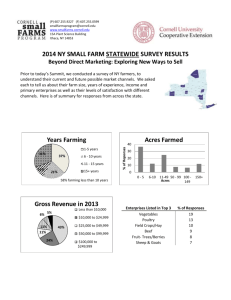
Report requested by Ofcom describing ... Accounting Documents for the year ...
advertisement

Report requested by Ofcom describing certain changes to the Accounting Documents for the year ended 31 March 2013 and illustrating the resulting differences to the Current Cost Financial Statements had those changes not applied 3 October 2013 Contents Section 4.1 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on costs allocated to each market ..................................................................................................................... 18 Report requested by Ofcom describing certain changes to the Accounting Documents for the year ended 31 March 2013 and illustrating the resulting differences to the Current Cost Financial Statements had those changes not applied Section 5 Explanation of reported methodology changes ............................................... 19 Section 5.1 – Allocation of Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexers (DSLAM) overhead and asset costs between WBA Markets 1, 2 and 3 ....................................... 20 Section 1 Introduction to the report requested by Ofcom describing certain changes to the Accounting Documents for the year ended 31 March 2013 and illustrating the resulting differences to the Current Cost Financial Statements had those changes not applied.......... 3 Section 5.2 – WBA bandwidth volumes ..................................................................... 21 Section 1.1 – Introduction .......................................................................................... 4 Section 5.4 – Effect of Digital Access Carrier System (DACS) on allocation of E-side and D-side copper costs to Wholesale Line Rental (WLR) .................................................. 23 st Section 5.3 – Allocation of 21 Century Network (21CN) equipment costs .................. 22 Section 1.2 – Structure of the report ........................................................................... 4 Section 2 Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary of 2012-13 Applying 2011-12 Methodologies ............................................................................................................... 5 Section 5.5 – Change in allocations for Special Fault Investigations (SFIs), Broadband Boost, Frame Repair, Dropwire Repair, Service Level Guarantees (SLGs) and Time Related Charges (TRCs) ............................................................................................. 24 Section 2.1 – Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary ..................................... 6 Section 5.6 – Openreach computing and development costs ...................................... 26 Section 3 Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies .................................................................. 8 Section 5.7 – Allocation of specialised accommodation space..................................... 27 Section 5.8 – Allocation of specific group provision ................................................... 28 Section 3.1 – Attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 as reported ......................... 9 Section 5.9 – Allocation of Career Transition Centre (CTC) costs .................................. 29 Section 3.2 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 restated on basis of 2011-12 methodologies .......................................................................................... 10 Section 5.10 – Allocation of vacant space in exchanges.............................................. 30 Section 5.11 – Allocation of Openreach overheads .................................................... 31 Section 3.3 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 impact of changes on results ................................................................................................................ 11 Section 5.12 – Merger of BT Innovate & Design (BTID) and BT Operate (BTO) to create BT Technology, Service & Operations (BT TSO) ........................................................... 32 Section 3.4 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 impact of changes on results as a percentage ........................................................................................ 12 Section 5.13 – Current Cost Accounting (CCA) valuation of Dropwire .......................... 34 Section 3.5 – Attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 as reported .................................................................................................................. 13 Section 5.14 – CCA valuation of exchange power equipment and specialised accommodation plant .............................................................................................. 35 Section 3.6 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 restated on basis of 2011-12 methodologies ................................................... 14 Section 6 Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC .................................... 36 Section 6.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services ................... 37 Section 3.7 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 impact of changes on results ........................................................................... 15 Section 6.1.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ............................ 38 Section 3.8 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 impact of changes on results in percentage terms ............................................. 16 Section 6.2 – Illustrative for Wholesale ISDN2 Exchange Line Services ........................ 42 Section 4 Illustrative difference of methodology changes on costs allocated to each market .................................................................................................................................... 17 Section 6.2.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale ISDN2 Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ................................................. 43 Section 6.3 – Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) ............................... 47 Page 1 Contents Section 6.14 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 2 ....................... 104 Section 6.3.1 – Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ....................................................... 49 Section 6.4 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) ...... 53 Section 6.14.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 2 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ............................................... 105 Section 6.4.1 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ............................ 54 Section 7 Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement .................................................................................................................................. 109 Section 6.5 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) .. 58 Section 7.1 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement 2013..................................................................................................... 110 Section 6.5.1 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ............................ 59 Section 6.6 – Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) ............................... 63 Section 6.6.1 – Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ....................................................... 65 Section 6.7 – Illustrative for Wholesale Local Access (WLA) ........................................ 69 Section 6.7.1 –Illustrative for Wholesale Local Access (WLA) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ................................................................. 70 Section 6.8 – Illustrative for Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks ...... 74 Section 6.8.1 – Illustrative for Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ............................ 75 Section 6.9 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Interconnect Circuits) ............................ 79 Section 6.9.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Interconnect Circuits) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ................................................. 80 Section 6.10 – Illustrative for Fixed Call Termination .................................................. 84 Section 6.10.1 – Illustrative for Fixed Call Termination calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ...................................................................... 85 Section 6.11 – Illustrative for Wholesale Trunk Segments ........................................... 89 Section 6.11.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Trunk Segments calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ................................................................. 90 Section 6.12 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Point of Handover) ............................. 94 Section 6.12.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Point of Handover) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ................................................. 95 Section 6.13 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 1 ......................... 99 Section 6.13.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 1 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ............................................... 100 Page 2 Section 1 – Introduction to the report requested by Ofcom describing certain changes to the Accounting Documents for the year ended 31 March 2013 and illustrating the resulting differences to the Current Cost Financial Statements had those changes not applied Section 1 Introduction to the report requested by Ofcom describing certain changes to the Accounting Documents for the year ended 31 March 2013 and illustrating the resulting differences to the Current Cost Financial Statements had those changes not applied Page 3 Section 1 – Introduction to the report requested by Ofcom describing certain changes to the Accounting Documents for the year ended 31 March 2013 and illustrating the resulting differences to the Current Cost Financial Statements had those changes not applied Section 1.1 – Introduction Section 1.2 – Structure of the report As a standard part of the process for producing and publishing BT’s Current Cost Financial Statements each year BT reviews its Accounting Documents, including the attribution and valuation methodologies set out in those Accounting Documents, to identify improvements that are superior to the prior year methodologies. BT updates the attribution and valuation methodologies, as set out in the Accounting Documents, to reflect changes in BT’s organisation and structure, market changes, technological changes, changes in available data and regulatory changes, all to ensure that the Current Cost Financial Statements are as robust as possible. BT’s methodology changes and corrections are subject to stringent internal review. As part of this review BT carefully considers the regulatory accounting principles which it applies in the required order of priority. The Current Cost Financial Statements for the year ended 31 March 2013 published on 31 July 2013 had an unqualified audit report. The Report follows the structure and layout requested by Ofcom. A description of each section is provided below: In respect of a number of attribution and valuation methodology changes that were changed between the Current Cost Financial Statements for the year ended 31 March 2012 and the Current Cost Financial Statements for the year ended 31 March 2013, being those attribution and valuation methodology changes and corrections detailed in this document, Ofcom requested BT to provide and publish a description of certain of the changes and produce tables showing the effect of those changes. This ‘Report requested by Ofcom describing certain changes to the Accounting Documents for the year ended 31 March 2013 and illustrating the resulting differences to the Current Cost Financial Statements had those changes not applied’ (the “Report”) is BT’s response to that request. The Report does not include the effect of changing the following methodologies as this would not be practicable: The Current Cost Accounting valuation of duct and copper assets from an absolute basis to an indexed RPI approach; Ethernet switch costs; and Average debtor days from 28 days to 22 days. The Report is not a replacement for, nor should it be regarded as an alternative to, BT’s published Current Cost Financial Statements for the year ended 31 March 2013. The Report is no more than a description of the methodology changes detailed in the Report and an illustration or view of the Current Cost Financial Statements for the year ended 31 March 2013 had those Statements been produced using the prior year 2011-12 methodologies. The Report has not been audited. Page 4 Section 2 – compares the consolidated results of the Access Markets, Other Wholesale Markets and Residual Markets as reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 to the results for those markets had certain changes to attribution and valuation methodologies not been applied. Section 3 – compares the attribution of wholesale current costs and wholesale current cost mean capital employed by individual Access Market, Other Wholesale Market and Residual Market as reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 to the results had certain changes to the attribution and valuation methodologies not been applied. Section 4 – provides the illustrative difference of methodology changes on costs allocated to individual Access Markets, Other Wholesale Markets and Residual Markets. Section 5 – provides an explanation of the reported methodology changes. Section 6 – compares the Fully Allocated Cost results of the individual Access Markets and Other Wholesale Markets at a service level as reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 to the results for those markets had certain changes to the attribution and valuation methodologies not been applied. Section 7 – compares the Network Activity Statement as reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 to the Network Activity Statement had certain changes to the attribution and valuation methodologies not been applied. Section 2 – Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary of 2012-13 Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Section 2 Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary of 2012-13 Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Page 5 Section 2 – Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary of 2012-13 Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Section 2.1 – Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary Revenue CCA operating costs CCA return before taxation MCE Return on MCE £m £m £m £m % Access Markets 4,495 3,072 1,423 11,640 12.2 % Other Wholesale Markets 1,053 794 259 1,478 17.5 % 5,548 3,866 1,682 13,118 12.8 % As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Markets Residual Activities Wholesale residual activities Retail residual activities Roundings Total Markets & Activities 2,565 1,966 599 2,437 24.6 % 14,615 13,650 965 103 936.9 % 17,180 15,616 1,564 2,540 61.6 % 2 (1) 3 1 22,730 19,481 3,249 15,659 n/a 20.7 % Revenue CCA operating costs CCA return before taxation MCE Return on MCE £m £m £m £m % Access Markets 4,495 3,044 1,451 11,681 12.4 % Other Wholesale Markets 1,053 817 236 1,404 16.8 % 5,548 3,861 1,687 13,085 12.9 % Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Markets Residual Activities Wholesale residual activities Retail residual activities Roundings Total Markets & Activities 2,565 1,987 578 2,275 25.4 % 14,615 13,720 895 253 353.8 % 17,180 15,707 1,473 2,528 58.3 % 2 2 3,162 15,615 2 22,730 19,568 Page 6 n/a 20.2 % Section 2 – Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary of 2012-13 Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Section 2.1 – Illustrative Consolidated Performance Summary (continued) Effect of changes on results Revenue CCA operating costs CCA return before taxation MCE Return on MCE £m £m £m £m % -0.2% Markets Access Markets 0 28 (28) (41) Other Wholesale Markets 0 (23) 23 74 0.7% 0 5 (5) 33 -0.1% Wholesale residual activities 0 (21) 21 162 Retail residual activities 0 (70) 70 (150) 0 (91) 91 12 Roundings 0 (1) 1 (1) Total Markets & Activities 0 (87) 87 44 Revenue CCA operating costs CCA return before taxation MCE % % % % Residual Activities Effect of changes on results as a percentage Markets Access Markets 0.0% 0.9% -1.9% -0.4% Other Wholesale Markets 0.0% -2.8% 9.7% 5.3% 0.0% 0.1% -0.3% 0.3% Wholesale residual activities 0.0% -1.1% 3.6% 7.1% Retail residual activities 0.0% -0.5% 7.8% -59.3% 0.0% -0.6% 6.2% 0.5% 0.0% -0.4% 2.8% 0.3% Residual Activities Total Markets & Activities Page 7 -0.8% 583.1% 3.3% n/a 0.5% Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Section 3 Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Page 8 Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Total Markets £m Wholesale Residual £m Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets £m Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 £m Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 £m Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets £m Technical areas (Point of Handover) £m Wholesale trunk segments £m Fixed call termination £m Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Wholesale local access £m Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £m Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £m Total Access Markets TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) £m TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) £m Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Wholesale analogue exchange line services Section 3.1 – Attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 as reported £m £m £m £m £m £m £m Operating Costs of Wholesale Services: EOI Charges Provision/Maintenance 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 119 59 178 (178) 0 169 8 10 36 2 2 11 120 358 12 0 2 11 2 1 28 17 7 52 197 607 Network Support 111 4 5 19 1 1 28 51 220 3 0 1 3 1 0 8 3 1 12 55 287 General Support 178 7 13 36 2 2 67 98 403 12 0 2 7 2 1 24 14 6 44 178 625 General Management 261 10 18 47 3 3 93 115 550 21 1 5 12 4 1 44 33 15 92 286 928 10 0 1 2 0 0 3 5 21 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 11 33 126 10 12 50 3 4 16 91 312 41 1 6 43 4 1 96 47 14 157 130 599 Bad Debts 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Other Costs 22 2 3 10 1 1 8 13 60 5 0 1 5 1 0 12 8 3 23 754 837 Finance and Billing Accommodation Depreciation - Land & Buildings 16 2 2 10 1 1 4 22 58 6 0 1 7 1 0 15 9 3 27 28 113 414 13 12 35 2 2 74 143 695 2 0 1 2 2 1 8 21 6 35 78 808 28 3 17 55 5 9 59 8 184 16 1 4 18 9 1 49 64 29 142 226 552 107 4 6 18 1 1 54 90 281 10 0 1 9 1 1 22 27 11 60 260 601 565 22 37 118 9 13 191 263 1,218 34 1 7 36 13 3 94 121 49 264 592 2,074 1,442 63 99 318 21 26 417 756 3,142 128 3 24 117 27 7 306 363 154 823 2,025 5,990 Holding Loss/(Gain) (203) (6) (3) (14) (1) (2) (23) (69) (321) (4) 0 (1) (4) (5) 0 (14) (4) (1) (19) (22) (362) Supplementary Depreciation 203 6 (1) (2) (1) (1) (5) 71 270 2 0 0 2 2 0 6 (10) (6) (10) (26) 234 Other Adjustments (19) 0 2 2 0 0 11 (15) (19) 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 (2) 0 0 (11) (30) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 63 97 304 19 23 400 743 3 23 116 24 7 300 347 147 794 - Access - Switch and Transmission - Other related Sub Total Depreciation Sub Total HCA Operating Costs CCA Adjustments: Roundings Total CCA Operating Costs 1,423 3,072 Page 9 127 1,966 5,832 Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Total Markets £m Wholesale Residual £m Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets £m Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 £m Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 £m Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets £m Technical areas (Point of Handover) £m Wholesale trunk segments £m Fixed call termination £m Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Wholesale local access £m Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £m Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £m Total Access Markets TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) £m TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) £m Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Wholesale analogue exchange line services Section 3.2 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 restated on basis of 2011-12 methodologies £m £m £m £m £m £m £m Operating Costs of Wholesale Services: EOI Charges Provision/Maintenance 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 119 60 179 (179) 0 163 7 10 38 1 2 8 113 342 12 0 2 11 2 1 28 17 7 52 205 599 Network Support 109 4 6 20 1 1 30 50 221 3 0 1 3 1 0 8 3 1 12 55 288 General Support 163 7 14 39 2 2 72 89 388 12 0 3 8 1 1 25 15 5 45 182 615 General Management 225 10 20 51 3 4 101 102 516 24 0 6 16 4 1 51 32 14 97 288 901 9 0 1 2 0 0 3 5 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 12 33 120 11 13 56 3 4 16 79 302 46 2 6 50 4 1 109 39 12 160 137 599 Bad Debts 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Other Costs 23 2 3 11 1 1 8 12 61 6 0 1 5 1 0 13 7 3 23 750 834 Finance and Billing Accommodation Depreciation - Land & Buildings 12 2 2 10 1 1 3 24 55 6 0 1 7 1 0 15 9 3 27 25 107 415 14 13 35 2 2 75 144 700 2 0 1 2 2 1 8 21 6 35 74 809 - Switch and Transmission 28 3 16 60 8 12 59 8 194 16 1 4 18 9 1 49 59 27 135 223 552 - Other related 67 3 7 24 2 2 86 62 253 9 0 2 8 2 1 22 33 14 69 265 587 522 22 38 129 13 17 223 238 1,202 33 1 8 35 14 3 94 122 50 266 587 2,055 1,334 63 105 346 24 31 461 688 3,052 136 3 27 128 27 7 328 355 152 835 2,037 5,924 Holding Loss/(Gain) (187) (6) (3) (15) (1) (2) (23) (64) (301) (4) 0 (2) (5) (5) 0 (16) (8) (1) (25) (23) (349) Supplementary Depreciation 200 6 (1) (3) (1) (1) (5) 69 264 1 0 0 1 2 0 4 (11) (6) (13) (28) 223 Other Adjustments 8 1 3 5 1 0 11 0 29 5 0 0 5 1 0 11 6 3 20 1 50 Roundings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 64 104 333 23 28 444 693 3 25 129 25 7 327 342 148 817 - Access Sub Total Depreciation Sub Total HCA Operating Costs CCA Adjustments: Total CCA Operating Costs 1,355 3,044 Page 10 138 1,987 5,848 Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies (1) 0 0 (2) 15 0 (1) (3) 0 0 36 0 (2) (4) 0 (1) Finance and Billing 1 0 0 0 0 Accommodation 6 (1) (1) (6) Bad Debts 0 0 0 Other Costs (1) 0 Depreciation - Land & Buildings 4 Total Markets (1) Wholesale Residual 0 Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets 3 (1) 1 0 0 (8) 8 0 0 0 (1) (1) 1 (1) (4) 10 1 1 (5) (2) 27 0 0 0 0 (1) 0 0 (13) 8 2 (3) (7) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 1 0 0 4 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 (1) £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 7 16 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 (1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (5) 9 15 0 0 (1) (1) 1 0 (1) (8) 13 34 (3) 1 (1) (4) 0 0 (7) 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 12 10 (5) (1) 0 (7) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 0 0 0 1 (1) (1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 (2) 3 0 0 (1) (1) (1) 0 0 0 (1) (1) (5) 0 0 Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services £m Wholesale analogue exchange line services Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 0 0 Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 0 1 Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets 0 (2) Technical areas (Point of Handover) 0 0 £m Wholesale trunk segments 0 £m £m £m £m EOI Charges Provision/Maintenance 0 0 6 1 Network Support 2 General Support General Management Effect of changes on results £m Fixed call termination £m Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £m Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £m Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) £m Total Access Markets TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) £m Wholesale local access Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services Section 3.3 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 impact of changes on results Operating Costs of Wholesale Services: - Access - Switch and Transmission - Other related Sub Total Depreciation Sub Total HCA Operating Costs 0 0 1 (5) (3) (3) 0 0 (10) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 2 7 3 0 40 1 (1) (6) (1) (1) (32) 28 28 1 0 (1) 1 (1) 0 0 (6) (3) (9) (5) 14 43 0 (1) (11) (4) (4) (32) 25 16 1 0 (1) 1 (1) 0 0 (1) (1) (2) 5 19 108 0 (6) (28) (3) (5) (44) 68 90 (8) 0 (3) (11) 0 0 (22) 8 2 (12) (12) 66 (16) 0 0 1 0 0 0 (5) (20) 0 0 1 1 0 0 2 4 0 6 1 (13) 3 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 6 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 3 2 11 (27) (1) (1) (3) (1) 0 0 (15) (48) (4) 0 0 (4) (1) 0 (9) (8) (3) (20) (12) (80) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 68 (1) (7) (29) (4) (5) (44) 50 28 (11) 0 (2) (13) (1) 0 (27) 5 (1) (23) (21) (16) CCA Adjustments: Holding Loss/(Gain) Supplementary Depreciation Other Adjustments Roundings Total CCA Operating Costs Page 11 Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies % % % % % EOI Charges Provision/Maintenance 3.7% 14.3% 0.0% -5.3% 100.0% 0.0% 37.5% 6.2% 4.7% Network Support 1.8% 0.0% -16.7% -5.0% 0.0% 0.0% -6.7% 2.0% -0.5% Total Markets 0.0% % Wholesale Residual 0.0% % Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets Technical areas (Point of Handover) 0.0% % Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 Wholesale trunk segments 0.0% % Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 Fixed call termination 0.0% % Effect of changes on results as a percentage Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) 