Lesson Plan
advertisement

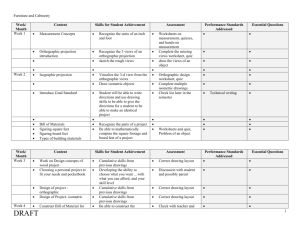
Lesson Plan Course Title: Engineering Design and Presentation Session Title: Introduction to Orthographic Projection or Multiview Drawings Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson/assignment, the student will be able to create a TV box; and, then draw the multiview or three views of the TV box given, and complete the title block and border correctly to match the example given. Specific Objectives: Explain why every object has 6 views Identify the 6 views drawn Explain why we only draw 3 views, and identify what those views are Select and explain why a view should be the front view Explain why we use hidden lines and why they need to be consistent Compare and contrast the difference, if any, between multiview projection and drawings Explain why multiviews need to be dimensioned correctly Explain why views need to line up correctly Cut out, tape, and create a TV Box to use when you draw the views Correctly draw and dimension the multiview of the TV Box Preparation TEKS Correlations: This lesson, as published, correlates to the following TEKS. Any changes/alterations to the activities may result in the elimination of any or all of the TEKS listed. Engineering Design and Presentation: 130.365 (c)(1)(E) ...identify and use appropriate work habits; 130.365 (c)(3)(A)(B) ...use time-management techniques to develop and maintain work schedules and meet deadlines; ...complete work according to established criteria; 130.365 (c)(4)(B)(E)(F)(G) ...follow safety guidelines as described in various manuals, instructions, and regulations; ...perform maintenance on selected tools, equipment, and machines; ...handle and store tools and materials correctly; ...describe the results of negligent or improper maintenance. 130.365 (c)(5)(A)(E) ...sketch single- and multi-view projections; ...project points and construct lines to build geometric forms; Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 1 130.365 (c)(6)(A)(B) ...understand and discuss principles of ideation; ...think critically, identify the system constraints, and make fact-based decisions; Interdisciplinary Correlations: English: 110.44 (b)(6)(B)(C)(E) ...rely on context to determine meanings of words and phrases such as figurative language, connotation and denotation of words, analogies, idioms, and technical vocabulary; ...apply meanings of prefixes, roots, and suffixes in order to comprehend; ...use reference material such as glossary, dictionary, thesaurus, and available technology to determine precise meanings and usage; Geometry: 111.34 (b)(4) ...select an appropriate representation (concrete, pictorial, graphical, verbal, or symbolic) in order to solve problems; 111.34 (b)(5)(A)(B)(C)(D) ...use numeric and geometric patterns to develop algebraic expressions representing geometric properties; ...use numeric and geometric patterns to make generalizations about geometric properties, including properties of polygons, ratios in similar figures and solids, and angle relationships in polygons and circles; ...use properties of transformations and their compositions to make connections between mathematics and the real world, such as tessellations; ...identify and apply patterns from right triangles to solve meaningful problems, including special right triangles (45-45-90 and 30-60-90) and triangles whose sides are Pythagorean triples; 111.34 (b)(6)(C) ...use orthographic and isometric views of three-dimensional geometric figures to represent and construct three-dimensional geometric figures and solve problems; 111.34 (b)(11)(A) ...use and extend similarity properties and transformations to explore and justify conjectures about geometric figures; Mathematical Models with Applications: 111.36 (c)(1)(A)(B)(C) …compare and analyze various models for solving a real-life problem; …use multiple approaches (algebraic, graphical, and geometric methods) to solve problems from a variety of disciplines; …select a method to solve a problem, defend the method, and justify the Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 2 reasonableness of the results. Teacher Preparation: Read through the PowerPoint provided and practice drawing the problem. Draw this for the students on an overhead or use a device like an elmo and show it on data projector screen. References: Texas approved publishers are: Goodheart-Willcox Delmar Learning Prentice Hall All have a companion workbook with more problems. Recommend using it or any other approved textbook, i.e., if you are ATC or TechPrep and must teach using local college textbook. Also “Google” and you can find tons of information on these subjects! Instructional Aids: 1. Introduction to multiview PowerPoint 2. TV box paper 3. Multiview graph paper Materials Needed: 1. One (1) sheet of TV box paper for each student 2. Scissors and clear tape for students to share -1 for every 2-3 students 3. One (1) sheet of multiview graph paper for each student 4. One (1) pencil, eraser, and triangle for each student 5. Handout – Review Questions Equipment Needed: 1. Data projector for PowerPoint 