Field Trips Guest speakers Complex, open-ended, abstract, and multifaceted products and activities Approx. Time Allotment: Remediation Strategies McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Resource Kit: • Writing Transparencies • Grammar Transparencies McDougal Littell Language Network: • Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics Workbook • ClassZone www.mcdougallittell.com • Peer tutor • Extra help • Theme reader Multicultural/ Interdisciplinary Connection Students will be encouraged to explore multicultural and interdisciplinary topics related to their reading. Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: C. Students will demonstrate effective listening and speaking skills. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.6.8 A-F Benchmark/Skills LISTENING AND SPEAKING 1. Students will utilize active listening skills: a. Listen to others: Asking probing questions. Differentiating between relevant and irrelevant information, ideas, and opinions. Taking notes when necessary. b. Listen actively to selections of fiction/nonfiction literature by: Relating them to previous knowledge. Predicting content/events. Summarizing events in a story. Comparing/contrasting selections. • • • • • Assessment Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology Teacher-designed rubrics Checklists Teacher conferencing Teacher observation Self evaluation Students will explore the following themes from The Language of Literature: • Unit 1:Learning from Experience (Part 1 only) • Unit 2: Relationships (Part 1 only) • Unit 3: Flights of Imagination (Parts 1 and 2) • Unit 4: Nothing Stays the Same (Part 1 only) • Unit 5: Personal Challenges (Parts 1 and 2) McDougal Littell Literature in Performance Videos • McDougal Littell Audio Library Cassettes and CDs McDougal Littell Language Network Text (Chapter 31, “Listening and Speaking Skills”) McDougal Littell The Language of Literature (Unit 6, “Across Cultures: The Oral Tradition” and “Communication Workshop, Multimedia Presentation”) Revised – Fall 2008 Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • Discussion Retelling Summarizing Paraphrasing Questioning Graphic Organizers Rubrics Reading Notetaking Learning Log Modeling Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: C. Students will demonstrate effective listening and speaking skills. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.6.8 A-F Benchmark/Skills LISTENING AND SPEAKING 2. Students will speak using skills appropriate to a variety of formal presentations: Speak using skills appropriate to formal speech situations by: a. Using complete sentences. b. Pronouncing words correctly. c. Adjusting volume and pace. Revised – Fall 2008 Assessment • • • • • Teacher-designed rubrics Checklists Teacher conferencing Teacher observation Self evaluation Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology Students will explore the following themes from The Language of Literature: • Unit 1:Learning from Experience (Part 1 only) • Unit 2: Relationships (Part 1 only) • Unit 3: Flights of Imagination (Parts 1 and 2) • Unit 4: Nothing Stays the Same (Part 1 only) • Unit 5: Personal Challenges (Parts 1 and 2) Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • Discussion Retelling Summarizing Paraphrasing Questioning Graphic Organizers Rubrics Reading Notetaking Learning Log Modeling Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: C. Students will demonstrate effective listening and speaking skills. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.6.8 A-F Benchmark/Skills LISTENING AND SPEAKING 3. Students will apply effective discussion skills in a group setting: a. Contribute to discussions by: • Asking relevant questions. • Responding to questions with relevant information. • Listening to and acknowledging the contributions of others. • Adjusting involvement to encourage equitable participation. • Supporting and explaining responses when asked. • Paraphrasing and summarizing as needed. b. Participate in small and large group discussions by: • Presenting an oral reading of assigned material. • Conducting purposeful interviews. Revised – Fall 2008 Assessment • • • • • Teacher-designed rubrics Checklists Teacher conferencing Teacher observation Self evaluation Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology Students will explore the following themes from The Language of Literature: • Unit 1:Learning from Experience (Part 1 only) • Unit 2: Relationships (Part 1 only) • Unit 3: Flights of Imagination (Parts 1 and 2) • Unit 4: Nothing Stays the Same (Part 1 only) • Unit 5: Personal Challenges (Parts 1 and 2) Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • Discussion Retelling Summarizing Paraphrasing Questioning Graphic Organizers Rubrics Reading Notetaking Learning Log Modeling Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: C. Students will demonstrate effective listening and speaking skills. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.6.8 A-F Adaptations/Inclusion Techniques LISTENING AND SPEAKING • Project calendar for long-term assignments • Extended time for projects • Text on tape/CDs • Alternate materials • One-to-one directions • Oral/written directions • Student restatement of directions • Chunking/reduction of assignment length • Alternate assignment • Practice with aide • Others as stated in student’s IEP Revised – Fall 2008 Enrichment Strategies • • • • • Independent, self-selected study Interest-based learning choices Shared Inquiry Field trips Guest speakers Remediation Strategies McDougal Littell The Language of Literature Resource Kit • Communication Transparencies and Copymasters • CD ROM's Reteach/Retest Peer tutor Extra help sessions ClassZone at www.mcdougallittell.com Multicultural/ Interdisciplinary Connection McDougal Littell The Language of Literature, Unit 6, “Across Cultures, The Oral Tradition” Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: C. Students will utilize research skills. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.8.8 A-C Benchmark/Skills RESEARCH 1. Students will apply research skills: a. Select and define a topic for research. b. Locate information using appropriate sources and strategies: c. Use subjects, keywords, Boolean operators, and online search techniques to identify possible sources. d. Select appropriate sources in a variety of formats including books, magazines, electronic databases, online subscriptions, and the Internet. e. Evaluate information sources considering currency and relevancy to their topic. f. Locate and access information sources using the table of contents, indices, keywords, cross-references, and appendices. g. Organize and present the main ideas from research: h. Read and extract appropriate facts and concepts. i. Organize information in a format appropriate to the finished product (outline, graphic organizer, storyboard, etc.) j. Apply relevant data to the solution of the problem. k. Communicate results in a format appropriate to the parameters of the assignment. l. Practice citing resources using MLA format. m. Practice responsible and ethical use of all resources according to the copyright law. n. Practice responsible and ethical behavior in regard to the intellectual property of peers. o. Reflect on use of research questions and process. Revised – Fall 2008 • • • • • • • • Assessment Aligned Materials/ Resources/Technology Rubric McDougal Littell Test Generator Self evaluation Teacher observation Teacher conferencing Writing pieces PSSA domain rubrics Teacher created rubrics Students will explore the following themes from The Language of Literature: • Unit 1:Learning from Experience (Part 1 only) • Unit 2: Relationships (Part 1 only) • Unit 3: Flights of Imagination (Parts 1 and 2) • Unit 4: Nothing Stays the Same (Part 1 only) • Unit 5: Personal Challenges (Parts 1 and 2) McDougal Littell ClassZone www.mcdougallitell.com McDougal Littell Writing Transparencies for Unit 5 McDougal Littell The Language of Literature: Teacher Resource Book, Unit 5, “Writing Workshop” McDougal Littell Language Network, Chapter 27 Student laptops Instructional Strategies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Mapping Brainstorming Discussion KWL charts Sequencing Making, assessing, and revising predictions Activating prior knowledge Previewing/surveying Summarizing Questioning Rubric Graphic organizers Modeling Learning logs Reading Grade 7 Essential Question, Concept or Theme: C. Students will utilize research skills. Approx. Time Allotment: Standards: 1.8.8 A-C Adaptations/Inclusion Techniques RESEARCH • Daily assignment book • Project calendar for long-term assignments • Extended time for projects • Alternate materials • One-to-one directions • Oral/written directions • Student restatement of directions • Chunking/reduction of assignment length • Alternate assignment • Use of student laptop • Graphic organizer • Individual aide • Others as indicated by student’s IEP Revised – Fall 2008 • • • • Enrichment Strategies Remediation Strategies Multiple intelligence projects Independent, self-selected study Incorporation of multimedia (PowerPoint) Interest-based learning choices McDougal Littell Resource Kit • Communication Transparencies and Copymasters • Reteach/Retest • Peer tutor • Extra help sessions • ClassZone at www.mcdougallittell.com Multicultural/ Interdisciplinary Connection • • Research connections to other curricula Opportunities to research multicultural topics