0.0% Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks 0.0% Total Access Markets 0.0% Wholesale local access 0.0% AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) 0.0% TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) % TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) % TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) % Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services % Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services % Wholesale analogue exchange line services Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks Section 3.4 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Costs 2013 impact of changes on results as a percentage % % % % % % 0.0% -1.7% -0.6% -0.6% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -3.9% 1.3% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -0.3% Operating Costs of Wholesale Services: General Support 9.2% 0.0% -7.1% -7.7% 0.0% 0.0% -6.9% 10.1% 3.9% 0.0% -33.3% -12.5% 100.0% 0.0% -4.0% -6.7% 20.0% -2.2% -2.2% 1.6% General Management 16.0% 0.0% -10.0% -7.8% 0.0% -25.0% -7.9% 12.7% 6.6% -12.5% -16.7% -25.0% 0.0% 0.0% -13.7% 3.1% 7.1% -5.2% -0.7% 3.0% Finance and Billing 11.1% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 5.0% 0.0% -8.3% 0.0% 0.0% 15.2% 3.3% -10.9% -5.1% 0.0% 0.4% Accommodation 5.0% -9.1% -7.7% -10.7% 0.0% 0.0% Other Costs -4.3% 0.0% 0.0% -9.1% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 8.3% -1.6% Depreciation - Land & Buildings 33.3% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 33.3% -8.3% 5.5% -0.2% -7.1% -7.7% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -1.3% -0.7% -0.7% 0.0% -50.0% 0.0% -14.0% 0.0% -16.7% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -11.9% 20.5% 16.7% -1.9% 0.0% -7.7% 14.3% 0.0% 0.0% 0.5% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 12.0% 5.6% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 5.4% -0.1% Bad Debts - Access - Switch and Transmission 0.0% 0.0% 6.3% -8.3% -37.5% -25.0% 0.0% 0.0% -5.2% 0.0% 59.7% 33.3% -14.3% -25.0% -50.0% -50.0% -37.2% 45.2% 11.1% 11.1% Sub Total Depreciation 8.2% 0.0% -2.6% -8.5% -30.8% -23.5% -14.3% 10.5% 1.3% 3.0% Sub Total HCA Operating Costs 8.1% 0.0% -5.7% -8.1% -12.5% -16.1% -9.5% 9.9% 2.9% -5.9% Holding Loss/(Gain) 8.6% 0.0% 0.0% -6.7% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 7.8% 6.6% 0.0% Supplementary Depreciation 1.5% 0.0% 0.0% -33.3% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 2.9% 2.3% 100.0% -337.5% -100.0% -33.3% -60.0% -100.0% -165.5% -80.0% 5.0% -1.6% -6.7% -8.7% -17.4% 0.9% -8.0% - Other related 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 8.5% 7.4% 5.2% 1.3% 0.0% -50.0% 12.5% -50.0% 0.0% 0.0% -18.2% -21.4% -13.0% -1.9% 2.4% 0.0% -12.5% 2.9% -7.1% 0.0% 0.0% -0.8% -2.0% -0.8% 0.9% 0.9% 0.0% -11.1% -8.6% 0.0% 0.0% -6.7% 2.3% 1.3% -1.4% -0.6% 1.1% -20.0% 0.0% -12.5% -50.0% 0.0% -24.0% -4.3% 3.7% 100.0% 0.0% 50.0% -9.1% 0.0% -23.1% -7.1% 4.9% -80.0% -100.0% -81.8% -133.3% -100.0% -1200.0% -160.0% -10.1% -4.0% -8.3% 1.5% -2.8% -1.1% -0.3% CCA Adjustments: Other Adjustments 0.0% -50.0% Roundings Total CCA Operating Costs -17.9% -9.9% 7.2% Page 12 0.0% -8.0% 0.0% -0.7% Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Non-current Assets Land & Buildings Fixed call termination Wholesale trunk segments Technical areas (Point of Handover) Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets Wholesale Residual Total Markets £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m 129 16 18 6 9 21 231 525 66 1 10 71 10 1 159 105 30 294 277 1,096 3,187 100 11 15 0 0 0 1,124 4,437 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 40 11 51 195 4,683 Access - Fibre 0 0 71 164 12 7 459 0 713 0 0 2 0 0 8 10 0 0 10 374 1,097 Access - Duct 2,679 87 51 271 19 31 448 904 4,490 79 0 19 85 92 3 278 97 24 399 317 5,206 94 14 8 0 0 0 0 16 132 48 2 5 51 0 0 106 0 0 106 78 316 Transmission 139 6 40 169 14 23 271 47 709 51 5 11 55 41 3 166 182 83 431 666 1,806 Other 344 15 22 76 5 6 156 284 908 34 1 5 32 6 1 79 92 33 204 651 1,763 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6,572 238 221 790 56 76 1,355 2,606 11,914 278 9 52 294 149 16 798 516 181 1,495 2,558 15,967 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 19 20 Access - Copper Switch Investments Total Non-current Assets 95 Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) £m Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks £m Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks £m Total Access Markets £m Wholesale local access AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £m TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £m TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services £m TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Wholesale analogue exchange line services Section 3.5 – Attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 as reported Current Assets Inventories Receivables - Internal 117 8 17 27 2 3 48 49 271 10 0 3 9 5 0 27 24 12 63 - External 436 26 79 118 10 18 203 146 1,036 40 2 10 34 25 3 114 113 62 289 1,246 2,571 Total Current Assets 553 34 96 145 12 21 251 195 1,307 50 2 13 43 30 3 141 138 74 353 1,213 2,873 (52) 282 Payables falling due within one year - Internal 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (7) (4) (11) 11 0 - External (615) (34) (92) (149) (12) (19) (279) (245) (1,445) (51) (2) (13) (44) (25) (4) (139) (130) (66) (335) (1,166) (2,946) Total payables falling due within one year (615) (34) (92) (149) (12) (19) (279) (245) (1,445) (51) (2) (13) (44) (25) (4) (139) (137) (70) (346) (1,155) (2,946) (62) 0 4 (4) 0 2 (28) (50) (138) (1) 0 0 (1) 5 (1) 2 1 4 7 58 (73) 238 225 786 56 78 277 9 52 293 154 15 800 517 185 1,502 2,616 (3) (4) (7) 0 0 (5) 0 (1) (4) 0 0 (10) (10) (4) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 235 221 779 56 78 9 51 289 154 15 790 507 181 Net Current Assets/(Payables) Total Assets less Current Payables Provisions for liabilities & charges 6,510 (69) Roundings Mean Capital Employed 6,441 1,327 2,556 11,776 (17) (36) (136) - - - 1,310 2,520 11,640 272 Non-current assets are net of government grants of £7.5m. Page 13 15,894 (24) (179) (339) - - - 1,478 2,437 15,555 Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Non-current Assets Land & Buildings Fixed call termination Wholesale trunk segments Technical areas (Point of Handover) Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets Wholesale Residual Total Markets £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m 125 16 18 6 10 22 281 573 65 1 10 70 9 1 156 93 27 276 230 1,079 3,182 99 11 15 0 0 0 1,118 4,425 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 38 12 50 182 4,657 Access - Fibre 0 0 73 167 13 7 467 0 727 0 0 2 0 0 8 10 0 0 10 361 1,098 Access - Duct 2,706 87 52 273 19 31 452 909 4,529 79 0 19 86 93 3 280 98 24 402 274 5,205 94 14 8 0 0 0 0 16 132 48 2 5 52 0 0 107 0 0 107 78 317 Transmission 139 6 39 184 21 32 271 47 739 51 5 10 55 41 2 164 171 77 412 655 1,806 Other 267 14 22 81 5 7 248 247 891 32 0 5 31 6 1 75 86 33 194 646 1,731 Access - Copper Switch Investments Total Non-current Assets 95 Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) £m Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks £m Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks £m Total Access Markets £m Wholesale local access AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £m TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £m TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services £m TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Wholesale analogue exchange line services Section 3.6 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 restated on basis of 2011-12 methodologies 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6,513 236 223 815 64 87 1,460 2,618 12,016 275 8 51 294 149 15 792 486 173 1,451 2,426 15,893 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 19 20 Current Assets Inventories Receivables - Internal 117 8 17 27 2 3 48 49 271 10 0 3 9 5 0 27 25 13 65 - External 436 26 79 118 10 18 203 145 1,035 40 2 10 34 25 3 114 114 62 290 1,244 2,569 553 34 96 145 12 21 251 194 1,306 50 2 13 43 30 3 141 140 75 356 1,210 2,872 Total Current Assets (53) 283 Payables falling due within one year - Internal - External Total payables falling due within one year Net Current Assets/(Payables) Total Assets less Current Payables Provisions for liabilities & charges Roundings Mean Capital Employed 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (7) (4) (11) (594) 0 (33) (94) (155) (12) (20) (288) (236) (1,432) (52) (2) (13) (46) (25) (4) (142) (129) (65) (336) (1,176) (2,944) (594) (33) (94) (155) (12) (20) (288) (236) (1,432) (52) (2) (13) (46) (25) (4) (142) (136) (69) (347) (1,165) (2,944) (41) 1 2 (10) 0 1 (37) (42) (126) (2) 0 0 (3) 5 (1) (1) 237 225 805 64 88 273 8 51 291 (22) (1) (1) (16) 0 (2) (17) 6,472 (97) 6,375 (6) (8) 0 - - - - - 231 217 783 63 87 0 1,423 (21) 1,402 0 2,576 (53) 2,523 0 11,890 (209) 11,681 Page 14 257 8 154 (1) 0 11 4 6 9 45 179 1,460 2,471 14 791 490 0 (36) (15) (5) - - - - - - - 49 274 153 14 755 475 174 (56) 1,404 (196) 2,275 0 (72) 15,821 (461) 15,360 Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) Wholesale local access Total Access Markets Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Fixed call termination Wholesale trunk segments Technical areas (Point of Handover) Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m 4 0 0 0 0 (1) (1) (50) (48) 1 0 0 1 1 0 3 Access - Copper 5 1 0 0 0 0 0 6 12 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Access - Fibre 0 0 (2) (3) (1) 0 (8) 0 (14) 0 0 0 0 0 0 Access - Duct (27) 0 (1) (2) 0 0 (4) (5) (39) 0 0 0 (1) (1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) Switch Transmission Total Markets TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) £m Wholesale Residual TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) £m Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services £m Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services £m Non-current Assets Land & Buildings Effect of changes on results Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 Wholesale analogue exchange line services Section 3.7 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 impact of changes on results £m £m £m £m £m 12 3 18 47 17 2 (1) 1 13 26 0 0 0 0 13 (1) 0 (2) (1) 0 (3) 43 1 0 0 (1) 0 0 (1) 0 (1) 0 0 1 (15) (7) (9) 0 0 (30) 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 11 6 19 11 0 77 1 0 (5) 0 (1) (92) 37 17 2 1 0 1 0 0 4 6 0 10 5 32 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 59 2 (2) (25) (8) (11) (105) (12) (102) 3 1 1 0 0 1 6 30 8 44 132 74 Inventories 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Receivables 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 - Internal 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) (1) (2) 1 (1) - External 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 0 (1) 2 2 Total Current Assets 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (2) (1) (3) 3 1 Other Investments Total Non-current Assets Current Assets Payables falling due within one year - Internal 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 - External (21) (1) 2 6 0 1 9 (9) (13) 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 (1) (1) 1 10 (2) Total payables falling due within one year (21) (1) 2 6 0 1 9 (9) (13) 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 (1) (1) 1 10 (2) Net Current Assets/(Payables) (21) (1) 2 6 0 1 9 (8) (12) 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 (3) (2) (2) 13 (1) Total Assets less Current Payables 38 1 0 (19) (8) (10) (96) (20) (114) 4 1 1 2 0 1 9 27 6 42 145 73 Provisions for liabilities & charges 28 3 4 15 1 1 4 17 73 11 0 1 13 1 0 26 5 1 32 17 122 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 66 4 4 (4) (7) (9) (92) (3) (41) 15 1 2 15 1 1 35 32 7 74 162 195 Roundings Mean Capital Employed Page 15 Section 3 – Illustrative Attribution of 2012-13 Wholesale Current Costs and Mean Capital Employed Applying 2011-12 Methodologies Wholesale analogue exchange line services Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) Wholesale local access Total Access Markets Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Fixed call termination Wholesale trunk segments Technical areas (Point of Handover) Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets Wholesale Residual Total Markets Section 3.8 – Illustrative attribution of Wholesale Current Cost Mean Capital Employed 2013 impact of changes on results in percentage terms £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m Non-current Assets Land & Buildings 3.2% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -10.0% -4.5% -17.8% -8.4% 1.5% 0.0% 0.0% 1.4% 11.1% 0.0% 1.9% 12.9% 11.1% 6.5% 20.4% 1.6% Access - Copper 0.2% 1.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.5% 0.3% 5.3% -8.3% 2.0% 7.1% 0.6% -2.7% -1.8% -7.7% 0.0% -1.7% 0.0% 3.6% -0.1% -0.7% 0.0% 0.0% -0.9% -0.7% 15.7% 0.0% -0.9% 0.0% -0.3% Effect of changes on results as a percentage Access - Fibre Access - Duct -1.0% 0.0% -1.9% Switch 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% Transmission Other -1.9% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -0.7% -0.6% -0.9% 0.0% 0.0% -1.2% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -1.9% 0.0% 10.0% 0.0% 0.0% 50.0% 1.2% 6.4% 7.8% 4.6% 1.7% 0.0% 0.0% 3.2% 0.0% 0.0% 5.3% 7.0% 0.0% 5.2% 0.8% 1.8% 2.0% 0.0% 0.0% 6.7% 0.8% 6.2% 4.6% 3.0% 5.4% 0.5% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 2.6% -8.2% -33.3% -28.1% 0.0% 0.0% -4.1% 0.0% 28.8% 7.1% 0.0% -6.2% 0.0% -14.3% -37.1% 15.0% 1.9% 6.3% 0.9% 0.8% -0.9% -3.1% -12.5% -12.6% -7.2% -0.5% -0.8% 1.1% -1.1% 0.0% -1.0% 0.0% -0.9% Investments Total Non-current Assets 12.5% Current Assets Inventories 0.0% Receivables - Internal 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -4.0% -7.7% -3.1% -1.9% -0.4% - External 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.7% 0.1% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -0.9% 0.0% -0.3% 0.2% 0.1% Total Current Assets 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.5% 0.1% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% -1.4% -1.3% -0.8% 0.2% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% - External 3.5% 3.0% -2.1% -3.9% 0.0% -5.0% -3.1% 3.8% 0.9% -1.9% 0.0% 0.0% -4.3% 0.0% 0.0% -2.1% 0.8% 1.5% -0.3% -0.9% 0.1% Total payables falling due within one year 3.5% 3.0% -2.1% -3.9% 0.0% -5.0% -3.1% 3.8% 0.9% -1.9% 0.0% 0.0% -4.3% 0.0% 0.0% -2.1% 0.7% 1.4% -0.3% -0.9% 0.1% 51.2% -100.0% 100.0% -60.0% 100.0% -24.3% 19.0% 9.5% -50.0% -66.7% 0.0% 0.0% -300.0% -75.0% -33.3% -22.2% 28.9% 1.4% 0.6% 0.4% 0.0% -2.4% -12.5% -11.4% -6.7% -0.8% -1.0% 1.5% 2.0% 0.7% 0.0% 7.1% 1.1% 5.5% 3.4% 2.9% 5.9% 0.5% -28.9% -50.0% -50.0% -68.2% -100.0% -100.0% -19.0% -32.1% -34.9% -68.8% -50.0% -76.5% -100.0% -72.2% -33.3% -20.0% -57.1% -8.7% -26.5% 1.0% 1.7% 1.8% -0.5% -11.1% -10.3% -6.6% -0.1% -0.4% 5.8% 4.1% 5.5% 0.7% 4.6% 6.7% 4.0% 5.3% 7.1% 1.3% Payables falling due within one year - Internal Net Current Assets/(Payables) Total Assets less Current Payables Provisions for liabilities & charges 12.5% Roundings Mean Capital Employed Page 16 12.5% 7.1% Section 4 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on costs allocated to each market Section 4 Illustrative difference of methodology changes on costs allocated to each market Page 17 Section 4 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on costs allocated to each market Wholesale analogue exchange line services Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services Wholesale business ISDN30 exchange line services TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) Wholesale local access Total Access Markets Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks Single transit on fixed public narrowband networks Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Fixed call termination Wholesale trunk segments Technical areas (Point of Handover) Sub-total Other Wholesale & SMP National Markets Wholesale broadband access - Market 1 Wholesale broadband access - Market 2 Total Other Wholesale & SMP Markets Wholesale Residual Total Wholesale Markets Retail Residual Roundings Total Markets Section 4.1 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on costs allocated to each market £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m £m 0 0 0 (1) (6) 24 (3) 18 0 7 3 12 13 9 16 10 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) (1) 0 0 (1) (1) (1) (1) 0 (1) 1 0 0 (8) 0 0 0 (2) (3) 0 1 (5) (3) (2) (4) 0 (1) 0 0 0 (2) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (4) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 0 0 0 0 0 (39) 0 (5) 0 2 (2) 3 (2) (1) 2 1 (1) 0 0 0 0 8 8 (1) 3 2 3 0 14 3 16 6 10 1 0 0 (14) (1) 2 (7) (7) 12 2 13 (5) 25 11 19 24 18 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 (2) (1) 0 0 0 (5) 1 1 (1) (3) 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 0 0 0 (1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (3) (1) 0 0 0 (5) 1 2 (1) (3) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (5) (2) 0 0 0 (11) 2 3 (2) (7) 1 8 (4) 6 0 0 0 8 0 0 0 0 (4) 0 (8) (1) 1 2 1 (6) 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 (1) 0 (3) (1) 1 1 9 (10) 7 0 0 0 5 (2) 0 0 0 (16) 2 (8) (4) (5) 4 (8) 9 7 0 (2) 5 2 (10) (2) 3 4 (5) (4) (9) (1) 4 2 1 (1) 0 (1) 0 (2) 0 0 0 16 (1) 4 9 2 19 17 9 0 (16) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (16) 1 (5) (8) (2) (20) (18) (4) (1) 1 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 1 (1) 0 1 1 (5) 0 (16) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 103 1 (6) (27) (2) (5) (42) 73 95 (8) 0 (2) (10) (1) 0 (21) 8 (5) (18) (5) 72 (88) 0 (16) Aggregate effect of non-material allocation methodology changes 4 0 0 2 (2) 0 (2) (5) (3) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 5 7 (7) (3) 18 0 15 Total effect of allocation methodology changes 107 1 (6) (25) (4) (5) (44) 68 92 (8) 0 (2) (10) (1) 0 (21) 10 0 (11) (12) 69 (70) 0 (1) (35) (1) 0 0 0 0 0 (12) (48) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (48) 0 0 (48) (4) (1) (1) (4) 0 0 0 (6) (16) (3) 0 0 (3) 0 0 (6) (5) (1) (12) (9) (37) 0 0 (37) 68 (1) (7) (29) (4) (5) (44) 50 28 (11) 0 (2) (13) (1) 0 (27) 5 (1) (23) (21) (16) (70) 0 (86) Ref. Changes in allocation methodologies 1 DSLAMs 2 WBA bandwidth volumes 3 21CN & Core Directors 4 DACS 5 Fault Rates (Dropwire & MDF) 6 Openreach computing and development 7 Specialised accommodation space 8 Specific group provision 9 SLGs 10 Career Transition Centre 11 SFIs, TRCs, Broadband Boost 12 Vacant space in exchanges 13 Openreach Overheads 14 BT TSO - Development 15 BT TSO - Computing 16 BT TSO - Operating costs Roundings Effect of significant allocation methodology changes Changes in valuation methodologies 17 CCA valuation of dropwire 18 CCA valuation of exchange power equipment and specialised accommodation plant Total effect of changes in allocation and valuation methodologies Page 18 Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5 Explanation of reported methodology changes Page 19 Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.1 – Allocation of Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexers (DSLAM) overhead and asset costs between WBA Markets 1, 2 and 3 change Reference number (Section 4.1) 1 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) More costs are allocated to WBA Markets 1 and 2 as these markets continue to service relatively large numbers of IPstream and Datastream customers, for which DSLAMs are required, whilst the majority of customers in Market 3 have transitioned to Wholesale Broadband Connect (WBC) which use Multi-Service Access Nodes (MSANs) instead of DSLAMs. The change impacted the DSLAM Overheads and DSLAM Depreciation components (CR188 and CR189 respectively) and the Datastream and IPstream services. Cost causality. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Support for the change Other – improvement identified by BT. Description of change DSLAMs are sited at the local exchange or concentrator sites, and contain the subscriber cards and concentration to provide broadband services (IPstream and Datastream) over the copper access network. The costs associated with these DSLAMs include both fixed and variable elements i.e. some of the costs are driven by the number of end users a DSLAM supports and others are fixed and incurred in relation to the number of DSLAMs themselves. DSLAM overhead costs: allocated evenly across all DSLAMs in the network and then further split into Datastream and IPstream services based on volumes of end-users for each DSLAM. DSLAM asset costs (i.e. depreciation): allocated to all DSLAMs except those which are fully depreciated and then further split into Datastream and IPstream based on volumes of end-users. Key changes in accounting documents Under the new methodology, the fixed and variable elements of DSLAM costs are reflected in the allocations: fixed DSLAM costs are allocated across all DSLAMs while variable costs are allocated directly to Datastream and IPstream according to volumes of end-users per DSLAM. Effect of the Of the total DSLAM overhead costs 68% of the costs are fixed in nature and relate to the number of DSLAMs, and the remaining 32% of costs are variable in relation to the number of end users. For DSLAM asset costs, line cards are directly variable with the number of end users and account for 14% of the total DSLAM asset cost and the remaining 86% of costs are fixed. There has been a transition in WBA Market 3 to WBC which uses MSANs instead of DSLAMs. The new methodology is more cost causal as it better reflects which WBA Markets use the DSLAM equipment. Under the old methodology, DSLAM costs were allocated as follows: A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change A detailed analysis of overhead costs by sector was undertaken and resulted in the following split of DSLAM overhead and asset costs into their fixed and variable elements: A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components Page 20 Set out key changes to accounting documents Updated descriptions in section 7 of the DAM for DSLAM Overheads and Depreciation components (CR188 and CR189 respectively). Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.2 – WBA bandwidth volumes Reference number (Section 4.1) 2 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) the change This change reflects a better data source being available. The new information was reviewed over a number of months and assessed to be a more appropriate proxy for allocating the consumed bandwidth than the previous approach. The new approach better reflects the characteristics of each WBA market than only using end users. Key changes in accounting documents Cost causality. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Changes in available evidence. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology Our previous data source of bandwidth volumes did not split the bandwidth between WBA Markets 1, 2 and 3. Therefore, under the old methodology the number of end users by WBA market (for each service) was used as a proxy to split the bandwidth volumes. In 2012/13 improved data has become available from the Wholesale Customer Reporting (WCR) system which shows the peak bandwidth recorded for each service in each WBA market. Peak bandwidth shows the highest bandwidth consumption for a given service during a measured period and was considered a better proxy for allocating the consumed bandwidth under the new methodology. Effect of the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes Lower costs are allocated to WBA Markets 1 and 2. Within WBA Markets 1 and 2 the main services affected are IPstream and Wholesale Broadband Connect and the components affected relate to 21CN components CN860, CN884, CN903, and CN878. Support for to support the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account Page 21 Set out key changes to accounting document Section 7.3.3 of the DAM has been amended to reflect the updated methodology. Descriptions for components CN860, CN884, CN903, and CN878 have also been updated. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.3 – Allocation of 21st Century Network (21CN) equipment costs Reference number (Section 4.1) 3 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) the Wholesale Broadband Connect and IPstream bandwidth services in WBA Markets 1, 2 and 3. The IPstream Connect components have been impacted by the change. Support for the change The BT 21CN design team have confirmed a change of use in the 21CN, which means it is no longer cost causal to allocate Core Director equipment costs to the TISBO markets. Cost causality. Trigger for change While the Core Directors were purchased in order to support the delivery of PPC services, they are currently used as part of the Broadband transport system switching the IPstream and Datastream traffic. When the legacy TDM platform is closed at the end of 2014, this equipment will be used to directly switch IPstream and Datastream traffic. Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Changes in available evidence. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology Accordingly, it is cost causal to reflect this change in use by allocating the Core Director equipment costs to WBA Markets 1, 2 and 3 rather than to the TISBO markets. Core Director equipment is used as a traffic switch resilience platform, which replicates on the modern 21CN the functionality of the legacy Time Divisional Multiplexing (TDM) platform. The legacy TDM platform has been used to carry PPC, Kilostream, Megastream, Voice and Broadband traffic and will be closed at the end of 2014. Key changes in accounting documents Core Director equipment was initially purchased to support the delivery of certain TDM services (specifically PPCs) over the 21CN. As a result, the old methodology allocated the Core Director equipment costs to the TISBO markets. Core Directors are no longer intended to support the delivery of TDM services. However, Broadband services (IPstream and Datastream) do currently (and will in future) use the Core Directors as part of its underlying traffic switch resilience platform. Accordingly, the new methodology allocates the Core Director equipment costs to WBA Markets 1, 2 and 3. Effect of the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The change results in costs being allocated to the WBA Markets rather than PPC Markets. The services impacted by the change are the PPC services and Page 22 Set out key changes to accounting documents The DAM has been updated to reflect the new methodology for Plant Groups 866A, 886A, 887A, 888A, 893A, 895A, 896A, 898A and Component CN878. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.4 – Effect of Digital Access Carrier System (DACS) on allocation of E-side and D-side copper costs to Wholesale Line Rental (WLR) Reference number (Section 4.1) 4 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) change The change has a small impact on the Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services Market. The main services affected are MPF Rentals and Wholesale basic analogue service rentals. Support for the change Cost causality. Trigger for change Description of change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other The new methodology is more cost causal as it reflects the lower average usage of E-side and D-side copper by WLR (as compared with LLU and MPF) by taking into account the effect of DACS technology on WLR lines. Other – re-instatement of methodology applied in the 2010/11 Regulatory Financial Statements (RFS) that was incorrectly omitted in the 2011/12 RFS that also aligns with DACS adjustment made by Ofcom in the WLR/LLU charge control published 7 March 2012. Not all DACS systems are fully utilised and we currently have 130,000 DACS lines systems carrying approximately 190,000 WLR lines. Therefore, 60,000 WLR lines are carried over a copper pair that already carries another WLR line. The total number of WLR lines is 18,300,000. The usage factor takes this into account by dividing total copper pairs required by WLR by the total number of WLR lines: A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology (18,300,000 – 60,000) / 18,300,000 = 0.996 Under the old methodology, E-side and D-side copper costs were allocated to WLR via a usage factor of 1. This was identical to the usage factor for Local Loop Unbundling (LLU) Metallic Path Facility (MPF) and for ISDN2 (per line). The new methodology is also consistent with Ofcom’s charge control modelling for the current WLR/LLU charge control – for example, see table in Figure A4.21 in Ofcom’s “Charge control review for LLU and WLR services Annexes” published 7 March 2012. The new methodology reflects the fact that some lines have DACS technology, which allows two WLR lines to be provided over a single copper pair (known as “Pair Gain”). Therefore, the presence of DACS results in a lower average usage of E-side and D-side copper per WLR line and an updated usage factor of less than 1 has been applied to WLR lines to reflect this. For ISDN2 and LLU MPF lines a usage factor of 1 is still applied as it is not possible to use DACS equipment on these lines. The methodology was previously applied in the 2010/11 RFS and has been re-instated to align with Ofcom’s modelling for the current WLR/LLU charge control. Key changes in accounting documents The new methodology does not impact SMPF as E-side and D-side copper costs are not allocated to SMPF. Effect of the affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most Page 23 Set out key changes to accounting documents Usage factors are not disclosed in the accounting documents so no changes have been made. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.5 – Change in allocations for Special Fault Investigations (SFIs), Broadband Boost, Frame Repair, Dropwire Repair, Service Level Guarantees (SLGs) and Time Related Charges (TRCs) Reference number (Section 4.1) 5,9,11 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) jumpers that each product required. The usage factors in the new methodology reflect the relative actual fault rates on frame and service levels of each product. This approach is consistent with the usage factors used for the repair of E-Side and D-Side copper cables. Dropwire repair Dropwire repair relates to the repair of any faults occurring in the copper cable that connects from the Distribution Point (pole/main cable) to the Network Terminating Equipment (house/building). Cost causality. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Under the old methodology dropwire repair costs were allocated to services on a 1:1 basis. This assumed there is a uniform cost of maintaining dropwire lines for WLR premium, WLR basic and MPF. Changes in available evidence. Description of change The usage factors in the new methodology reflect the relative actual fault rates on copper cables and service levels of each product. This approach is consistent with the usage factors used for the repair of E-Side and D-Side copper cables. A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology SFIs/Broadband Boost SFIs are a chargeable investigation product that attempts to identify and resolve problems affecting Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL). SLGs The old methodology attributed SLG payments to products on the basis of service centre assurance attributions. However, SLG payments are based on the price of the service to which they relate and the incidence of SLG payments by product. Under the old methodology, these costs were allocated using Class of Work (CoW) bookings. Under the new methodology, these costs are allocated using Openreach Kilo-Man Hours (KMH) data as this provides more accurate information on engineering time by the type of activity. The new methodology separates out the internal and external SLG costs and allocates them to the respective internal and external service based on price, volume and fault rate. This better reflects the driver of the SLG (fault rate) and the size of the SLG payment (based upon price). The same change in allocation methodology has been applied to Broadband Boost which is a chargeable investigation product that attempts to identify and resolve problems affecting Broadband speed and reliability. TRCs Frame Repair TRCs refer to the provision of additional services where the work is not covered within BT service level agreements. Frame Repair relates to the repairs carried out on copper main distribution frames (MDF). Copper frame repair costs are attributed to services that use MDF based on usage factors. Under the old methodology, TRC costs were allocated using CoW bookings. Following a review of the 2012/13 costs, it was found that these bookings did not fully capture costs for “fault not found” activities or for volume deals. The new methodology allocates a share of Openreach provisioning Under the old methodology, the usage factors represented the number of Page 24 Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes and general repair costs to TRCs to ensure TRCs are allocated an appropriate amount of costs for “Fault Not Found” and volume deals. Effect of the change seasonal fluctuations and thus provides more robust information. The new methodology is consistent with Ofcom’s charge control modelling for the current WLR/LLU charge control – for example, see Figure A4.33 in Ofcom’s “Charge control review for LLU and WLR services Annexes” published 7 March 2012. A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes SLGs The markets most impacted by the changes are Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services, Wholesale Local Access and TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s). The main services affected are PPC services, MPF Rentals, Wholesale basic and premium analogue service rentals, MPF new provides and Residual services. Support for the change New plant groups and components enable the internal and external SLG costs to be ring-fenced and attributed to the corresponding internal and external services on the basis of product price, volume and fault rate. This better reflects the cost causality of SLGs being fault rate and the size of SLGs being based upon price. A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change TRCs Under the previous methodology, some costs relating to TRCs (specifically, “Fault Not Found” and “Volume Deals”) were not being correctly allocated to TRCs. The new methodology improves the accuracy of the cost allocation for these activities. SFIs/Broadband Boost KMH data analysis provides more accurate information on engineering time by activity type, allowing for a more precise and cost causal allocation of repair costs. KMH data has been used by Ofcom as part of their modelling for the current and previous WLR/LLU charge control. Key changes in accounting documents Dropwire Repair/Frame Repair A detailed analysis was performed of care level differentials that calculated a cost difference between care levels. Actual fault rate data (captured on a weekly basis) was analysed over a twelve month period to eliminate Page 25 Set out key changes to accounting documents The base methodologies for PDTORSFI, PDTURSFI, PDTUDL, PDTUEL, PDTSBSBB and DTNPSAA in the DAM have been updated to reflect the new methodologies. Usage factors are not disclosed in the accounting documents so no changes have been made for updates to usage factors. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.6 – Openreach computing and development costs extension services rentals. Reference number (Section 4.1) 6 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) These depreciation costs are caused by investments in various computing and development projects undertaken within Openreach, which have yet to be fully depreciated. Cost causality. Other – improvement identified by BT. Current year depreciation charges reflect both the current and historic investments causing these costs, whereas current year capital expenditure only takes account of the investments made in a given year. The new methodology takes into account all development projects on the fixed asset register rather than only current year additions so depreciation is attributed in a more cost causal manner. A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology The new methodology is also less open to distortion where significant capital expenditure is incurred in any given year. Trigger for change Description of change Support for the change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Previously computing and development depreciation costs within Openreach were allocated using an analysis of current year capital expenditure. Key changes in accounting documents To better reflect that depreciation costs relate to current and prior year development projects the methodology has been changed so computing and development costs within Openreach are allocated based on the current year depreciation charge in the fixed asset register. Effect of the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The markets most impacted by the change are Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services, Wholesale Local Access and AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s). The main services impacted by the change are Wholesale premium and basic analogue service transfers, MPF rentals, Main link rental charges, Ethernet Access Direct rentals and Wholesale Page 26 A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change Set out key changes to accounting documents Updated DAM description for Plant Group 772A. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.7 – Allocation of specialised accommodation space Reference number (Section 4.1) 7 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) Support for the change The planning rules regarding ventilation space contain a secondary condition requiring that such space should be allocated on the higher of the equipment dimensions x 3.85 or 500 watts per square metre. This secondary condition is stipulated by the power planning team in BT TSO to take into consideration the specific requirement of any high power consumption equipment which generates a very high heat footprint. 1 The planning rule is already reflected in the LLU price list, footnote 7 , that states: Cost causality. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other “The billable area is calculated by whichever is the greater of the physical footprint of the Product ordered multiplied by 3.85 or the heat dissipation requirement of the Product ordered. (Heat dissipation requirement is calculated as follows: the maximum permissible AC power capacity of the product per sq m is 500w. E.g. A product with a maximum permissible AC power capacity of 8800w @ 500w per sq m = 8800/500 = 17.6 sq m billable area. The billable area is indicated in the offer document.” Changes in available evidence. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology Specialised accommodation is the space allocated to equipment in the telephone exchange. The space required for each piece of equipment is based on: (i) the dimension of the equipment; (ii) walk around space; and (iii) additional space required by planning rules to enable sufficient ventilation for equipment based on its power consumption. The updated methodology reflects this rule and aligns the cost allocation with the way in which CPs are already charged for accommodation costs. Under the old methodology, the cost of the space required for ventilation was prorated on the space required for the equipment dimensions plus additional walk around space. Key changes in accounting documents However, the old methodology did not take into account an additional consideration for ventilation planning relating to equipment power consumption. Under the new methodology this is now taken into account. Communication Providers (CPs) are charged for this space. Effect of the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change Set out key changes to accounting documents The cost allocation is explained in Activity Group 106 in the DAM. A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The market most impacted by the change is WBA Market 1. The main services affected are IPstream services and Wholesale call termination local exchange segment. 1 http://www.openreach.co.uk/orpg/home/products/pricing/loadProductPriceDetails.do?dat a=BXz41J6zPqN4Eur3If4yDkmrHjN3v60VLJJlTHqZbd8lMnGHsqdC0vzO163bJmh34D91D7 M0q8u%2F%0AIlSgtIFAKw%3D%3D Page 27 Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.8 – Allocation of specific group provision Reference number (Section 4.1) 8 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) the change The hearing conditions experienced by engineers have arisen as a consequence of the copper line testing equipment used. As these costs were caused by the use of equipment specific to the provision of copperbased services, objectively these costs should not be borne by the noncopper services such as Ethernet and it is more cost causal to allocate these costs to copper services. Cost causality. Trigger for change Key changes in accounting documents Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Other – improvement identified by BT. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology BT is subject to health related claims for deafness amongst current and former employees arising from the use of copper line testing equipment (tone generator/oscillator) previously used by engineers. The claims are self-insured by BT and a specific provision is held by BT Group to cover the cost of these claims. The old methodology allocated the costs of this specific group provision to all Openreach services using Openreach pay. The new methodology allocates these costs to copper services only to reflect the fact that the equipment was only used to test copper lines. Effect of the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The markets most impacted by the change are Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services and AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s). The main services affected are MPF Rentals and Wholesale premium and basic analogue service rentals. Support for to support the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account Page 28 Set out key changes to accounting documents DAM description has been updated to reflect this provision being allocated to the line testing equipment Plant Group 240A. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.9 – Allocation of Career Transition Centre (CTC) costs Reference number (Section 4.1) 10 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) premium and basic analogue service rentals and MPF rentals. Support for the change CTC employees are effectively a BT-wide resource as they have the appropriate skills and experience to be utilised in business units across BT, not just the business unit employing them immediately prior to their entry into the CTC. Employees are redeployed to business units other than those employing them before entering the CTC. This indicates that, like other corporate overheads, they are a resource that can be and are in practice utilised across BT. Cost causality. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Therefore, the new methodology results in a more cost causal allocation of these costs than the old methodology. It is also an improvement in terms of the distribution of benefits as the previous approach could result in a disproportionate share of costs being applied to a subset of the businesses which are undertaking programmes to reduce the number of employees. Other – improvement identified by BT. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology The CTC is a unit within BT group where employees, who are deemed surplus to requirements in their current Line of Business (LoB), are pooled whilst they await redeployment to another part of BT. This methodology change only relates to the period of time which an employee spends in the CTC – the allocation methodology associated with subsequent redeployment (or redundancy) remains unchanged. Key changes in accounting documents Under the old methodology the employment costs of employees in the CTC were allocated back to the LoB where the employee worked before entering the CTC. The new methodology recognises that employees in the CTC are a resource that can be utilised by any LoB across BT so should be allocated in the same way as other corporate overheads – on a pay and return on assets basis. Effect of the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The market most impacted by the change is Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services. The main services impacted by the change are Wholesale Page 29 Set out key changes to accounting documents Appendix F of the DAM has been updated to reflect the new methodology of using Activity Group 112 (corporate costs) to allocate CTC costs. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.10 – Allocation of vacant space in exchanges Reference number (Section 4.1) 12 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) termination local exchange segment. Support for the change There is significant management concern that over time there will be less and less occupancy of operational buildings for network use and the situation will arise where many buildings will have little use other than as a termination point for the access network. Accordingly, various business initiatives are being developed to attempt to rationalise the use of space in these buildings. For example, where possible vacant exchange space is sub-let as e.g. office space. Cost causality. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other For the first stage of allocation, the level of forecast demand for LLU space is based on forecasts received from other Communication Providers (CPs) for new Points of Presence (POP) at exchanges. We are required to reserve space in our exchanges for CPs so it is more cost causal that this space is allocated to Openreach LLU assets. Other – improvement identified by BT. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology Under the old methodology, vacant space in exchanges was allocated to ‘occupied space’ on a pro-rata basis. For the second stage of allocation, business cases for moving from existing exchanges to smaller and more economical exchanges were reviewed. These showed that the cost was higher than the savings made from moving to smaller exchanges. This is because the act of moving copper lines from one exchange to another is labour intensive, time consuming and likely to result in unacceptable levels of service disruption to customers. Therefore, it is cost causal that MDF and cable chambers are allocated the cost of vacant space as they are preventing a reduction of the size of the operational building portfolio. Under the new methodology, a two stage approach has been adopted: first, a share of vacant space is allocated directly to Openreach LLU assets according to forecast future occupancy; second, the remaining vacant space is allocated to Main Distribution Frames (MDF) and Cable chambers. The new approach first recognises the need to provide space for LLU operators and second the prohibitive costs and disruption to services of rehousing MDF and cable chambers in order to reduce the size of the operational building portfolio. Effect of the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change Key changes in accounting documents A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The markets most impacted by the change are Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services and Wholesale Local Access. The main services impacted by the change are Wholesale premium and basic analogue service rentals, MPF rentals, co-mingling rentals, Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (inc Operator Assistance) and Wholesale call Page 30 Set out key changes to accounting documents Activity Group 106 in the DAM has been updated to reflect the new methodology. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.11 – Allocation of Openreach overheads Reference number (Section 4.1) 13 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) Support for the change The Openreach general management overheads are now allocated on the basis of pay and a return on assets in order to reflect the fact that they are not only influenced by the number of employees within Openreach, but also by a wider set of activities associated with managing the assets of the business. This includes ensuring the assets, as well as employees, are acquired and operated effectively and efficiently. The pay element of the allocation reflects the people management aspect of the overhead costs and the return on assets element represents the asset management aspect. Cost causality and consistency. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other The new methodology follows from a detailed analysis of the activities contributing to the Openreach overheads. It is more cost causal because it reflects the nature of these activities more accurately, recognising that some overheads are not only influenced by the number of employees but also the activities of running the business. Other – improvement identified by BT. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology Openreach overheads are the expenses of operating Openreach, associated with the continued functioning of the business. These expenses cannot be directly associated with the products or services being offered. The methodology is also consistent with the treatment of corporate overheads. Under the old methodology, all Openreach overheads were allocated based on Openreach pay. Key changes in accounting documents Following a detailed review of Openreach overheads, it has been possible to distinguish between service/activity related overheads and general management related overheads (e.g. leadership team, finance, legal). Under the new methodology, these latter general management overheads are allocated on the basis of pay and a return on assets. This is consistent with how BT allocates corporate overheads. Effect of the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The market most impacted by the change is Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services. The main services impacted by the change are Wholesale premium and basic analogue service rentals and MPF rentals. Page 31 Set out key changes to accounting documents DAM descriptions for the COMCOS_PCT and COMCOS bases have been updated to reflect the new methodology. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.12 – Merger of BT Innovate & Design (BTID) and BT Operate (BTO) to create BT Technology, Service & Operations (BT TSO) base (pay and return on assets) that is consistent with the approach used for Openreach and corporate overheads. Reference number (Section 4.1) 14,15,16 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) BT TSO computing assets These assets were previously owned by BTO. The depreciation of these assets was allocated using the previously allocated pay of the BTO Service Infrastructure business unit. Cost causality, consistency. Trigger for change Description of change BT TSO costs that are corporate in nature are allocated using the corporate overheads base as the costs benefit the whole of BT. Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other This business unit has been split up and no longer exists in the new BT TSO organisation. Other – creation of BT TSO and better alignment between regulatory and management accounts. We have reviewed the nature of these assets in the course of the creation of BT TSO and we now consider these assets to be for the benefit of the whole of BT and so we have allocated them using the corporate overhead base. A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology BT TSO capitalised development assets BT TSO operating costs These assets were previously owned by BTO and relate to system development work carried out by BTID. The depreciation of these assets was allocated to plant groups in proportion to the allocation of BTO pay. Prior to the merger of BTO and BTID, BT took account of their various activities separately by using numerous different cost drivers, but there was a large amount of these costs that remained general and unspecified. These “fixed costs” were allocated pro-rata to costs with known drivers. BTO has now been split up and does not exist as a separate entity in the new BT TSO organisation. Following the merger of BTID and BTO into BT TSO, effective 1 January 2013, a review was performed to provide clarity over the drivers of BT TSO costs. BT TSO has now established direct trades wherever a specific activity for a business unit within BT is identified and the treatment of these trades is either unchanged from the previous BTID/BTO treatment or updated to reflect better information. These systems are used to support the BT TSO operational units so we have chosen to allocate the costs in the same way as we allocate the fixed costs in those units: the BT TSO managed assets base. Effect of the change When no specific activity is directly attributable to a business unit, fixed trades have been established to formally allocate these costs: BT TSO operational units are functions that are primarily focused on supporting and maintaining BT TSO managed assets so a BT TSO managed assets base is used to allocate these costs. The activities of these units relate to managing the BT TSO network. BT TSO overhead units are allocated using a BT TSO overheads A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The markets most impacted by the changes are Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services, Wholesale Local Access and WBA Market 1. The main services impacted by the change are Wholesale premium and basic analogue service rentals, MPF rentals, Co-mingling new provides, Comingling rentals, and Residual services. Page 32 Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Support for the change are therefore corporate in nature. A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change BT TSO capitalised development assets BT TSO operating costs The BTO business unit no longer exists within the new BT TSO organisation so it is no longer practical to allocate the costs in proportion to BTO activities. BTO used to support all of BT in a variety of different ways. For example, it was responsible for operating BT’s non-Openreach networks and platforms, it provided power and ventilation to BT’s operational buildings and it managed BT’s computing operations and security functions. Previously BT took account of these various activities by using numerous different cost drivers, but there was a large amount of these costs that remained general and unspecified. These “fixed costs” were allocated prorata to costs with known drivers. These assets are used to support the BT TSO operations so our approach is consistent with the allocation of other BT TSO fixed costs. Key changes in accounting documents Following the creation of BT TSO it became impracticable to allocate fixed costs in proportion to BTO and BTID business units since these units no longer exist. For example, the BTO Service Infrastructure unit costs were previously allocated prorata with the known and specific activities. However, the creation of BT TSO meant the Service Infrastructure unit was re-organised into several different units and merged with BTID units meaning the previous allocation method could no longer be used. Each trade in the new BT TSO organisation was reviewed and how the costs should be allocated was considered. For direct trades, i.e. a specific activity for a business unit within BT, the costs are allocated in the same way as the prior year or updated to reflect more detailed information available. The review of trades also ensured there was better alignment between the regulatory and management accounts to ensure the most robust and transparent information is used within BT. General costs, which are ‘common’ or ‘shared’ in nature, consist mainly of BT TSO central functions (such as HR, the CEO office, Research and Innovation and Business and Operational Strategy), BT TSO Operational units (such as Fleet, Consultancy, Conferencing and the Energy & Carbon unit), BT TSO own use (such as security and IT) and the BT wide Oracle licence. Rather than continuing with the previous approach of allocating these costs in different ways a simpler and more transparent approach has been used by establishing fixed trades as described above. BT TSO computing assets These assets are comprised of personal laptops and main frame computers along with other associated capital expenditure, for example the creation of computer rooms to house the main frames. Both of these asset classes are available to the use of all people in BT and Page 33 Set out key changes to accounting documents Activity Group 102 and 103 descriptions have been included in the DAM and BT TSO base references have been updated to reflect the new methodologies. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.13 – Current Cost Accounting (CCA) valuation of Dropwire Reference number (Section 4.1) 17 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) been changed to an indexed RPI basis. Key changes in accounting documents Consistency. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Other – improvement identified by BT. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology Under the old methodology the CCA valuation of dropwire was based on the historic cost of the asset indexed using an internally generated index. Under the new methodology the historic cost of the dropwire asset is indexed using the RPI index. The new methodology is consistent with the CCA valuation of duct and copper assets. Effect of the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The markets most impacted by the change are Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services and Wholesale Local Access. The main services impacted by the change are Wholesale premium and basic analogue service rentals and MPF rentals. Support for the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account to support the change The CCA valuation of duct and copper assets was changed in 2012/13 from an absolute basis to an indexed RPI basis. To be consistent with the valuation of other network assets the CCA valuation of dropwire has also Page 34 Set out key changes to accounting documents The Detailed Valuation Methodology 2013 section 2.3 has been updated for the change in the CCA valuation of dropwire assets. Section 5 – Explanation of reported methodology changes Section 5.14 – CCA valuation of exchange power equipment and specialised accommodation plant Reference number (Section 4.1) 18 Key driver for change State key driver based on Regulatory Accounting Principles (Select from: 1) cost causality; 2) objectivity; 3) consistency; 4) UK GAAP; 5) Transparency; or 6) Sampling) the change The HCA value of the exchange power equipment and specialised accommodation plant assets in 2012/13 was diverging from the CCA value of the assets. The new methodology provides a more cost causal valuation for the assets and is based on independent indices from the ONS. Key changes in accounting documents Cost causality. Trigger for change Select from 1)BT judgement 2) Regulatory decision 3) changes in available evidence 4) other Other – improvement identified by BT. Description of change A short explanation of the new methodology and how it differs from the old methodology Exchange power equipment and specialised accommodation plant were previously valued on a Historic Cost Accounting (HCA) basis. The value of these assets on a HCA basis and a CCA basis had diverged. In order to provide a more cost causal valuation of the assets they are now valued on an indexed historic basis. Indices from the Office of National Statistics (ONS) have been used to value the different types of assets. Effect of the change A description of the impact of the change in terms of the components most affected and the general impact of the change and the markets and services that are most affected by the changes The markets most impacted by the change are Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services, TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s), Wholesale Local Access and WBA Market 1. The main services impacted by the change are Wholesale basic analogue service rentals, co-mingling new provides, co-mingling rentals, IPStream services, Wholesale call termination local exchange segment and Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (incl Operator Assistance). Support for to support the change A detailed justification for the change and the evidence taken into account Page 35 Set out key changes to accounting documents The Detailed Valuation Methodology 2013 sections 2.12 and 2.13 have been updated for the change in the CCA valuation of exchange power equipment and specialised accommodation plant. Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6 Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Page 36 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service Wholesale basic analogue internal service rentals Wholesale basic analogue external service rentals 102.30 102.30 100.00 100.00 2.30 2.30 2.3% 2.3% Wholesale premium analogue internal service rentals Wholesale premium analogue external service rentals 105.05 105.05 101.84 101.84 3.21 3.21 3.2% 3.2% Wholesale basic analogue internal service connections 45.46 38.64 6.82 17.7% Wholesale premium analogue internal service connections Wholesale premium and basic analogue external service connections 45.46 45.46 38.64 38.64 6.82 6.82 17.7% 17.7% Page 37 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.1.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors Wholesale Access specific £/trans Routeing & records £/line 4.50 MDF Hardware jumpering £/line 17.13 E side copper capital £/line 9.36 9.32 E side copper current £/line 1.82 1.82 2.19 D side copper capital £/line 51.38 51.21 51.23 D side copper current £/line 7.01 7.02 8.42 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.80 1.81 1.81 Local exchanges general frames current £/line 0.86 0.86 1.04 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.20 0.20 0.20 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line 15.10 15.10 15.11 Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line 3.66 3.67 4.40 PSTN line cards £/line 7.31 7.31 7.32 Broadband line testing systems £/line 2.50 0.69 0.69 Combi Card voice £/line 0.24 0.24 0.24 Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £29m 0.82 0.82 Sales product management (q) % £17m 0.17 0.19 Service Centres - Provision (q) % £112m Directories (q) % £37m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 12.37 Wholesale premium and basic analogue connections £ Unit (d) Wholesale premium analogue internal service connections £ Components Wholesale basic analogue internal service connections As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Wholesale premium analogue rentals Average cost per unit Wholesale basic analogue rentals Wholesale analogue exchange line services £ £ £ 12.40 12.40 12.40 4.50 4.50 4.50 17.17 17.17 17.17 9.33 0.09 0.09 0.09 11.30 11.30 11.30 2.06 2.06 102.30 105.05 45.46 45.46 45.46 Page 38 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.1.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Wholesale premium analogue internal service connections Wholesale premium and basic analogue connections £ £ 2.88 2.91 2.91 2.91 5.08 5.08 5.08 5.08 Average cost per unit Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies £ Wholesale premium analogue rentals £ Wholesale basic analogue rentals Wholesale basic analogue internal service connections Wholesale analogue exchange line services £ Components Unit (d) Wholesale Access specific £/trans Routeing & records £/line MDF Hardware jumpering £/line 18.41 E side copper capital £/line 8.83 8.83 E side copper current £/line 2.02 2.02 2.42 D side copper capital £/line 46.86 46.86 46.88 D side copper current £/line 6.83 6.83 8.21 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.08 1.08 1.08 Local exchanges general frames current £/line 1.00 1.00 1.00 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.18 0.18 0.18 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line 16.77 16.77 16.78 Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line 4.52 4.52 4.52 PSTN line cards £/line 7.99 7.98 7.99 Broadband line testing systems £/line 2.24 0.59 0.59 Combi Card voice £/line 0.24 0.24 0.24 Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £37m 0.87 0.87 Sales product management (q) % £18m 0.18 0.20 Service Centres - Provision (q) % £118m Directories (q) % £37m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 18.46 18.46 18.46 8.83 0.09 0.09 0.09 12.10 12.10 12.10 2.05 2.05 100.00 101.84 38.64 38.64 38.64 Page 39 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.1.1 - Illustrative for Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Wholesale Access specific £/trans Routeing & records £/line (0.58) MDF Hardware jumpering £/line (1.28) E side copper capital £/line 0.53 0.49 0.50 E side copper current £/line (0.20) (0.20) (0.23) D side copper capital £/line 4.52 4.35 4.35 D side copper current £/line 0.18 0.19 0.21 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 0.72 0.73 0.73 Local exchanges general frames current £/line (0.14) (0.14) 0.04 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.02 0.02 0.02 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line (1.67) (1.67) (1.67) Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line (0.86) (0.85) (0.12) PSTN line cards £/line (0.68) (0.67) (0.67) Broadband line testing systems £/line 0.26 0.10 0.10 Combi Card voice £/line - - Service Centres - Assurance (q) % (£8m) (0.05) (0.05) Sales product management (q) % (£1m) (0.01) (0.01) Service Centres - Provision (q) % (£6m) Directories (q) % £0m 0.01 0.01 2.30 3.21 Fully Allocated Costs (£) 9.49 Wholesale premium and basic analogue connections £ Unit (d) Wholesale premium analogue internal service connections £ Components Wholesale basic analogue internal service connections Effect of changes on results Wholesale premium analogue rentals Average cost per unit Wholesale basic analogue rentals Wholesale analogue exchange line services £ £ £ 9.49 9.49 9.49 (0.58) (0.58) (0.58) (1.29) (1.29) (1.29) - (0.80) (0.80) (0.80) 6.82 Page 40 6.82 6.82 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.1.1 - Illustrative for Wholesale Analogue Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Wholesale premium and basic analogue connections % Wholesale premium analogue internal service connections % Wholesale basic analogue internal service connections Effect of changes on results as a percentage Wholesale premium analogue rentals Average cost per unit Wholesale basic analogue rentals Wholesale analogue exchange line services % % % Components Unit (d) Wholesale Access specific £/trans 330% 326% 326% 326% Routeing & records £/line -11% -11% -11% -11% MDF Hardware jumpering £/line -7% -7% -7% -7% E side copper capital £/line 6% 6% 6% E side copper current £/line -10% -10% -10% D side copper capital £/line 10% 9% 9% D side copper current £/line 3% 3% 3% Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 67% 68% 68% Local exchanges general frames current £/line -14% -14% 4% PSTN line test equipment £/line 11% 11% 11% Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line -10% -10% -10% Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line -19% -19% -3% PSTN line cards £/line -9% -8% -8% Broadband line testing systems £/line 12% 17% 17% Combi Card voice £/line 0% 0% 0% Service Centres - Assurance (q) % -22% -6% -6% Sales product management (q) % -6% -6% -5% Service Centres - Provision (q) % -5% Directories (q) % 0% Fully Allocated Costs % 0% 0% 2% 3% 0% 0% 0% -7% -7% -7% 18% 18% 18% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 41 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.2 – Illustrative for Wholesale ISDN2 Exchange Line Services 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service Wholesale ISDN2 internal service rentals Wholesale ISDN2 external service rentals 71.77 71.70 72.12 72.05 (0.35) (0.35) -0.5% -0.5% Wholesale ISDN2 internal service connections Wholesale ISDN2 external service connections 28.31 28.18 25.23 25.10 3.08 3.08 12.2% 12.3% Wholesale ISDN2 internal service transfers Wholesale ISDN2 external service transfers 17.65 17.62 13.72 13.68 3.93 3.94 28.6% 28.8% Page 42 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.2.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale ISDN2 Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors £ £ Unit (d) Wholesale Access specific £/trans 12.37 6.26 6.25 Routeing & records £/line 4.50 1.52 1.52 MDF Hardware jumpering £/line 17.13 8.70 8.67 E side copper capital £/line 9.36 E side copper current £/line 1.82 1.56 1.56 D side copper capital £/line 51.38 25.75 25.75 D side copper current £/line 7.01 6.01 6.01 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.80 0.90 0.90 Local exchanges general frames current £/line 0.86 0.52 0.52 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.20 0.16 0.16 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line 15.10 7.57 7.57 ISDN2 drop maintenance £/channel 2.01 2.01 2.01 ISDN2 line cards £/channel 17.46 17.46 17.46 ISDN2 NTE £/channel 3.77 3.77 3.77 Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £29m 0.82 0.82 Sales product management (q) % £17m 0.55 0.48 Service Centres - Provision (q) % £112m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 4.69 71.77 £ 6.22 Wholesale ISDN2 external service transfers £ Components Wholesale ISDN2 internal service transfers Wholesale ISDN2 internal service connections £ Wholesale ISDN2 external service connections Wholesale ISDN2 external service rentals As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Wholesale ISDN2 internal service rentals Average cost per unit Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services £ 6.21 4.69 71.70 0.42 0.36 0.11 0.10 11.41 11.38 11.32 11.31 28.31 28.18 17.65 17.62 Page 43 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.2.1 - Illustrative for Wholesale ISDN2 Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ Unit (d) Wholesale Access specific £/trans 2.88 1.52 1.50 Routeing & records £/line 5.08 1.71 1.71 MDF Hardware jumpering £/line 18.41 9.34 9.32 E side copper capital £/line 8.83 E side copper current £/line 2.02 1.73 1.73 D side copper capital £/line 46.86 23.48 23.48 D side copper current £/line 6.83 5.85 5.85 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.08 0.54 0.54 Local exchanges general frames current £/line 1.00 0.50 0.50 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.18 0.14 0.14 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line 16.77 8.41 8.41 ISDN2 drop maintenance £/channel 2.25 2.25 2.25 ISDN2 line cards £/channel 19.04 19.04 19.04 ISDN2 NTE £/channel 4.31 4.31 4.31 Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £37m 0.87 0.87 Sales product management (q) % £18m 0.58 0.51 Service Centres - Provision (q) % £118m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 4.42 72.12 £ 1.47 Wholesale ISDN2 external service transfers £ Components Wholesale ISDN2 internal service transfers Wholesale ISDN2 internal service connections £ Wholesale ISDN2 external service connections Wholesale ISDN2 external service rentals Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Wholesale ISDN2 internal service rentals Average cost per unit Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services £ 1.46 4.42 72.05 0.45 0.38 0.12 0.10 12.21 12.19 12.13 12.12 25.23 25.10 13.72 13.68 Page 44 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.2.1 - Illustrative for Wholesale ISDN2 Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ £ Components Unit (d) Wholesale Access specific £/trans 9.49 4.74 4.75 Routeing & records £/line (0.58) (0.19) (0.19) MDF Hardware jumpering £/line (1.28) (0.64) (0.65) E side copper capital £/line 0.53 E side copper current £/line D side copper capital £/line 4.52 2.27 2.27 D side copper current £/line 0.18 0.16 0.16 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 0.72 0.36 0.36 Local exchanges general frames current £/line (0.14) 0.02 0.02 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.02 0.02 0.02 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line (1.67) (0.84) (0.84) ISDN2 drop maintenance £/channel (0.24) (0.24) (0.24) ISDN2 line cards £/channel (1.58) (1.58) (1.58) ISDN2 NTE £/channel (0.54) (0.54) (0.54) Service Centres - Assurance (q) % (£8m) (0.05) (0.05) Sales product management (q) % (£1m) (0.03) (0.03) (0.03) (0.02) (0.01) Service Centres - Provision (q) % (£6m) (0.81) (0.81) Fully Allocated Costs (£) 0.27 4.75 Wholesale ISDN2 external service transfers £ Wholesale ISDN2 internal service transfers Wholesale ISDN2 internal service connections £ Wholesale ISDN2 external service connections Wholesale ISDN2 external service rentals Effect of changes on results Wholesale ISDN2 internal service rentals Average cost per unit Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services £ 4.75 0.27 (0.20) (0.17) (0.17) (0.80) (0.35) (0.35) 3.08 Page 45 3.08 3.93 (0.81) 3.94 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.2.1 - Illustrative for Wholesale ISDN2 Exchange Line Services calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) % % % Wholesale ISDN2 external service transfers % Wholesale ISDN2 internal service transfers Wholesale ISDN2 internal service connections % Wholesale ISDN2 external service connections Wholesale ISDN2 external service rentals Effect of changes on results as a percentage Wholesale ISDN2 internal service rentals Average cost per unit Wholesale ISDN2 exchange line services % Components Unit (d) Wholesale Access specific £/trans 330% 312% 317% 323% Routeing & records £/line -11% -11% -11% MDF Hardware jumpering £/line -7% -7% -7% E side copper capital £/line 6% 6% 6% E side copper current £/line -10% -10% -10% D side copper capital £/line 10% 10% 10% D side copper current £/line 3% 3% 3% Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 67% 67% 67% Local exchanges general frames current £/line -14% 4% 4% PSTN line test equipment £/line 11% 14% 14% Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line -10% -10% -10% ISDN2 drop maintenance £/channel -11% -11% -11% ISDN2 line cards £/channel -8% -8% -8% ISDN2 NTE £/channel -13% -13% -13% Service Centres - Assurance (q) % -22% -6% -6% Sales product management (q) % -6% -5% -6% -7% -5% -8% 0% Service Centres - Provision (q) % -5% -7% -7% -7% -7% 12% 12% 29% 29% Fully Allocated Costs % 0% 0% 325% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 46 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.3 – Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % 1,960.96 1,960.96 2,350.69 2,350.69 (389.73) (389.73) -16.6% -16.6% Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - link Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year (ao) Total Internal 176.18 193.72 (17.54) -9.1% Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year (ao) Total External 176.18 193.72 (17.54) -9.1% Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - distribution Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total Internal 4.12 4.00 0.12 3.0% Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total External 4.12 4.00 0.12 3.0% Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - trunk Trunk segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total Internal 4.29 4.18 0.11 2.6% Trunk segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total External 4.29 4.18 0.11 2.6% Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - local end Local end fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year (ao) Total Internal 494.23 504.07 (9.84) -2.0% Local end fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year (ao) Total External 494.23 504.07 (9.84) -2.0% Service Internal Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - connections External Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - connections Page 47 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.3 – Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) continued 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % 5,510.81 5,510.81 6,916.41 6,916.41 (1,405.60) (1,405.60) -20.3% -20.3% Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - link Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total internal 195.71 286.20 (90.49) -31.6% Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total External 195.71 286.20 (90.49) -31.6% Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - distribution Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total Internal 36.09 36.41 (0.32) -0.9% Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total External 36.09 36.41 (0.32) -0.9% 551.31 567.74 (16.43) -2.9% External Radio Backhaul Service - sub 2Mbit/s connections 2,714.40 3,256.30 (541.90) -16.6% Internal Radio Backhaul Service - 2Mbit/s connections External Radio Backhaul Service - 2Mbit/s connections 5,494.82 5,494.82 6,899.91 6,899.91 (1,405.09) (1,405.09) -20.4% -20.4% External Netstream 16 LL 2Mbit/s connections 5,437.00 6,841.00 (1,404.00) -20.5% Service Internal Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - connections External Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - connections Weighted average local end price for CLZ/non CLZ // Nationally averaged cost Page 48 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.3.1 – Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors £ £ £ £ £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 33.06 PC rental 64kbit/s link £/link 168.09 PC rental 2Mbit/s link £/link 174.32 PC rental 64kbit/s link per km transmission £/km 4.02 64kbit/s PC link connection cct provision (y) £/circuit 1,999.40 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit 5,409.66 PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le 392.94 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le 263.18 24.52 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le 650.76 464.90 E side copper capital £/line 9.36 9.36 E side copper current £/line 1.82 1.82 0.16 D side copper capital £/line 51.38 51.40 12.36 D side copper current £/line 7.01 7.02 0.62 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.80 1.81 0.43 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % Core/Metro connectivity (q) % - MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % £0m Access Cards (other services) (q) % £25m SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £31m Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ External Netstream 16 LL 2Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - 2 Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - sub 2 Mbit/s connections Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - link £ Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - connections £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - trunk £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - distribution £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - link As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 8Mbit/s) £ 33.19 168.35 175.18 4.02 4.03 1,931.28 2,684.72 5,410.17 5,408.61 5,403.00 29.68 86.21 34.00 5,510.81 195.71 36.09 551.31 2,714.40 5,494.82 5,437.00 392.08 2.25 0.01 6.16 29.68 7.83 0.10 0.26 30.74 1,960.96 176.18 4.12 4.29 494.23 100.64 Page 49 20.52 2.90 39.91 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.3.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ £ £ £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 33.27 PC rental 64kbit/s link £/link 185.35 PC rental 2Mbit/s link £/link 190.25 PC rental 64kbit/s link per km transmission £/km 3.89 64kbit/s PC link connection cct provision (y) £/circuit 2,401.81 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit 6,811.63 PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le 407.43 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le 278.27 26.71 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le 675.01 485.23 E side copper capital £/line 8.83 8.83 E side copper current £/line 2.02 2.02 0.18 D side copper capital £/line 46.86 46.88 11.28 D side copper current £/line 6.83 6.84 0.61 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.08 1.08 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £9m 3.85 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % £63m 43.08 MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % £7m 26.90 Access Cards (other services) (q) % £28m SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £32m Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ External Netstream 16 LL 2Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - 2 Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - sub 2 Mbit/s connections Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - link £ Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - connections £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - trunk £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - distribution £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - link Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 8Mbit/s) £ 33.40 185.61 191.11 3.89 3.91 2,319.93 3,225.54 6,812.13 6,810.58 6,805.00 30.76 89.33 36.00 6,916.41 286.20 36.41 567.74 3,256.30 6,899.91 6,841.00 406.57 30.76 8.11 0.11 0.27 31.85 2,350.69 193.72 4.00 4.18 504.07 2.12 0.26 104.28 Page 50 21.26 3.01 41.35 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.3.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ £ £ £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km (0.21) PC rental 64kbit/s link £/link (17.26) PC rental 2Mbit/s link £/link (15.93) PC rental 64kbit/s link per km transmission £/km 0.13 64kbit/s PC link connection cct provision (y) £/circuit (402.41) 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit (1,401.97) PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le (14.49) PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le (15.09) (2.19) PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le (24.25) (20.33) E side copper capital £/line 0.53 0.53 0.13 E side copper current £/line (0.20) (0.20) (0.02) D side copper capital £/line 4.52 4.52 1.08 D side copper current £/line 0.18 0.18 0.01 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 0.72 0.73 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % (£9m) (3.85) Core/Metro connectivity (q) % (£63m) (43.08) MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % (£7m) (26.89) Access Cards (other services) (q) % (£3m) SG & A partial private circuits (q) % (£1m) Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ External Netstream 16 LL 2Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - 2 Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - sub 2 Mbit/s connections Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - link £ Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - connections £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - trunk £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - distribution £ Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - link Effect of changes on results Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 8Mbit/s) £ (0.21) (17.26) (15.93) 0.13 0.12 (388.65) (540.82) (1,401.96) (1,401.97) (1,402.00) (14.49) 0.17 6.16 (1.08) (0.28) (0.01) (0.01) (389.73) (17.54) 0.12 0.11 (1.11) (3.64) (0.74) (0.11) (1.44) (9.84) (1,405.60) (90.49) (0.32) (16.43) Page 51 (1.08) (3.12) (2.00) (541.90) (1,405.09) (1,404.00) Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.3.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (up to and including 8Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) % % % % % Components Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km -1% PC rental 64kbit/s link £/link -9% PC rental 2Mbit/s link £/link -8% PC rental 64kbit/s link per km transmission £/km 3% 64kbit/s PC link connection cct provision (y) £/circuit -17% 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit -21% PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le -4% PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le -5% PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le -4% E side copper capital £/line 6% 6% 6% E side copper current £/line -10% -10% -11% D side copper capital £/line 10% 10% 10% D side copper current £/line 3% 3% 2% Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 67% 68% 65% Edge Ethernet ports (q) % -100% -100% Core/Metro connectivity (q) % -100% -100% MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % -100% -100% Access Cards (other services) (q) % -11% SG & A partial private circuits (q) % -3% Fully Allocated Costs % % % External Netstream 16 LL 2Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - 2 Mbit/s connections Radio Backhaul Service - sub 2 Mbit/s connections Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - link % Partial and Private Circuits 2Mbit/s - connections % Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - local end % Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - trunk % Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - link Effect of changes on results as a percentage Partial and Private Circuits 64kbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 8Mbit/s) % -1% -9% -8% 3% 3% -17% -17% -21% -21% -21% -4% -8% -4% 100% -4% -3% -9% -4% -3% -3% -3% -4% -3% -4% -3% -6% -17% -9% 3% 3% -2% -20% -32% -1% -3% -17% -20% -21% (ao) The price for 64kbit/s enhanced maintenance is weighted to include different 64kbit/s equivalent services. (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (y) Unit costs calculated as a weighted average of the 64kbit PC link connection cct provision & 64kbit PC link connection cct rearrangements. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 52 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.4 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service Internal Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - connections External Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - connections 5,504.12 5,504.12 6,909.50 6,909.50 (1,405.38) (1,405.38) -20.3% -20.3% Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - link Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total Internal 1,403.83 2,732.96 (1,329.13) -48.6% Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total External 1,403.83 2,732.96 (1,329.13) -48.6% Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - distribution Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total Internal 298.70 301.60 (2.90) -1.0% Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total External 298.70 301.60 (2.90) -1.0% Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - local end Local end fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total Internal 3,793.72 4,719.61 (925.89) -19.6% Local end fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total External 3,793.72 4,719.61 (925.89) -19.6% Page 53 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.4.1 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 273.05 PC rental 34Mbit/s link £/link 1,246.82 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit 5,409.66 PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le 3,553.49 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % Core/Metro connectivity (q) % - MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % £0m Access Cards (other services) (q) % £25m SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £31m Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - link As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) £ 273.04 1,246.81 5,409.52 3,508.60 £9m 0.01 0.26 131.54 94.60 5,504.12 156.75 25.66 153.58 1,403.83 298.70 3,793.72 Page 54 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.4.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 275.01 PC rental 34Mbit/s link £/link 1,315.53 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit 6,811.63 PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le 3,635.04 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £9m 65.40 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % £63m 732.38 MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % £7m 457.24 Access Cards (other services) (q) % £28m SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £32m Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - link Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) £ 275.01 1,315.52 6,811.48 3,590.16 970.32 98.02 6,909.50 162.42 26.59 159.13 2,732.96 301.60 4,719.61 Page 55 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.4.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km (1.96) PC rental 34Mbit/s link £/link (68.71) 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £0m (65.39) Core/Metro connectivity (q) % (£63m) (732.38) MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % (£7m) (456.98) Access Cards (other services) (q) % (£3m) SG & A partial private circuits (q) % (£1m) Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - link Effect of changes on results Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) £ (1.97) (68.71) (1,401.97) (1,401.96) (81.55) (81.56) (838.78) (3.42) (5.67) (1,405.38) (1,329.13) (0.93) (5.55) (2.90) (925.89) Page 56 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.4.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) % % % Components Unit (d) PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km -1% PC rental 34Mbit/s link £/link -5% 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le Edge Ethernet ports (q) % 0% -100% Core/Metro connectivity (q) % -100% -100% MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % -100% -100% Access Cards (other services) (q) % -11% SG & A partial private circuits (q) % -3% Fully Allocated Costs % -21% Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - link Effect of changes on results as a percentage Partial and Private Circuits 34/45Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 8Mbit/s up to and including 45Mbit/s) % -1% -5% -21% -2% -2% -86% -3% -3% -3% -3% -20% -49% -1% -20% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 57 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.5 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service Internal Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - connections External Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - connections 5,517.87 5,517.87 6,923.74 6,923.74 (1,405.87) (1,405.87) -20.3% -20.3% Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - link Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total Internal 6,290.61 11,839.33 (5,548.72) -46.9% Main link fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total External 6,290.61 11,839.33 (5,548.72) -46.9% Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - distribution Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total Internal 543.50 542.13 1.37 0.3% Terminating segment charge per year Enhanced maintenance per kilometre charge per year Total External 543.50 542.13 1.37 0.3% Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - local end Local end fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total Internal 6,538.84 6,625.40 (86.56) -1.3% Local end fixed charge per year Enhanced maintenance fixed charge per year Total External 6,538.84 6,625.40 (86.56) -1.3% Page 58 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.5.1 – Illustrative for TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 520.20 PC rental 140Mbit/s link £/link 5,803.25 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit 5,409.66 PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le 5,989.94 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % Core/Metro connectivity (q) % - MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % £0m Access Cards (other services) (q) % £25m SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £31m Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - link As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £ £ 520.70 5,816.00 5,410.87 5,861.94 £9m 0.04 1.05 131.54 107.00 5,517.87 473.52 22.80 545.36 6,290.61 543.50 6,538.84 Page 59 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.5.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 518.01 PC rental 140Mbit/s link £/link 6,168.16 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit 6,811.63 PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le 6,188.34 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £9m 269.30 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % £63m 3,015.67 MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % £7m 1,882.75 Access Cards (other services) (q) % £28m SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £32m Fully Allocated Costs (£) Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - link Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £ £ 518.51 6,180.98 6,812.87 6,060.33 110.87 490.63 23.62 565.07 6,923.74 11,839.33 542.13 6,625.40 Page 60 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.5.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ Components Unit (d) PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 2.19 PC rental 140Mbit/s link £/link (364.91) 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £0m (269.26) Core/Metro connectivity (q) % (£63m) (3,015.67) MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % (£7m) (1,881.70) Access Cards (other services) (q) % (£3m) SG & A partial private circuits (q) % (£1m) Fully Allocated Costs (£) Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - link Effect of changes on results Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) £ £ 2.19 (364.98) (1,401.97) (1,402.00) (198.40) (198.39) 131.54 (3.87) (17.11) (0.82) (19.71) (1,405.87) (5,548.72) 1.37 (86.56) Page 61 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.5.1 - Illustrative for TISBO (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) % % % Components Unit (d) PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km distribution £/km 0% PC rental 140Mbit/s link £/link -6% 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision £/circuit PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le Edge Ethernet ports (q) % 0% -100% Core/Metro connectivity (q) % -100% -100% MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link (q) % -100% -100% Access Cards (other services) (q) % -11% SG & A partial private circuits (q) % -3% Fully Allocated Costs % -21% Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - local end Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - distribution Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - link Effect of changes on results as a percentage Partial and Private Circuits 140/155Mbit/s - connections Average cost per unit Traditional interface symmetric broadband origination (above 45Mbit/s up to and including 155Mbit/s) % 0% -6% -21% -3% -3% 100% -3% -3% -3% -3% -20% -47% 0% -1% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 62 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.6 – Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service Wholesale extension services 10Mbit/s rentals - Internal Wholesale extension services 10Mbit/s rentals - External 1,623.34 1,623.34 1,767.69 1,767.69 (144.35) (144.35) -8.2% -8.2% Wholesale extension services 100Mbit/s rentals - Internal Wholesale extension services 100Mbit/s rentals - External 1,708.91 1,708.91 1,861.36 1,861.36 (152.45) (152.45) -8.2% -8.2% Wholesale extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals - Internal Wholesale extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals - External 3,017.69 3,017.69 3,258.06 3,258.06 (240.37) (240.37) -7.4% -7.4% Wholesale extension services other bandwidth rentals - Internal Wholesale extension services other bandwidth rentals - External 1,165.07 1,293.16 1,279.12 1,415.01 (114.05) (121.85) -8.9% -8.6% Backhaul extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals - External 2,923.44 3,159.50 (236.06) -7.5% Backhaul extension services other bandwidth rentals - External 1,904.99 2,070.50 (165.51) -8.0% EAD Local Access 10Mbit/s rentals - Internal EAD Local Access 10Mbit/s rentals - External 1,840.31 1,838.89 1,910.89 1,909.43 (70.58) (70.54) -3.7% -3.7% EAD Local Access 100Mbit/s rentals - Internal EAD Local Access 100Mbit/s rentals - External 1,893.20 1,892.48 1,968.16 1,967.42 (74.96) (74.94) -3.8% -3.8% EAD Local Access 1000Mbit/s rentals - Internal EAD Local Access 1000Mbit/s rentals - External 2,589.88 2,587.21 2,719.10 2,716.36 (129.22) (129.15) -4.8% -4.8% Page 63 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.6 – Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service EAD Other 10Mbit/s rentals - Internal EAD Other 10Mbit/s rentals - External 2,999.39 3,024.88 3,297.26 3,322.72 (297.87) (297.84) -9.0% -9.0% EAD Other 100Mbit/s rentals - Internal EAD Other 100Mbit/s rentals - External 3,123.86 3,166.26 3,427.05 3,469.40 (303.19) (303.14) -8.8% -8.7% EAD Other 1000Mbit/s rentals - Internal EAD Other 1000Mbit/s rentals - External 4,725.63 4,747.10 5,090.29 5,111.65 (364.66) (364.55) -7.2% -7.1% EAD Local Access 10Mbit/s connections - Internal EAD Local Access 10Mbit/s connections - External 948.42 947.73 1,265.19 1,264.47 (316.77) (316.74) -25.0% -25.0% EAD Local Access 100Mbit/s connections - Internal EAD Local Access 100Mbit/s connections - External 957.93 957.49 1,274.98 1,274.53 (317.05) (317.04) -24.9% -24.9% EAD Local Access 1000Mbit/s connections - Internal EAD Local Access 1000Mbit/s connections - External 955.66 963.52 1,272.64 1,280.74 (316.98) (317.22) -24.9% -24.8% EAD Other 10Mbit/s connections - Internal EAD Other 10Mbit/s connections - External 947.45 946.80 1,264.19 1,263.52 (316.74) (316.72) -25.1% -25.1% EAD Other 100Mbit/s connections - Internal EAD Other 100Mbit/s connections - External 957.36 957.33 1,274.40 1,274.36 (317.04) (317.03) -24.9% -24.9% EAD Other 1000Mbit/s connections - Internal EAD Other 1000Mbit/s connections - External 971.26 983.64 1,288.72 1,301.48 (317.46) (317.84) -24.6% -24.4% 5,006.67 962.76 5,121.27 1,279.53 (114.60) (316.77) -2.2% -24.8% 138.76 138.76 156.04 156.04 (17.28) (17.28) -11.1% -11.1% Ethernet Backhaul Direct rentals - External Ethernet Backhaul Direct connections - External Main link rental charges - Internal Main link rental charges - External Page 64 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.6.1 – Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors Wholesale & LAN extension services fibre etc £/le Wholesale & LAN extension services BNS £/circuit Backhaul extension services fibre etc £/le 1,094.43 Ethernet Electronics £/le 527.23 Ethernet main links £/le 113.98 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/le 7,423.01 Access Cards (other services) (q) % £25m 5.62 56.25 562.48 562.48 263.52 5.62 5.62 56.25 56.25 562.48 562.48 5.62 5.62 56.25 56.25 562.48 562.48 Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £29m 10.10 10.10 10.10 10.10 10.10 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 20.20 Sales product management (q) % £17m 14.01 18.54 44.63 7.60 3.30 12.80 12.06 13.98 13.60 31.22 29.83 20.12 19.65 24.01 23.27 56.85 54.95 Service Centres - Provision (q) £/le £112m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 2,564.33 1,124.82 1,100.47 1,201.02 986.89 986.21 987.97 987.63 1,003.85 1,002.57 2,138.65 2,164.61 2,208.60 2,251.74 3,113.97 3,137.34 814.80 814.80 814.80 814.80 £ £ £ £ £ £ £ 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 199.30 6.72 6.39 11.28 11.07 10.19 13.96 6.26 5.94 11.01 10.99 17.67 23.61 £ £ 97.34 Main link rental charges £ Ethernet Backhaul Direct connections - External £ Ethernet Backhaul Direct rentals - External £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections External £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections External £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections External £ Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections Internal £ EAD LA 1000 External Connections £ EAD LA 1000 Internal Connections £ EAD LA 100 External Connections £ EAD LA 100 Internal Connections £ Unit (d) EAD LA 10 External Connections £ Components EAD LA 10 Internal Connections Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals - Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals External Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - External £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals Internal Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals External EAD LA 1000 External Rentals 99.65 EAD LA 1000 Internal Rentals 99.65 EAD LA 100 External Rentals £ EAD LA 100 Internal Rentals £ EAD LA 10 External Rentals £ EAD LA 10 Internal Rentals Backhaul extension services other bandwidth rental - External £ Backhaul extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals - External £ Wholesale extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals Wholesale extension services 100Mbit/s rentals As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Wholesale extension services 10Mbit/s rentals Average cost per unit Alternative interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £ 199.30 24.06 1,078.60 1,062.56 468.79 523.55 1,199.46 1,165.01 465.86 972.13 972.13 814.80 814.80 814.80 814.80 972.13 972.13 113.97 4,872.62 1,623.34 1,708.91 3,017.69 2,923.44 1,904.99 1,840.31 1,838.89 1,893.20 1,892.48 2,589.88 2,587.21 2,999.39 3,024.88 3,123.86 3,166.26 4,725.63 4,747.10 Page 65 21.08 20.20 7.30 6.94 12.25 12.02 11.07 15.16 6.79 6.46 11.95 11.94 19.19 25.63 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 735.10 16.51 735.10 7.28 0.73 948.42 947.73 957.93 957.49 955.66 963.52 947.45 946.80 957.36 957.33 971.26 983.64 5,006.67 962.76 138.76 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.6.1 - Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Wholesale & LAN extension services fibre etc £/le 3,013.04 1,232.98 1,208.63 1,309.13 Wholesale & LAN extension services BNS £/circuit 1,025.54 Backhaul extension services fibre etc £/le 1,093.21 Ethernet Electronics £/le 559.55 Ethernet main links £/le 104.82 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/le 7,474.98 Access Cards (other services) (q) % £28m 6.10 61.04 610.45 Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £37m 14.98 14.98 Sales product management (q) % £18m 14.82 19.62 Service Centres - Provision (q) £/le £118m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 209.01 209.01 994.29 993.61 995.37 995.03 1,011.25 1,009.97 2,372.91 2,398.87 2,443.65 2,486.78 3,355.32 3,378.69 495.69 866.99 866.99 866.99 866.99 1,034.40 1,034.40 610.45 285.99 6.10 6.10 61.04 61.04 610.45 14.98 14.98 14.98 29.97 29.97 29.97 29.97 47.22 8.05 3.49 13.54 12.76 14.79 14.39 £ £ £ £ £ £ £ 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 418.01 6.72 6.39 11.28 11.07 10.19 13.96 6.26 5.94 11.01 10.99 17.67 23.61 £ £ 316.05 418.01 4,757.78 21.08 Main link rental charges £ Ethernet Backhaul Direct connections - External £ Ethernet Backhaul Direct rentals - External £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections External £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections External £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections External £ Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections Internal £ EAD LA 1000 External Connections £ EAD LA 1000 Internal Connections £ EAD LA 100 External Connections £ EAD LA 100 Internal Connections Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals - Internal £ EAD LA 10 External Connections Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - External £ EAD LA 10 Internal Connections Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals External EAD LA 1000 External Rentals £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals Internal EAD LA 1000 Internal Rentals £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals External EAD LA 100 External Rentals £ EAD LA 100 Internal Rentals £ Unit (d) EAD LA 10 External Rentals £ Components EAD LA 10 Internal Rentals Backhaul extension services other bandwidth rental - External £ Backhaul extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals - External £ Wholesale extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals Wholesale extension services 100Mbit/s rentals Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Wholesale extension services 10Mbit/s rentals Average cost per unit Alternative interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £ 50.47 1,077.38 1,061.34 498.81 557.09 1,276.28 1,239.63 866.99 866.99 866.99 866.99 1,034.40 1,034.40 610.45 6.10 6.10 61.04 61.04 610.45 610.45 29.97 29.97 29.97 29.97 29.97 29.97 29.97 29.97 33.03 31.57 21.29 20.79 25.40 24.62 60.15 58.14 104.80 29.97 7.73 7.34 12.96 12.72 11.71 16.04 7.19 6.84 12.65 12.63 20.31 27.13 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 832.73 17.47 7.71 0.77 832.73 1,767.69 1,861.36 3,258.06 3,159.50 2,070.50 1,910.89 1,909.43 1,968.16 1,967.42 2,719.10 2,716.36 3,297.26 3,322.72 3,427.05 3,469.40 5,090.29 5,111.65 1,265.19 1,264.47 1,274.98 1,274.53 1,272.64 1,280.74 1,264.19 1,263.52 1,274.40 1,274.36 1,288.72 1,301.48 5,121.27 1,279.53 156.04 Page 66 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.6.1 - Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) (52.19) (52.19) (62.27) 1.22 £/le (32.32) Ethernet main links £/le 9.16 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/le (51.97) Access Cards (other services) (q) % (£3m) (0.48) (4.79) (47.97) (47.97) (22.47) (0.48) (0.48) (4.79) (4.79) (47.97) (47.97) (0.48) (0.48) (4.79) (4.79) (47.97) (47.97) Service Centres - Assurance (q) % (£8m) (4.88) (4.88) (4.88) (4.88) (4.88) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) (9.77) Sales product management (q) % (£1m) (0.81) (1.08) (2.59) (0.45) (0.19) (0.74) (0.70) (0.81) (0.79) (1.81) (1.74) (1.17) (1.14) (1.39) (1.35) (3.30) (3.19) Service Centres - Provision (q) £/le (£6m) Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ Main link rental charges (52.19) £/le Ethernet Electronics £ Ethernet Backhaul Direct connections - External (52.19) Backhaul extension services fibre etc (448.71) (108.16) (108.16) (108.11) (109.36) (109.36) £ Ethernet Backhaul Direct rentals - External (7.40) (234.26) (234.26) (235.05) (235.04) (241.35) (241.35) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (218.71) (26.41) £/circuit £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections External (7.40) £/le Wholesale & LAN extension services BNS £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections Internal (7.40) Wholesale & LAN extension services fibre etc £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections External (7.40) £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections Internal (7.40) £ Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections External (7.40) £ Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections Internal £ EAD LA 1000 External Connections £ EAD LA 1000 Internal Connections £ EAD LA 100 External Connections £ EAD LA 100 Internal Connections Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals - Internal £ Unit (d) EAD LA 10 External Connections Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - External £ Components EAD LA 10 Internal Connections Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - Internal £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals External EAD LA 1000 External Rentals £ Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals Internal EAD LA 1000 Internal Rentals £ Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals External EAD LA 100 External Rentals £ EAD LA 100 Internal Rentals £ EAD LA 10 External Rentals £ EAD LA 10 Internal Rentals Backhaul extension services other bandwidth rental - External £ Backhaul extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals - External £ Wholesale extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals Wholesale extension services 100Mbit/s rentals Effect of changes on results Wholesale extension services 10Mbit/s rentals Average cost per unit Alternative interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 1Gbit/s) £ (1,025.54) (30.02) (33.54) (76.82) 1.22 1.22 (74.62) (29.83) (62.27) (52.19) (52.19) (52.19) (52.19) (62.27) (62.27) 9.17 114.84 (144.35) (152.45) (240.37) (236.06) (165.51) (70.58) (70.54) (74.96) (9.77) (0.43) (0.40) (0.71) (0.70) (0.64) (0.88) (0.40) (0.38) (0.70) (0.69) (1.12) (1.50) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (97.63) (0.96) (0.43) (0.04) (97.63) (74.94) (129.22) (129.15) (297.87) (297.84) (303.19) (303.14) (364.66) (364.55) (316.77) (316.74) (317.05) (317.04) (316.98) (317.22) (316.74) (316.72) (317.04) (317.03) (317.46) (317.84) (114.60) (316.77) (17.28) Page 67 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.6.1 - Illustrative for AISBO (up to and including 1Gbit/s) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Service Centres - Assurance (q) Sales product management (q) Service Centres - Provision (q) Fully Allocated Costs % Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - Internal Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s rentals - External Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals - Internal % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % -69% -52% -52% 2% 0% -1% -1% -1% -1% -1% -1% -10% -10% -10% -9% -7% -7% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% -52% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Main link rental charges EAD LA 1000 External Rentals Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals External EAD LA 1000 Internal Rentals Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s rentals Internal EAD LA 100 External Rentals % Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s rentals External EAD LA 100 Internal Rentals Backhaul extension services other bandwidth rental - External EAD LA 10 External Rentals Backhaul extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals - External EAD LA 10 Internal Rentals Wholesale extension services 1000Mbit/s rentals % Ethernet Backhaul Direct connections - External % % Ethernet Backhaul Direct rentals - External £/le Access Cards (other services) (q) 0% % Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections External 21CN Backhaul Link & Length -52% 0% % Ethernet Access Direct 1000Mbit/s connections Internal 9% -52% % Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections External -6% £/le -8% % Ethernet Access Direct 100Mbit/s connections Internal £/le Ethernet main links -9% % Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections External Ethernet Electronics -9% % Ethernet Access Direct 10Mbit/s connections Internal 0% -15% % EAD LA 1000 External Connections £/le % EAD LA 1000 Internal Connections £/circuit Backhaul extension services fibre etc % EAD LA 100 External Connections £/le Wholesale & LAN extension services BNS % EAD LA 100 Internal Connections Wholesale & LAN extension services fibre etc % EAD LA 10 External Connections Unit (d) EAD LA 10 Internal Connections Components Wholesale extension services 100Mbit/s rentals Effect of changes on results as a percentage Wholesale extension services 10Mbit/s rentals Average cost per unit Alternative interface symmetric broadband origination (up to and including 1Gbit/s) -100% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -6% -11% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% -8% % -22% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% -33% % -6% -5% -6% -5% -6% -5% -5% -5% -5% -5% -5% -6% -5% -5% -5% -5% -5% -5% £/le -5% 9% -1% -8% -8% -7% -7% -8% -4% -4% -4% -4% -5% -5% -9% -9% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 68 -9% -9% -7% -7% -33% -6% -5% -5% -6% -5% -5% -6% -6% -6% -5% -6% -6% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -12% -25% -25% -25% -25% -25% -25% -25% -25% -25% -25% -25% -24% -5% -6% -5% -12% -2% -25% -11% Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.7 – Illustrative for Wholesale Local Access (WLA) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service MPF New Provides 36.23 35.95 0.28 0.8% MPF Single Migrations 30.74 30.96 (0.22) -0.7% MPF Bulk Migrations 21.78 21.56 0.22 1.0% MPF Ceases 20.26 22.65 (2.39) -10.6% MPF Rentals 109.88 102.57 7.31 7.1% 16,157.35 14,748.98 1,408.37 9.5% 7,756.23 7,767.49 (11.26) -0.1% Tie Cables 44.05 44.89 (0.84) -1.9% SMPF New Provides 26.38 26.27 0.11 0.4% SMPF Single Migrations 30.21 30.40 (0.19) -0.6% SMPF Bulk Migrations 21.71 21.51 0.20 0.9% SMPF Ceases 20.30 22.70 (2.40) -10.6% SMPF Rentals 8.37 6.99 1.38 19.7% Co-mingling New Provides Co-mingling Rentals Page 69 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.7.1 –Illustrative for Wholesale Local Access (WLA) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ SMPF Rentals SMPF Ceases SMPF Bulk Migrations SMPF Single Migrations SMPF New Provides Tie Cables Co-mingling Rentals Co-mingling New Provides MPF Rentals MPF Ceases MPF Bulk Migrations MPF Single Migrations As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 MPF New Provides Average cost per unit Wholesale local access £ £ Components Unit (d) Routeing & records £/line 4.50 MDF Hardware jumpering £/line 17.13 E side copper capital £/line 9.36 E side copper current £/line 1.82 2.49 D side copper capital £/line 51.38 51.35 D side copper current £/line 7.01 9.60 1.77 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.80 3.61 1.81 Local exchanges general frames current £/line 0.86 2.21 0.74 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.20 0.20 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line 15.10 15.09 Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line 3.66 5.01 Broadband line testing systems £/line 2.50 8.12 Local Loop Unbundling room build £/room Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals £/hostel rental 2,859.57 2,859.49 Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals power & vent £/hostel rental 4,884.75 4,884.62 Local Loop Unbundling tie cables £/cable Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £29m Sales product management (q) % £17m 0.25 0.17 0.16 0.13 0.18 20.55 Service Centres - Provision (q) % £112m 5.55 4.44 4.23 1.70 0.41 1.71 Local Loop Unbundling systems development (q) % £32m 1.33 1.32 1.32 1.32 1.32 1.32 DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % £195m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 4.50 24.60 24.81 16.07 17.11 20.45 24.33 16.07 17.19 9.35 16,133.42 0.46 1.15 16,133.77 39.91 39.91 0.94 0.94 0.95 9.86 0.14 0.13 0.12 0.11 0.09 0.05 1.72 4.47 4.44 4.21 1.70 0.01 1.33 1.33 1.32 1.32 1.32 1.33 1.32 0.19 0.86 36.23 30.74 21.78 20.26 109.88 16,157.35 7,756.23 44.05 26.38 30.21 21.71 20.30 Page 70 8.37 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.7.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Local Access (WLA) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ SMPF Rentals SMPF Ceases SMPF Bulk Migrations SMPF Single Migrations SMPF New Provides Tie Cables Co-mingling Rentals Co-mingling New Provides MPF Rentals MPF Ceases MPF Bulk Migrations MPF Single Migrations Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies MPF New Provides Average cost per unit Wholesale local access £ £ Components Unit (d) Routeing & records £/line 5.08 MDF Hardware jumpering £/line 18.41 E side copper capital £/line 8.83 E side copper current £/line 2.02 2.76 D side copper capital £/line 46.86 46.83 D side copper current £/line 6.83 9.35 1.72 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 1.08 2.15 1.08 Local exchanges general frames current £/line 1.00 1.99 1.00 PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.18 0.18 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line 16.77 16.76 Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line 4.52 4.51 Broadband line testing systems £/line 2.24 7.00 Local Loop Unbundling room build £/room Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals £/hostel rental 2,578.43 2,578.36 Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals power & vent £/hostel rental 5,176.83 5,176.69 Local Loop Unbundling tie cables £/cable Service Centres - Assurance (q) % £37m Sales product management (q) % £18m 0.26 0.18 0.17 0.14 Service Centres - Provision (q) % £118m 3.75 3.71 3.71 3.71 Local Loop Unbundling systems development (q) % £10m 0.42 0.41 0.41 0.41 DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % £199m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 5.08 26.44 26.66 17.27 18.39 21.98 26.15 17.27 18.48 8.82 14,722.80 0.51 0.99 14,723.09 38.98 38.98 1.60 0.20 21.74 1.60 1.60 10.43 0.15 0.13 0.13 0.12 0.10 3.74 3.74 3.71 3.71 3.71 0.42 0.42 0.41 0.41 0.41 3.73 0.42 0.42 0.41 0.31 0.05 0.42 0.91 35.95 30.96 21.56 22.65 102.57 14,748.98 7,767.49 44.89 26.27 30.40 21.51 22.70 Page 71 6.99 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.7.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Local Access (WLA) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ SMPF Rentals SMPF Ceases SMPF Bulk Migrations SMPF Single Migrations SMPF New Provides Tie Cables Co-mingling Rentals Co-mingling New Provides MPF Rentals MPF Ceases MPF Bulk Migrations MPF Single Migrations Effect of changes on results MPF New Provides Average cost per unit Wholesale local access £ £ Components Unit (d) Routeing & records £/line (0.58) (0.58) MDF Hardware jumpering £/line (1.28) (1.84) (1.85) (1.20) (1.28) E side copper capital £/line 0.53 0.53 E side copper current £/line (0.20) (0.27) D side copper capital £/line 4.52 4.52 D side copper current £/line 0.18 0.25 Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 0.72 1.46 0.73 Local exchanges general frames current £/line (0.14) 0.22 (0.26) PSTN line test equipment £/line 0.02 0.02 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line (1.67) (1.67) Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line (0.86) 0.50 Broadband line testing systems £/line 0.26 1.12 Local Loop Unbundling room build £/room Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals £/hostel rental 281.14 281.13 Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals power & vent £/hostel rental (292.08) (292.07) Local Loop Unbundling tie cables £/cable Service Centres - Assurance (q) % (£8m) (0.66) Sales product management (q) % (£1m) (0.01) (0.01) (0.01) (0.01) (0.02) (1.19) Service Centres - Provision (q) % (£6m) 1.80 0.73 0.52 (2.01) 0.41 (2.02) Local Loop Unbundling systems development (q) % £22m 0.91 0.91 0.91 0.90 0.90 DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % (£4m) Fully Allocated Costs (£) (1.53) (1.82) (1.20) (1.29) 1,410.62 (0.05) 0.05 0.16 1,410.68 0.93 0.93 0.91 (0.66) (0.65) (0.12) (0.57) (0.01) 0.91 (0.01) (0.01) (0.01) (2.02) 0.73 0.73 0.50 (2.01) 0.91 0.91 0.91 0.91 0.91 0.01 0.91 (0.05) 0.28 (0.22) 0.22 (2.39) 7.31 Page 72 1,408.37 (11.26) (0.84) 0.11 (0.19) 0.20 (2.40) 1.38 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.7.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Local Access (WLA) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) % % % % -7% -7% -7% % % % % % % % % -7% -7% -7% -7% SMPF Rentals SMPF Ceases SMPF Bulk Migrations SMPF Single Migrations SMPF New Provides Tie Cables Co-mingling Rentals Co-mingling New Provides MPF Rentals MPF Ceases MPF Bulk Migrations MPF Single Migrations Effect of changes on results as a percentage MPF New Provides Average cost per unit Wholesale local access % Components Unit (d) Routeing & records £/line -11% -11% MDF Hardware jumpering £/line -107% -7% E side copper capital £/line 6% 6% E side copper current £/line -10% -10% D side copper capital £/line 10% 10% D side copper current £/line 3% 3% 3% Local exchanges general frames capital £/line 67% 68% 68% Local exchanges general frames current £/line -14% 11% -26% PSTN line test equipment £/line 11% 11% Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE £/line -10% -10% Residential PSTN drop maintenance £/line -19% 11% Broadband line testing systems £/line 12% 16% Local Loop Unbundling room build £/room 10% Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals £/hostel rental 11% 11% Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals power & vent £/hostel rental -6% -6% Local Loop Unbundling tie cables £/cable Service Centres - Assurance (q) % -22% Sales product management (q) % -6% -4% -6% -6% -7% Service Centres - Provision (q) % -5% 48% 20% 14% -54% Local Loop Unbundling systems development (q) % DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % Fully Allocated Costs % -10% 16% 10% 2% 2% -41% 220% 217% 222% 222% 222% -10% -5% -41% -41% -5% -7% 0% -8% -8% -10% -54% 20% 20% 13% -54% -54% 214% 214% -39% 0% 222% 217% 217% 222% 222% 222% 217% -2% -5% 1% -1% 1% -11% 7% 10% 0% -2% 0% -1% 1% -11% 20% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 73 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.8 – Illustrative for Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies ppm ppm ppm % Service Internal Wholesale call originating local exchange segment PSTN and ISDN (excl OA) External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment PSTN and ISDN (excl OA) 0.264 0.264 0.282 0.282 (0.018) (0.018) -6.4% -6.4% Internal Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (incl Operator Assistance) External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (incl Operator Assistance) 0.220 0.220 0.236 0.236 (0.016) (0.016) -6.8% -6.8% Internal Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (ISDN) (incl OA) 0.284 0.303 (0.019) -6.3% Internal Wholesale call origination local exchange Stick (PSTN & ISDN) 0.136 0.145 (0.009) -6.2% Internal Wholesale PPP External Wholesale PPP 0.006 0.006 0.006 0.006 - 0.0% 0.0% Page 74 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.8.1 – Illustrative for Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors ppm ppm ppm ppm Components Unit (d) Local exchange concentrator ppm 0.067 0.079 0.064 0.086 Local exchange processor ppm 0.063 0.074 0.060 0.080 Remote - local transmission link ppm 0.039 0.037 0.031 0.040 0.030 Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) 0.023 0.040 0.034 0.043 0.032 Product management policy & planning ppm 0.006 Emergency OA (999) non chargeable ppm 0.021 0.021 0.021 0.021 Core/Metro (voice) ppm 0.001 0.003 0.002 0.003 0.002 iNode (call set up and features) (q) % £17m 0.010 0.008 0.011 0.008 0.264 0.220 0.284 0.136 Fully Allocated Costs (ppm) Internal and External Wholesale PPP Internal Wholesale call origination local exchange Stick (PSTN & ISDN) Internal Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (ISDN) (incl OA) Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (incl Operator Assistance) As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment PSTN and ISDN (excl OA) Average cost per unit Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks Retail PPP Call Origination Basket (ad) Sticks Basket ppm 0.064 0.006 Page 75 0.006 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.8.1 – Illustrative for Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) ppm ppm ppm ppm Components Unit (d) Local exchange concentrator ppm 0.074 0.087 0.071 0.094 Local exchange processor ppm 0.070 0.082 0.067 0.089 Remote - local transmission link ppm 0.044 0.042 0.035 0.045 0.034 Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) 0.022 0.038 0.032 0.041 0.031 Product management policy & planning ppm 0.006 Emergency OA (999) non chargeable ppm 0.021 0.021 0.021 0.021 Core/Metro (voice) ppm 0.001 0.003 0.002 0.003 0.002 iNode (call set up and features) (q) % £16m 0.009 0.008 0.010 0.008 0.282 0.236 0.303 0.145 Fully Allocated Costs (ppm) Internal and External Wholesale PPP Internal Wholesale call origination local exchange Stick (PSTN & ISDN) Internal Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (ISDN) (incl OA) Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (incl Operator Assistance) Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment PSTN and ISDN (excl OA) Average cost per unit Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks Retail PPP Call Origination Basket (ad) Sticks Basket ppm 0.070 0.006 Page 76 0.006 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.8.1 – Illustrative for Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) ppm (0.007) (0.008) (0.006) (0.007) (0.009) (0.005) (0.004) (0.005) (0.004) 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.001 Local exchange concentrator ppm (0.007) (0.008) Local exchange processor ppm (0.007) (0.008) Remote - local transmission link ppm (0.005) Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) 0.001 Product management policy & planning ppm 0.000 Emergency OA (999) non chargeable ppm 0.000 Core/Metro (voice) ppm 0.000 iNode (call set up and features) (q) % Fully Allocated Costs (ppm) 0.001 (0.018) Internal and External Wholesale PPP Internal Wholesale call origination local exchange Stick (PSTN & ISDN) ppm Unit (d) ppm Internal Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (ISDN) (incl OA) ppm Components £1m Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (incl Operator Assistance) Effect of changes on results Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment PSTN and ISDN (excl OA) Average cost per unit Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks Retail PPP Call Origination Basket (ad) Sticks Basket ppm 0.001 (0.016) (0.019) (0.009) Page 77 - Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.8.1 – Illustrative for Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Call origination on fixed public narrowband networks Internal Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (ISDN) (incl OA) % % % Components Unit (d) Local exchange concentrator ppm -9% -9% -10% -9% Local exchange processor ppm -110% -10% -10% -10% Remote - local transmission link ppm -11% -12% -11% -11% -12% Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) 5% 5% 6% 5% 3% Product management policy & planning ppm 0% Emergency OA (999) non chargeable ppm 0% 0% 0% 0% Core/Metro (voice) ppm 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% iNode (call set up and features) (q) % 6% 11% 0% 10% 0% -6% -7% -6% -6% Fully Allocated Costs % PPP Basket Internal and External Wholesale PPP % Retail Sticks Internal Wholesale call origination local exchange Stick (PSTN & ISDN) % Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment (incl Operator Assistance) Effect of changes on results as a percentage Internal and External Wholesale call originating local exchange segment PSTN and ISDN (excl OA) Average cost per unit Call Origination Basket (ad) -9% 0% 0% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (ad) Does not include the service Wholesale Call originating local exchange segment (ISDN) (excl. Operator Assistance) due to immaterial volumes. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 78 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.9 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Interconnect Circuits) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % 1,205.82 608.32 11.72 1,533.34 658.61 12.00 (327.52) (50.29) (0.28) -21.4% -7.6% -2.3% In Span Interconnect with Interconnect Extension Circuit (end to end circuit) External Wholesale IEC connections External Wholesale IEC rentals - fixed External Wholesale IEC rentals - per km 537.72 351.88 11.71 696.70 383.39 11.99 (158.98) (31.51) (0.28) -22.8% -8.2% -2.3% In Span Interconnect External Wholesale intra-building circuits connections External Wholesale intra-building circuits rentals External Wholesale ISI rentals 407.53 101.14 291.78 533.64 105.03 315.41 (126.11) (3.89) (23.63) -23.6% -3.7% -7.5% 59.49 59.40 External Wholesale rearrangements 515.86 657.58 (141.72) -21.6% Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed 507.18 553.58 (46.40) -8.4% 11.72 12.00 (0.28) -2.3% 101.14 105.03 (3.89) -3.7% Service Customer Sited Interconnect (end to end circuit) External Wholesale standard CSI connections External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km External Nominated ISI - per km Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km Internal Wholesale intra-building circuits rentals Page 79 0.09 0.2% Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.9.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Interconnect Circuits) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors Interconnect local end rental 2Mbit/s £/circuit 181.24 Interconnect 2Mbit/s connection £/circuit 984.56 Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit 196.82 Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit 205.23 Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit per km £/km Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit per km £/km In Span Interconnect circuits (ISI) transmission £/100m Nominated In Span I/Connect cct (ISI) transmission £/100m 51.97 Intra Building Circuit (IBC) connection £/circuit 319.12 Intra Building Circuit (IBC) rental £/circuit 90.10 90.10 SG&A Interconnect (q) % £5m 195.86 131.75 2.41 1,205.82 608.32 11.72 Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ £ £ £ £ £ 181.24 £ £ Internal Wholesale intrabuilding circuits rentals Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed External Wholesale rearrangements Internal Interconnect External Nominated ISI - per km External Wholesale ISI rentals External Wholesale intrabuilding circuits rentals External Wholesale intrabuilding circuits connections £ Unit (d) External Wholesale IEC rentals - per km £ Components External Wholesale IEC rentals - fixed External Wholesale IEC connections £ External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km £ External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 External Wholesale standard CSI connections Average cost per unit Customer Sited Interconnect (end to end circuit) Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) In Span Interconnect with Interconnect In span Interconnect Extension Circuit (end to end circuit) £ 181.24 690.84 112.67 466.77 196.82 205.23 205.23 9.30 9.30 9.31 9.31 9.31 291.78 291.78 51.97 319.12 319.12 319.12 90.10 105.93 64.96 90.10 2.41 537.72 351.88 11.71 Page 80 88.41 11.04 90.10 7.52 49.09 120.71 407.53 101.14 291.78 59.49 515.86 507.18 2.41 11.04 11.72 101.14 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.9.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Interconnect Circuits) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Interconnect local end rental 2Mbit/s £/circuit 185.45 Interconnect 2Mbit/s connection £/circuit 1,249.32 Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit 212.83 Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit 221.41 Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit per km £/km Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit per km £/km In Span Interconnect circuits (ISI) transmission £/100m Nominated In Span I/Connect cct (ISI) transmission £/100m 50.26 Intra Building Circuit (IBC) connection £/circuit 426.17 Intra Building Circuit (IBC) rental £/circuit 91.61 91.61 SG&A Interconnect (q) % £6m 238.07 160.14 2.92 1,533.34 658.61 12.00 Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ £ £ £ £ £ 185.45 £ £ Internal Wholesale intrabuilding circuits rentals Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed External Wholesale rearrangements Internal Interconnect External Nominated ISI - per km External Wholesale intrabuilding circuits rentals External Wholesale ISI rentals In span Interconnect External Wholesale intrabuilding circuits connections £ Unit (d) External Wholesale IEC rentals per km £ Components External Wholesale IEC rentals fixed External Wholesale IEC connections £ External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km £ External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies External Wholesale standard CSI connections Average cost per unit Customer Sited Interconnect (end to end circuit) In Span Interconnect with Interconnect Extension Circuit (end to end circuit) £ 185.45 869.10 141.74 597.91 212.83 221.41 221.41 9.07 9.07 9.08 9.08 9.08 315.41 315.41 50.26 426.17 426.17 426.17 91.61 128.79 78.95 91.61 2.92 696.70 383.39 11.99 Page 81 107.47 13.42 91.61 9.14 59.67 146.72 533.64 105.03 315.41 59.40 657.58 553.58 2.92 13.42 12.00 105.03 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.9.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Interconnect Circuits) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Unit (d) Interconnect local end rental 2Mbit/s £/circuit (4.21) Interconnect 2Mbit/s connection £/circuit (264.76) Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit (16.01) Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit (16.18) Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit per km £/km Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit per km £/km In Span Interconnect circuits (ISI) transmission £/100m Nominated In Span I/Connect cct (ISI) transmission £/100m 1.71 Intra Building Circuit (IBC) connection £/circuit (107.05) Intra Building Circuit (IBC) rental £/circuit (1.51) (1.51) SG&A Interconnect (q) % (£1m) (42.21) (28.39) Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ £ £ £ £ £ (4.21) £ £ Internal Wholesale intra-building circuits rentals Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed External Wholesale rearrangements External Nominated ISI - per km Internal Interconnect External Wholesale ISI rentals External Wholesale intra-building circuits rentals In span Interconnect External Wholesale intra-building circuits connections £ External Wholesale IEC rentals per km £ External Wholesale IEC rentals fixed External Wholesale IEC connections £ Components External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km £ External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed Effect of changes on results External Wholesale standard CSI connections Average cost per unit Customer Sited Interconnect (end to end circuit) In Span Interconnect with Interconnect Extension Circuit (end to end circuit) £ (4.21) (178.26) (29.07) (131.14) (16.01) (16.18) (16.18) 0.23 0.23 0.23 0.23 0.23 (23.63) (23.63) 1.71 (107.05) (107.05) (327.52) (50.29) (107.05) (1.51) (0.51) (22.86) (13.99) (0.51) (1.51) (19.06) (0.28) (158.98) (31.51) (0.28) (126.11) Page 82 (2.38) (3.89) (23.63) (1.51) (1.62) (10.58) (26.01) (0.51) (2.38) 0.09 (141.72) (46.40) (0.28) (3.89) Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.9.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Interconnect Circuits) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Technical areas (Interconnect Circuits) Components Unit (d) Interconnect local end rental 2Mbit/s £/circuit -2% Interconnect 2Mbit/s connection £/circuit -21% Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit -8% Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit/s link £/circuit -7% Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit per km £/km Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit per km £/km In Span Interconnect circuits (ISI) transmission £/100m Nominated In Span I/Connect cct (ISI) transmission £/100m 3% Intra Building Circuit (IBC) connection £/circuit -25% Intra Building Circuit (IBC) rental £/circuit SG&A Interconnect (q) % Fully Allocated Costs % % % % % Internal Wholesale intrabuilding circuits rentals % -2% % -2% -21% -21% -22% -8% -7% -7% 3% 3% 3% 3% 3% -7% -7% 3% -25% -2% -17% % Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km % Internal Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed % External Wholesale rearrangements % Internal Interconnect External Nominated ISI - per km % External Wholesale ISI rentals External Wholesale IEC rentals - fixed % External Wholesale intrabuilding circuits rentals External Wholesale IEC connections % In span Interconnect External Wholesale intrabuilding circuits connections External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - per km % External Wholesale IEC rentals - per km External Wholesale standard CSI rentals - fixed Effect of changes on results as a percentage External Wholesale standard CSI connections Average cost per unit Customer Sited Interconnect (end to end circuit) In Span Interconnect with Interconnect Extension Circuit (end to end circuit) -25% -2% -25% -2% -2% -18% -18% -17% -18% -18% -17% -18% -18% -21% -8% -2% -23% -8% -2% -24% -4% -2% -7% -18% -18% -18% -17% -18% 0% -22% -8% -2% -4% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. Page 83 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.10 – Illustrative for Fixed Call Termination 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies ppm ppm ppm % Service Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange segment External Wholesale call termination local exchange segment 0.205 0.205 0.221 0.221 (0.016) (0.016) -7.2% -7.2% Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange segment (ISDN) 0.266 0.284 (0.018) -6.3% Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange stick (PSTN & ISDN) 0.136 0.145 (0.009) -6.2% Page 84 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.10.1 – Illustrative for Fixed Call Termination calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors Fixed call termination Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange stick (PSTN & ISDN) ppm Retail Stick Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange segment (ISDN) As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Wholesale call termination local exchange segment Average cost per unit Call Termination ppm ppm Components Unit (d) Local exchange concentrator ppm 0.067 0.066 0.087 Local exchange processor ppm 0.063 0.062 0.081 Remote - local transmission link ppm 0.039 0.032 0.040 0.030 Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) 0.023 0.034 0.044 0.032 Core/Metro (voice) ppm 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.002 iNode (call set up and features) (q) % £17m 0.009 0.011 0.008 0.205 0.266 0.136 Fully Allocated Costs (ppm) 0.064 Page 85 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.10.1 – Illustrative for Fixed Call Termination calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Fixed call termination Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange stick (PSTN & ISDN) ppm Retail Stick Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange segment (ISDN) Restated on basis of 2011/12 methodologies Wholesale call termination local exchange segment Average cost per unit Call Termination ppm ppm Components Unit (d) Local exchange concentrator ppm 0.074 0.073 0.095 Local exchange processor ppm 0.070 0.069 0.090 Remote - local transmission link ppm 0.044 0.036 0.045 0.034 Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) 0.022 0.033 0.041 0.031 Core/Metro (voice) ppm 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.002 iNode (call set up and features) (q) % £16m 0.008 0.010 0.008 0.221 0.284 0.145 Fully Allocated Costs (ppm) Page 86 0.070 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.10.1 – Illustrative for Fixed Call Termination calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Fixed call termination Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange stick (PSTN & ISDN) ppm (0.007) (0.007) (0.008) (0.006) (0.007) (0.007) (0.009) (0.005) (0.004) Wholesale call termination local exchange segment ppm Average cost per unit Effect of changes on results ppm Components Unit (d) Local exchange concentrator ppm Local exchange processor ppm Remote - local transmission link ppm Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) Core/Metro (voice) ppm iNode (call set up and features) (q) % Fully Allocated Costs (ppm) Retail Stick Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange segment (ISDN) Call Termination (0.005) (0.004) 0.001 0.001 0.003 0.001 £1m 0.001 0.001 (0.016) (0.018) (0.009) Page 87 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.10.1 – Illustrative for Fixed Call Termination calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Fixed call termination Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange stick (PSTN & ISDN) % Retail Stick Internal Wholesale call termination local exchange segment (ISDN) Effect of changes on results as a percentage Wholesale call termination local exchange segment Average cost per unit Call Termination % % Components Unit (d) Local exchange concentrator ppm -9% -10% -8% Local exchange processor ppm -10% -10% -10% Remote - local transmission link ppm -11% -11% -11% -12% Remote - local transmission length ppm (per 10km) 5% 3% 7% 3% Core/Metro (voice) ppm 0% 0% 0% 0% iNode (call set up and features) (q) % 6% 13% 10% 0% -7% -6% -6% Fully Allocated Costs % -9% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 88 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.11 – Illustrative for Wholesale Trunk Segments 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % Service Partial and Private circuits 2Mbit/s - trunk Trunk charge per year Enhanced maintenance per km charge per year Total Internal 15.01 15.21 (0.20) -1.3% Trunk charge per year Enhanced maintenance per km charge per year Total External 15.01 15.21 (0.20) -1.3% Partial and Private circuits 34/45Mbit/s - trunk Trunk charge per year Enhanced maintenance per km charge per year Total Internal 139.38 141.55 (2.17) -1.5% Trunk charge per year Enhanced maintenance per km charge per year Total External 139.38 141.55 (2.17) -1.5% Partial and Private circuits 140/155Mbit/s - trunk Trunk charge per year Enhanced maintenance per km charge per year Total Internal 208.39 208.39 - 0.0% Trunk charge per year Enhanced maintenance per km charge per year Total External 208.39 208.39 - 0.0% Internal Partial and Private circuits 622Mbit/s - trunk 986.18 991.33 (5.15) -0.5% Page 89 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.11.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Trunk Segments calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 12.60 PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 120.97 PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 200.13 PC rental 622Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 960.93 SG & A partial private circuits (q) % Fully Allocated Costs (£) £31m £ £ Partial and Private circuits 622Mbit/s - trunk Partial and Private circuits 140/155Mbit/s - trunk £ Components Partial and Private circuits 34/45Mbit/s - trunk As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Partial and Private circuits 2Mbit/s - trunk Average cost per unit Wholesale trunk segments £ 12.68 120.85 198.99 960.93 2.33 18.53 15.01 139.38 9.40 25.25 208.39 986.18 Page 90 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.11.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Trunk Segments calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 12.71 PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 122.46 PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 199.67 PC rental 622Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 965.15 SG & A partial private circuits (q) % Fully Allocated Costs (£) £32m £ £ Partial and Private circuits 622Mbit/s - trunk Partial and Private circuits 140/155Mbit/s - trunk £ Components Partial and Private circuits 34/45Mbit/s - trunk Restated on basis on 2011/12 methodologies Partial and Private circuits 2Mbit/s - trunk Average cost per unit Wholesale trunk segments £ 12.79 122.35 198.65 965.15 2.42 19.20 15.21 141.55 9.74 26.18 208.39 991.33 Page 91 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.11.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Trunk Segments calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km (0.11) PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km (1.49) PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 0.46 PC rental 622Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km (4.22) SG & A partial private circuits (q) % (£1m) Fully Allocated Costs (£) £ £ Partial and Private circuits 622Mbit/s - trunk Partial and Private circuits 140/155Mbit/s - trunk £ Components Partial and Private circuits 34/45Mbit/s - trunk Effect of changes on results Partial and Private circuits 2Mbit/s - trunk Average cost per unit Wholesale trunk segments £ (0.11) (1.50) 0.34 (4.22) (0.09) (0.67) (0.34) (0.93) (0.20) (2.17) - (5.15) Page 92 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.11.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Trunk Segments calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) Components Unit (d) PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km -1% PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km -1% PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 0% PC rental 622Mbit/s link per km trunk £/km 0% SG & A partial private circuits (q) % Fully Allocated Costs % -3% Partial and Private circuits 34/45Mbit/s - trunk Partial and Private circuits 140/155Mbit/s - trunk Partial and Private circuits 622Mbit/s - trunk Effect of changes on results as a percentage Partial and Private circuits 2Mbit/s - trunk Average cost per unit Wholesale trunk segments % % % % -1% -1% 0% 0% -4% -3% -3% -4% -1% -2% 0% -1% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 93 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.12 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Point of Handover) 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ Service External Customer Sited Handover connections External Customer Sited Handover rentals External In Span Handover connections External In Span Handover rentals £ - - 1,776.80 1,779.52 - - £ % - - (2.72) -0.2% - - 52.21 53.57 (1.36) -2.5% 141.27 139.55 1.72 1.2% 76.46 79.14 (2.68) -3.4% External 3rd Party POH Rental 2Mbit/s non CLZ - circuit 142.61 140.57 2.04 1.5% External 3rd Party POH Rental Other - circuit 167.27 165.16 2.11 1.3% External 3rd Party POH Rentals - equipment External 3rd Party POH Rental 64kbit/s - circuit Page 94 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.12.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Point of Handover) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors £ Unit (d) Point of Handover electronics £/eq PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le 392.94 PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le 3,553.49 14.98 PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le 5,989.94 2.61 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le 263.18 9.57 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le 650.76 99.71 Access Cards (other services) (q) % £25m 5.75 SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £31m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 1,141.05 1,712.24 £ £ £ Components External 3rd Party POH Rental Other - circuit External 3rd Party POH Rentals - equipment In Span Handover rentals In Span Handover connections £ External 3rd Party POH Rental 2Mbit/s non CLZ circuit £ External 3rd Party POH Rental 64kbit/s - circuit £ Customer Sited Handover rentals As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Customer Sited Handover connections Average cost per unit Technical Areas (Point of Handover) £ 24.69 7.76 70.78 64.56 - 1,776.80 27.52 0.89 9.56 6.29 11.91 114.75 133.80 5.68 - 52.21 141.27 76.46 Page 95 6.26 6.92 9.69 10.70 142.61 167.27 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.12.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Point of Handover) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ Point of Handover electronics £/eq PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le 407.43 PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le 3,635.04 15.27 PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le 6,188.34 2.69 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le 278.27 9.90 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le 675.01 102.74 Access Cards (other services) (q) % £28m SG & A partial private circuits (q) % £32m Fully Allocated Costs (£) 1,153.83 1,712.60 £ £ External 3rd Party POH Rental Other - circuit External 3rd Party POH Rentals - equipment In Span Handover rentals In Span Handover connections £ Unit (d) External 3rd Party POH Rental 2Mbit/s non CLZ circuit £ Components External 3rd Party POH Rental 64kbit/s - circuit £ Customer Sited Handover rentals Restated on basis on 2011/12 methodologies Customer Sited Handover connections Average cost per unit Technical Areas (Point of Handover) £ 25.05 8.03 73.25 66.92 - 1,779.52 28.52 0.92 9.74 6.49 12.32 118.21 137.85 5.89 - 53.57 139.55 79.14 Page 96 10.04 11.08 140.57 165.16 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.12.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Point of Handover) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ £ £ External 3rd Party POH Rental Other - circuit External 3rd Party POH Rentals - equipment In Span Handover rentals In Span Handover connections £ External 3rd Party POH Rental 2Mbit/s non CLZ circuit £ External 3rd Party POH Rental 64kbit/s - circuit £ Customer Sited Handover rentals Effect of changes on results Customer Sited Handover connections Average cost per unit Technical Areas (Point of Handover) £ Components Unit (d) Point of Handover electronics £/eq (12.78) PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le (14.49) (0.27) (2.47) PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le (81.55) (0.29) PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le (198.40) (0.08) PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le (15.09) (0.33) (0.41) PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le (24.25) (3.03) (3.46) Access Cards (other services) (q) % (£3m) 5.75 6.26 6.92 SG & A partial private circuits (q) % (£1m) Fully Allocated Costs (£) (0.36) - (0.36) (0.18) (0.20) (4.05) (2.36) (1.00) (0.03) (0.21) (0.35) (0.38) (2.72) - (1.36) 1.72 (2.68) 2.04 2.11 Page 97 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.12.1 – Illustrative for Technical Areas (Point of Handover) calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) % % % % % % % External 3rd Party POH Rental Other - circuit External 3rd Party POH Rental 2Mbit/s non CLZ - circuit External 3rd Party POH Rental 64kbit/s - circuit External 3rd Party POH Rentals - equipment In Span Handover rentals In Span Handover connections Customer Sited Handover rentals Effect of changes on results as a percentage Customer Sited Handover connections Average cost per unit Technical Areas (Point of Handover) % Components Unit (d) Point of Handover electronics £/eq -1% PC rental 64kbit/s link local end £/le -4% -3% PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end £/le -2% -2% PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end £/le -3% -3% PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper £/le -5% -3% -3% PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre £/le -4% -3% -3% -3% Access Cards (other services) (q) % -11% SG & A partial private circuits (q) % -3% Fully Allocated Costs % 0% -1% -4% - 0% - -3% -2% -3% -4% -3% -4% -3% -3% -3% 1% -3% 1% 1% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. Page 98 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.13 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 1 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) Service Internal End user access connections Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs External end user access connections Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal WBC end user access Rentals Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs External WBC end user access Rentals Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal WBC bandwidth Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs External WBC bandwidth Mkt 1 EOI Wholesale Costs 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % 33.54 5.15 38.69 33.54 6.31 39.85 (1.16) (1.16) 0.0% -18.4% -2.9% 33.54 5.15 38.69 33.54 6.31 39.85 (1.16) (1.16) 0.0% -18.4% -2.9% 25.69 77.38 103.07 25.69 72.44 98.13 4.94 4.94 0.0% 6.8% 5.0% 26.44 77.09 103.53 26.44 72.20 98.64 4.89 4.89 0.0% 6.8% 5.0% 7.19 60.12 67.31 7.19 59.66 66.85 0.46 0.46 0.0% 0.8% 0.7% 7.39 64.08 71.47 7.39 65.01 72.40 (0.93) (0.93) 0.0% -1.4% -1.3% 18.03 26.60 44.63 18.03 27.07 45.10 (0.47) (0.47) 0.0% -1.7% -1.0% 18.03 26.60 44.63 18.03 27.07 45.10 (0.47) (0.47) 0.0% -1.7% -1.0% 6.04 18.56 24.60 6.04 17.38 23.42 1.18 1.18 0.0% 6.8% 5.0% 5.90 18.57 24.47 5.90 17.39 23.29 1.18 1.18 0.0% 6.8% 5.1% Page 99 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.13.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 1 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors 1.85 1.86 2.65 2.65 £ £ £ 1.83 1.83 Unit (d) Broadband line testing systems £/line 2.50 ADSL connections £/conn 2.66 Combi Card Broadband Access £/line 19.91 ATM customer interface 2Mbit/s £/port 92.26 0.01 0.01 ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port 982.59 0.08 0.08 ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port 286.23 0.99 0.99 ATM network interface £/port 98.13 0.43 0.43 ATM network switching £/use 3.01 2.57 2.57 Inter ATM transmissions £/use 42.88 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit 7,423.01 Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 10.78 SG&A Broadband (q) % £92m Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % £52m Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £9m 0.86 0.86 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % £47m 1.60 1.60 DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % £195m 4.29 8.17 EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs (£) 19.91 19.91 External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 £ Components Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 £ External WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 1 External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 £ Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 £ £ External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 External end user access connections Mkt 1 As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Internal End user access connections Mkt 1 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 1 - BT only operator £ £ 4.30 4.30 19.91 19.91 10.84 10.84 4.30 4.30 10.39 10.39 2.70 2.70 5.23 5.39 7.56 7.64 10.39 10.39 4.97 4.97 3.05 3.05 0.86 0.86 16.24 16.24 50.54 50.08 (0.20) (0.20) (0.15) (0.15) (0.04) (0.04) (0.11) (0.11) (0.04) (0.03) 5.15 5.15 77.38 77.09 60.12 64.08 26.60 26.60 18.56 18.57 Page 100 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.13.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 1 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) 1.98 1.99 3.72 3.72 £ £ £ 1.96 1.96 £ £ 4.19 4.19 4.19 9.47 9.47 9.47 3.15 3.15 0.61 0.61 Components Unit (d) Broadband line testing systems £/line 2.24 ADSL connections £/conn 3.73 Combi Card Broadband Access £/line 20.08 ATM customer interface 2Mbit/s £/port 99.20 0.01 0.01 ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port 1,061.78 0.08 0.08 ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port 307.89 1.07 1.07 ATM network interface £/port 105.49 0.47 0.47 ATM network switching £/use 3.22 2.75 2.75 Inter ATM transmissions £/use 43.88 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit 7,474.98 4.19 Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 9.96 9.47 SG&A Broadband (q) % £94m 7.81 7.89 Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % £51m Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £9m Core/Metro connectivity (q) % £63m DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % £199m EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs (£) External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 £ Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 £ External WBC end user accessRentals Mkt 1 External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 £ Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 £ £ External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 External end user access connections Mkt 1 Restated on basis on 2011/12 methodologies Internal End user access connections Mkt 1 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 1 - BT only operator 20.08 20.08 20.08 20.08 11.09 11.09 2.79 2.79 5.42 5.59 5.14 5.14 16.31 16.31 0.61 45.11 44.69 0.61 5.84 11.11 (0.20) (0.20) (0.15) (0.15) (0.04) (0.04) (0.11) (0.11) (0.04) (0.03) 6.31 6.31 72.44 72.20 59.66 65.01 27.07 27.07 17.38 17.39 Page 101 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.13.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 1 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 1 External WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 1 £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.92 0.92 0.92 Components Unit (d) Broadband line testing systems £/line ADSL connections £/conn (1.07) (1.07) (1.07) Combi Card Broadband Access £/line (0.17) ATM customer interface 2Mbit/s £/port (6.94) ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port (79.19) ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port (21.66) (0.08) (0.08) ATM network interface £/port (7.36) (0.04) (0.04) ATM network switching £/use (0.21) (0.18) (0.18) Inter ATM transmissions £/use (1.00) (0.25) (0.25) 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit (51.97) 0.11 Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 0.82 0.92 SG&A Broadband (q) % Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % £1m Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £0m 0.25 0.25 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % (£16m) 1.60 1.60 DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % (£4m) 0.26 External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 £ Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 External end user access connections Mkt 1 Effect of changes on results Internal End user access connections Mkt 1 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 1 - BT only operator (0.13) (0.13) (0.13) (0.13) (0.17) (0.17) (0.17) (0.17) (£2m) (0.09) (0.09) (0.19) (0.20) (0.25) (0.25) (0.17) (0.17) (0.10) (0.10) (0.07) (0.07) 5.43 5.39 (1.55) (2.94) 4.94 4.89 0.25 0.25 1.18 1.18 EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs (£) (1.16) (1.16) 0.46 (0.93) (0.47) (0.47) Page 102 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.13.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 1 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) -7% -7% -1% -1% -29% -29% % % % -7% -7% -1% -1% % External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 % Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 % External WBC end user accessRentals Mkt 1 External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 % Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 1 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 1 % % External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 1 External end user access connections Mkt 1 Effect of changes on results as a percentage Internal End user access connections Mkt 1 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 1 - BT only operator % Components Unit (d) Broadband line testing systems £/line ADSL connections £/conn Combi Card Broadband Access £/line -1% ATM customer interface 2Mbit/s £/port -7% ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port -7% 0% 0% ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port -7% -7% -7% ATM network interface £/port -7% -9% -9% ATM network switching £/use -7% -7% -7% Inter ATM transmissions £/use -2% -2% -2% 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit -1% 3% 3% 3% 3% Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 8% 10% 10% 10% 10% SG&A Broadband (q) % -2% -3% -3% -3% -3% Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % 2% 0% 0% Edge Ethernet ports (q) % 0% 41% 41% 41% 41% Core/Metro connectivity (q) % -25% DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % -2% EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs % 12% -29% 0% -3% -3% -4% -4% 0% -3% -3% 12% 12% -27% -26% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% -18% -18% 7% 7% 1% -1% -2% -2% 7% 7% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. (ap) Reduction in FAC due to notional creditor generated by the EOI charge from Openreach to WBA markets. Page 103 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.14 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 2 2012/13 FAC (on 2012/13 basis) Service Internal End user access connections Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs External end user access connections Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal WBC end user access Rentals Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs External WBC end user access Rentals Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs Internal WBC bandwidth Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs External WBC bandwidth Mkt 2 EOI Wholesale Costs 2012/13 FAC (on Effect of Effect of 2011/12 change in change in basis) methodologies methodologies £ £ £ % 33.54 5.35 38.89 33.54 6.52 40.06 (1.17) (1.17) 0.0% -17.9% -2.9% 33.54 5.35 38.89 33.54 6.52 40.06 (1.17) (1.17) 0.0% -17.9% -2.9% 26.33 86.36 112.69 26.33 84.93 111.26 1.43 1.43 0.0% 1.7% 1.3% 26.70 89.52 116.22 26.70 87.99 114.69 1.53 1.53 0.0% 1.7% 1.3% 8.36 59.71 68.07 8.36 58.81 67.17 0.90 0.90 0.0% 1.5% 1.3% 4.06 58.81 62.87 4.06 57.56 61.62 1.25 1.25 0.0% 2.2% 2.0% 18.03 26.60 44.63 18.03 27.07 45.10 (0.47) (0.47) 0.0% -1.7% -1.0% 18.03 26.60 44.63 18.03 27.07 45.10 (0.47) (0.47) 0.0% -1.7% -1.0% 5.44 18.57 24.01 5.44 17.39 22.83 1.18 1.18 0.0% 6.8% 5.2% 5.45 18.57 24.02 5.45 17.39 22.84 1.18 1.18 0.0% 6.8% 5.2% Page 104 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.14.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 2 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors 1.90 1.91 2.67 2.67 £ Broadband line testing systems £/line 2.50 ADSL connections £/conn 2.66 Combi Card Broadband Access £/line 19.91 ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port 982.59 0.07 0.07 ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port 286.23 1.13 1.13 ATM network interface £/port 98.13 0.47 0.47 ATM network switching £/use 3.01 2.92 2.92 Inter ATM transmissions £/use 42.88 10.89 10.89 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit 7,423.01 4.30 4.30 Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 10.78 10.39 10.39 SG&A Broadband (q) % £92m 9.77 9.82 Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % £52m 14.56 14.56 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £9m 0.86 0.86 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % £47m 1.60 1.60 DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % £195m EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs (£) 19.91 19.91 2.88 2.88 5.77 5.89 58.93 61.97 £ 1.83 1.83 £ £ 4.30 4.30 19.91 19.91 2.80 (0.20) (0.20) (0.15) (0.16) (0.05) 5.35 £ External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 £ Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 £ Unit (d) External WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 £ Components Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 £ £ External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 External end user access connections Mkt 2 As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Internal End user access connections Mkt 2 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 2 - 2 to 3 principal operators 5.35 86.36 89.52 59.71 Page 105 10.39 10.39 4.97 4.97 3.05 3.05 0.86 0.86 1.82 (0.02) (0.11) (0.11) (0.03) (0.03) 58.81 26.60 26.60 18.57 18.57 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.14.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 2 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) 2.02 2.03 3.73 3.73 £ 4.19 4.19 9.47 9.47 9.47 3.15 3.15 0.61 0.61 £/line 2.24 ADSL connections £/conn 3.73 Combi Card Broadband Access £/line 20.08 ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port 1,061.78 0.07 0.07 ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port 307.89 1.21 1.21 ATM network interface £/port 105.49 0.51 0.51 ATM network switching £/use 3.22 3.12 3.12 Inter ATM transmissions £/use 43.88 11.15 11.15 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit 7,474.98 4.19 Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 9.96 9.47 SG&A Broadband (q) % £94m 6.10 10.09 10.14 Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % £51m 14.63 14.63 Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £9m 0.61 0.61 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % £63m DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % £199m EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs (£) 20.08 20.08 57.00 59.94 20.08 20.08 3.81 (0.20) (0.20) (0.15) (0.16) (0.05) 6.52 1.96 4.19 Broadband line testing systems 5.98 1.96 £ Unit (d) 2.99 £ £ Components 2.99 £ External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 £ Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 £ External WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 £ Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 £ £ External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 External end user access connections Mkt 2 Restated on basis on 2011/12 methodologies Internal End user access connections Mkt 2 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 2 - 2 to 3 principal operators 6.52 84.93 87.99 58.81 5.14 5.14 2.48 (0.02) (0.11) (0.11) (0.03) (0.03) 57.56 27.07 27.07 17.39 17.39 Page 106 Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.14.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 2 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) £ £ £ £ £ 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.92 0.92 0.92 Components Unit (d) Broadband line testing systems £/line ADSL connections £/conn Combi Card Broadband Access £/line (0.17) ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port (79.19) ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port (21.66) (0.08) (0.08) ATM network interface £/port (7.36) (0.04) (0.04) ATM network switching £/use (0.21) (0.20) (0.20) Inter ATM transmissions £/use (1.00) (0.26) (0.26) 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit (51.97) 0.11 Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 0.82 0.92 SG&A Broadband (q) % Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % £1m (0.07) (0.07) Edge Ethernet ports (q) % £0m 0.25 0.25 Core/Metro connectivity (q) % (£16m) 1.60 1.60 DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % (£4m) 1.93 2.03 (1.01) (0.66) 1.43 1.53 0.26 £ External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 £ Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 £ External WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 £ Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 £ External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 External end user access connections Mkt 2 Effect of changes on results Internal End user access connections Mkt 2 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 2 - 2 to 3 principal operators (0.12) (0.12) (0.13) (0.13) (0.17) (0.17) (0.17) (0.17) (1.07) (1.06) (1.06) (£2m) (0.11) (0.11) (0.21) (0.21) (0.32) (0.32) (0.17) (0.17) (0.10) (0.10) 0.25 0.25 1.18 1.18 EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs (£) (1.17) (1.17) 0.90 Page 107 1.25 (0.47) (0.47) Section 6 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on FAC Section 6.14.1 – Illustrative for Wholesale Broadband Access Market 2 calculation of FAC based on component costs and usage factors (continued) -6% -6% -1% -1% -28% -28% % % % -7% -7% -1% -1% % External WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 % Internal WBC BW - Revenues Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 % External WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 External IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 % Internal WBC end user access-Rentals Mkt 2 Internal IPstream Connect End user access Rentals Mkt 2 % % External IPstream Connect Bandwidth Mkt 2 External end user access connections Mkt 2 Effect of changes on results as a percentage Internal End user access connections Mkt 2 Average cost per unit Wholesale broadband access market 2 - 2 to 3 principal operators % Components Unit (d) Broadband line testing systems £/line ADSL connections £/conn Combi Card Broadband Access £/line -1% ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s £/port -7% 0% 0% ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s £/port -7% -7% -7% ATM network interface £/port -7% -8% -8% ATM network switching £/use -7% -6% -6% Inter ATM transmissions £/use -2% -2% -2% 21CN Backhaul Link & Length £/circuit -1% 3% 3% 3% 3% Core/Metro (broadband) £/circuit 8% 10% 10% 10% 10% SG&A Broadband (q) % -2% -3% -3% -3% -3% Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) (q) % 2% 0% 0% Edge Ethernet ports (q) % 0% 41% 41% 41% 41% Core/Metro connectivity (q) % -25% DSLAM capital/maintenance (q) % -2% EOI Notional Creditors (ap) Fully Allocated Costs % 12% -29% -4% -4% -4% -3% -3% -3% 3% 3% -27% -27% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% -18% -18% 2% 2% 2% 2% -2% -2% 7% 7% (d) ppm = pence per minute; £/2Mbit cct = £ per 2Mbit/s circuit; £/km = £ per kilometre; £/100m = £ per 100 metres; £/trans = £ per transaction; £/circuit = £ per circuit; £/ hostel rental = £ per hostel rental; % = % utilisation; £/line = £ per line; £/room = £ per room; £/cable = £ per cable; £/link = £ per link; £/eq = £ per equipment units; £/le = £ per local end; £/conn = £ per connection; £/channel = £ per channel; £/fibre km = £ per fibre km. (q) This is the total cost not unit cost for this component. (ap) Reduction in FAC due to notional creditor generated by the EOI charge from Openreach to WBA markets. Page 108 Section 7 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement Section 7 Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement Page 109 Section 7 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement Section 7.1 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement 2013 Fully Allocated Cost (£m) As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Total of Average costs operating costs per min/unit on and capital costs a current cost relating to basis relating to current year current year Volume £m Based on 11/12 methodologies Total of Average costs operating costs per min/unit on and capital costs a current cost relating to basis relating to current year current year Volume £ £m 134,312 mm 132,820 mm 0.067p 100 0.063p 93 110,823 mm 200,847 mm 0.039p 48 0.023p 45 133,452 mm 11,764 circuits 0.006p 8 £181.24 2 £ Difference Total of operating costs and capital costs relating to current year Volume £m Average costs per min/unit on a current cost basis relating to current year £ SMP Cost Accounting components Local exchange concentrator 91 Local exchange processor 83 Remote - local transmission link 43 Remote - local transmission length 47 Product management policy & planning 8 Interconnect local end rental 2Mbit/s 2 Interconnect 2Mbit/s connection 1 Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit/s link 2 Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit/s link 2 Interconnect extension circuits (IEC) 2Mbit per km 3 Customer Sited Interconnect cct (CSI) 2Mbit per km 3 In Span Interconnect circuits (ISI) transmission 2 Nominated In Span I/Connect cct (ISI) transmission 1 Intra Building Circuit (IBC) connection 1 Intra Building Circuit (IBC) rental 6 PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km distribution 60 PC rental 2Mbit/s link per km trunk 18 PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km distribution 9 PC rental 34Mbit/s link per km trunk 5 PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km distribution 11 PC rental 140Mbit/s link per km trunk 10 PC rental 622Mbit/s link per km trunk 10 Point of Handover electronics 2 PC rental 64kbit/s link 32 PC rental 2Mbit/s link 22 PC rental 34Mbit/s link 2 PC rental 140Mbit/s link 6 PC rental 64kbit/s link per km transmission 64kbit/s PC link connection cct provision 22 1 2Mbit/s and above PC link connection cct provision 39 PC rental 64kbit/s link local end 23 PC rental 34Mbit/s link local end 9 PC rental 140Mbit/s link local end 8 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end copper 7 PC rental 2Mbit/s local end fibre 106 Wholesale & LAN extension services fibre etc 263 Backhaul extension services fibre etc Wholesale & LAN extension services BNS 14 - 1,322 circuits 11,108 circuits £984.56 2 £196.82 2 11,764 circuits 267,802 km 318,848 km £205.23 2 £9.30 3 £9.31 3 6,069 100m 18,141 100m £291.78 2 2,114 circuits 70,637 circuits 1,809,195 km 1,399,309 km 31,045 km 49,717 km 21,349 km 46,915 km 10,029 km 60 £12.60 18 £273.05 9 £120.97 5 £520.20 11 1,676 eq 187,696 links £1,141.05 2 £168.09 34 130,595 links 1,893 links £174.32 25 £1,246.82 2 £5,803.25 7 £4.02 22 987 links 5,653,602 km 553 circuits 7,251 circuits 58,805 le 2,686 le 1,437 le 26,628 le 162,792 le 102,322 le 12,967 le - circuits 281,159 le 530,231 fibre km SG & A partial private circuits 31 (a) 0 52,152 mm 61,779 mm 44 £33.06 10 61 13 7 10 149 Wholesale Access specific 1 £960.93 Ethernet main links Emergency OA (999) non chargeable 1 £90.10 £200.13 Ethernet Electronics National OA non chargeable £51.97 £319.12 3,587,019 trans £1,999.40 1 £5,409.66 49 £392.94 24 £3,553.49 9 £5,989.94 9 £263.18 7 £650.76 110 £2,564.33 308 134,312 mm 132,820 mm 0.074p (9) 0 mm (0.007p) 0.070p (10) 0 mm (0.007p) 110,823 mm 200,847 mm 0.044p (5) 0 mm (0.005p) 0.022p 2 0 mm 0.001p 133,452 mm 11,764 circuits 0.006p 0 0 mm 0.000p £185.45 0 0 circuits (£4.21) 1,322 circuits 11,108 circuits £1,249.32 (1) 0 circuits (£264.76) £212.83 0 0 circuits (£16.01) 11,764 circuits 267,802 km 318,848 km £221.41 0 0 circuits (£16.18) £9.07 0 0 km £9.08 0 0 km 6,069 100m 18,141 100m £315.41 0 0 100m 0 0 100m 0 0 circuits (£107.05) £91.61 (1) 0 circuits (£1.51) £33.27 0 0 km (£0.21) £12.71 0 0 km (£0.11) £275.01 0 0 km (£1.96) 49,717 km 21,349 km £122.46 0 0 km (£1.49) £518.01 0 0 km 46,915 km 10,029 km £199.67 0 0 km £0.46 £965.15 0 0 km (£4.22) 1,676 eq 187,696 links £1,153.83 0 0 eq (£12.78) £185.35 (2) 0 links (£17.26) 130,595 links 1,893 links £190.25 (3) 0 links (£15.93) £1,315.53 0 0 links (£68.71) £6,168.16 (1) 0 links (£364.91) 1,399,309 km 31,045 km 987 links 5,653,602 km 553 circuits 7,251 circuits 58,805 le 2,686 le 1,437 le 26,628 le 162,792 le 102,322 le 59 circuits 12,967 le £1,094.43 - 0 14 £527.23 157 £113.98 56 (a) 32 (a) 0.000p 0 0.021p 13 52,152 mm 61,779 mm £12.37 10 Page 110 £0.23 (£23.63) £426.17 2,114 circuits 70,637 circuits 1,809,195 km 281,159 le 530,231 fibre km 3,587,019 trans £50.26 £0.23 £3.89 £1.71 £2.19 0 0 km £2,401.81 0 0 circuits (£402.41) £6,811.63 (10) 0 circuits (£1,401.97) £0.13 £407.43 (1) 0 le £3,635.04 0 0 le (£81.55) £6,188.34 (1) 0 le (£198.40) £278.27 (£14.49) 0 0 le £675.01 (4) 0 le (£24.25) £3,013.04 (45) 0 le (£448.71) £1,025.54 £1,093.21 14 (14) 12,908 le (12,967) circuits £559.55 (8) 0 le £104.82 5 0 fibre km (a) 0.000p (1) (a) (£15.09) £68.89 (£1,093.21) (£32.32) £9.16 (a) 0 0 mm 0.000p 0.021p 0 0 mm 0.000p £2.88 34 0 trans £9.49 Section 7 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement Section 7.1 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement 2013 (continued) Fully Allocated Cost (£m) As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Total of Average costs operating costs per min/unit on and capital costs a current cost relating to basis relating to current year current year Volume £m £ Based on 11/12 methodologies Total of Average costs operating costs per min/unit on and capital costs a current cost relating to basis relating to current year current year Volume £m £ Difference Total of operating costs and capital costs relating to current year Volume £m Average costs per min/unit on a current cost basis relating to current year £ SMP Cost Accounting components Routeing & records 13 MDF Hardware jumpering 179 E side copper capital 237 E side copper current 57 D side copper capital 1,304 D side copper current 220 Local exchanges general frames capital 75 Local exchanges general frames current 38 PSTN line test equipment 5 Dropwire capital & PSTN NTE 377 Residential PSTN drop maintenance 102 ISDN2 drop maintenance 2 PSTN line cards 133 ISDN2 line cards 19 Pair gain 0 ISDN2 NTE 5 Broadband line testing systems DSLAM capital/maintenance ADSL connections 88 195 5 Local Loop Unbundling room build 33 Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals 41 Local Loop Unbundling hostel rentals power & vent 71 Local Loop Unbundling tie cables 13 Local Loop Unbundling systems development 32 2,912,052 lines 10,498,323 lines 25,380,248 lines 31,380,432 lines 25,380,248 lines £4.50 15 £17.13 191 £9.36 225 £1.82 63 £51.38 1,192 31,380,432 lines 41,805,541 lines £7.01 214 £1.80 45 44,419,476 lines 25,446,022 lines £0.86 41 £0.20 5 24,997,742 lines 27,600,073 lines £15.10 419 £3.66 110 1,137,834 channels 18,278,817 lines 1,137,834 channels £2.01 3 £7.31 145 £17.46 22 18,278,817 eq 1,137,834 channels £0.00 0 £3.77 5 35,053,425 lines (a) £2.50 78 (a) 199 £2.66 6 £16,133.42 30 £2,859.57 37 £4,884.75 74 £39.91 13 (a) 10 1,724,885 conns 2,028 rooms 14,338 hostels 14,338 hostels 348,940 cables (a) 2,912,052 lines 10,359,521 lines 25,442,012 lines 31,380,432 lines 25,442,012 lines £5.08 (2) 0 lines (£0.58) £18.41 (12) 138,802 lines (£1.28) £8.83 12 (61,764) lines £0.53 £2.02 (6) 0 lines (£0.20) £4.52 112 (61,764) lines 31,380,432 lines 41,805,541 lines £6.83 6 0 lines £1.08 30 0 lines £0.72 41,436,233 lines 25,446,022 lines £1.00 (3) 2,983,243 lines (£0.14) £0.18 0 0 lines £0.02 24,997,742 lines 24,428,825 lines £16.77 (42) 0 lines (£1.67) (8) 3,171,248 lines (£0.86) 1,137,834 channels 18,278,817 lines 1,137,834 channels £46.86 £4.52 £2.25 (1) £7.99 (12) £19.04 (3) 18,278,817 eq 1,137,834 channels £0.00 0 0 eq £4.31 0 0 channels 35,053,425 lines (a) £2.24 10 1,724,885 conns 2,028 rooms 14,338 hostels 14,338 hostels 348,940 cables (a) £0.18 0 channels (£0.24) 0 lines (£0.68) 0 channels (£1.58) 0 lines £0.26 (a) (4) £3.73 (1) 0 conns (£1.07) £1,410.62 £14,722.80 (a) £0.00 (£0.54) (a) 3 0 rooms £2,578.43 4 0 hostels £281.14 £5,176.83 (3) 0 hostels (£292.08) £38.98 0 (a) 22 (a) 0 cables £0.93 (a) 37 (a) (a) 37 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) Service Centres - Provision 112 (a) (a) 118 (a) (a) (6) (a) (a) Sales product management 17 (a) (a) 18 (a) (a) (1) (a) (a) Service Centres - Assurance 29 (a) (a) 37 (a) (a) (8) (a) £0.24 3 £19.91 155 £0.00 0 0.001p 3 Directories Combi Card voice 3 Combi Card Broadband Access 153 Access Cards (ISDN2 services) 0 Core/Metro (voice) 3 Border gateway & signalling firewall MSAN-POSI Voice Link Access Cards (other services) MSAN-METRO Connectivity Link Core/Metro connectivity Edge Ethernet ports 18,278,817 lines 7,722,603 lines 1,137,834 channels 236,996 mm 18,278,817 lines 7,722,603 lines 1,137,834 channels 236,996 mm (a) £0.24 0 0 lines £0.00 £20.08 (2) 0 lines £0.00 0 0 channels 0.001p 0 0 mm 0.000p 0 mm 0.000p 0 mm 0.000p (£0.17) £0.00 0 141,900 mm 136,980 mm 0.000p 0 141,900 mm 136,980 mm 25 (a) (a) 28 (a) (a) (3) (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) 7 (a) (a) (7) (a) (a) 47 (a) (a) 63 (a) (a) (16) (a) (a) 9 (a) (a) 9 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) 0 iNode (call set up and features) 17 ATM customer interface 2Mbit/s 0 ATM customer interface 34Mbit/s 1 ATM customer interface > 155Mbit/s 4 ATM network interface 2 ATM network switching 12 (a) 0.000p 0 (a) 16 2,118 ports 803 ports £92.26 0 £982.59 1 13,914 ports £286.23 4 £98.13 2 £3.01 13 20,494 ports 4,130,538 usage Page 111 0.000p 0.000p 0 0 (a) (a) 2,118 ports 803 ports (a) 1 £99.20 0 0 ports (£6.94) £1,061.78 0 0 ports (£79.19) 13,914 ports £307.89 0 0 ports (£21.66) £105.49 0 0 ports (£7.36) (1) 0 usage (£0.21) 20,494 ports 4,130,538 usage £3.22 (a) Section 7 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement Section 7.1 – Illustrative difference of methodology changes on Network Activity Statement 2013 (continued) Fully Allocated Cost (£m) As reported for the year ended 31 March 2013 Total of Average costs operating costs per min/unit on and capital costs a current cost relating to basis relating to current year current year Volume £m Based on 11/12 methodologies Total of Average costs operating costs per min/unit on and capital costs a current cost relating to basis relating to current year current year Volume £ £m £ £42.88 45 1,015,272 usage (a) 51 £7,423.01 83 Difference Total of operating costs and capital costs relating to current year Volume £m Average costs per min/unit on a current cost basis relating to current year £ SMP Cost Accounting components Inter ATM transmissions 44 Broadband backhaul circuits (excl Virtual Paths) 52 21CN Backhaul Link & Length 82 1,015,272 usage (a) £43.88 121 £10.78 112 £9.96 9 20 (a) (a) 20 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) High Tisbo Equipment Depn 2 (a) (a) 2 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) Very High Tisbo Equipment Depn 0 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) Low Tisbo Excess Construction 10 (a) (a) 10 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) AISBO Excess Construction 19 (a) (a) 19 (a) (a) 0 (a) (a) 92 (a) (a) 94 (a) (a) (2) (a) (a) 5 (a) (a) 6 (a) (a) (1) (a) (a) SG&A Broadband SG&A Interconnect Main exchange switching (n) ISDN30 connections (n) ISDN30 access (n) ISDN30 line cards (n) (n) Access Cards (ISDN30 services) SMP Accounting Separation components Residual components Roundings Total (1) 128 n/a n/a 134 n/a n/a 1,691 n/a n/a 1,682 n/a n/a 9 3 n/a n/a 7 n/a n/a (4) 7,256 7,254 (a) This component is attributed on a % basis so no volume or unit cost is derivable. (n) Accounting Separation components require no costs to be disclosed. Page 112 (6) 2 (a) (£1.00) Low Tisbo Equipment Depn £7,474.98 1 0 usage (a) 11,094 circuits 11,272,969 circuits Core/Metro (broadband) (a) (1) 11,094 circuits 11,272,969 circuits (a) 0 circuits (£51.97) 0 circuits £0.82