2. Class set of hard copy of PowerPoint presentation for students to use 3. Overhead projector, transparency of multiview graph paper, and overhead pen(s) OR an elmo like device to demonstrate how to draw the problem Learner Preparation: 1. Complete the drafting facts unit 2. Complete geometric construction unit 3. Complete drafting scales and dimensioning unit Introduction Introduction (LSI Quadrant I): SAY: Today we will begin our unit on how to draw orthographic projection, or multiview drawings. ASK: Does anyone remember how many sides every object has? (6) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 3 ASK: Who can tell me the 3 views we draw and name them? (Top, Front, Right Side) ASK: Why don’t we draw all 6 of the views? Because it’s redundant since the back is just the mirror image of the front, usually. ASK: Why do we only draw these 3 views? Refer to PowerPoint. ASK: Why do we draw hidden lines? Refer to PowerPoint. ASK: What is the difference between orthographic projection and multiview drawings? Refer to PowerPoint. SHOW: Example of correct layout. ASK: What letter of the alphabet does this layout look like? (L) ASK: Why do we use pencils and not pens? (So you can erase mistakes) ASK: Why do we use triangles and not a ruler or scale? (Because rulers will leave bumps or ridges that are on them, instead of straight and smooth line.) ASK: Why do you draw lightly first and darken last? (Because it’s easier to erase mistakes and when done make your final dark lines.) ASK and SHOW: Can you draw on the graph paper? (Yes) SAY and SHOW: Let’s draw the 3 views of the TV box. Get your box and look at the views and follow along as I show how to draw it. (Refer to PowerPoint.) ASK: Why is the border the darkest line? (Because it’s like the picture frame, it makes the drawing pop out and show like it’s supposed to.) ASK: Why do we use the rubric to self assess our work? (In the real world you need to be able to look at your work and decide if you’re doing a good job or not. If you don’t self adjust as needed you can be out of a job soon.) SAY: Let’s get to work. It’s time for you to draw your own now. Outline Outline (LSI Quadrant II): Instructors can use the PowerPoint presentation, slides, handouts, and note pages in conjunction with the following outline. MI Outline Notes to Instructor I. Cut out, tape, and create a TV Box to use when you Make sure you have enough scissors and draw the views. tape. Teacher can enlarge and make a bigger one to use as class example. . II. Explain why every object has 6 views. Refer to previous lessons as they should know this by now. Again show examples of objects and their 6 views. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 4 III. Identify the 6 views drawn. A. Top B. Front C. Right Side D. Bottom E. Back F. Left Side Be able to list what these are and what the opposite view is. For example Front and Back. IV. Explain why we only draw 3 views and identify what those are. A. Top B. Front C. Right Side Explain why you only draw the 3 views - top, front, and right side. V. Select and explain why a view should be the front view. Use the example of a car. Is the view where the head lights are the front view? No, because it doesn’t have the most information. The side with the door, windshields, etc… is the front view. Hidden lines are to show parts that are cut out, recessed, holes, etc. VI. Explain why we use hidden lines and why they need to be consistent. VII. Compare and contrast the difference if any between orthographic projection and drawings. VIII. Explain why views need to line up correctly. Lines must be consistent so it doesn’t look like a mistake and people can tell it’s a hidden line. Projection is simply how you line up the views and project the parts of it. The multivew drawing is what you get from the projection. They have to line up in the “L” shape. If they line up with projection it’s easier to Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 5 draw and the sizes will be uniform. IX. Explain why multiviews need to be dimensioned correctly. The point of dimensions is so you can take and have it made. Without dimensions it won’t be made correctly. X. Correctly draw and dimension the mutliview of the TV Box. Show students an example and how to draw it. Then have them actually draw it. You can use a TV because it’s a concrete object that students are all familiar with. Copy and paste Multiple Intelligences Graphic in appropriate place in left column. Verbal Linguistic Logical Mathematical Visual Spatial Musical Rhythmic Bodily Kinesthetic Intrapersonal Interpersonal Naturalist Existentialist Application Guided Practice (LSI Quadrant III): The teacher must explain the PowerPoint as they go through the lesson. Do NOT just read it or let students read it. Explain and give personal examples as they go. When students start the drawing make sure to monitor to ensure they are doing the work. Independent Practice (LSI Quadrant III): Make their own TV box and then actually draw the 3 views on the graph paper using the box as a visual aid. Summary Review (LSI Quadrants I and IV): Q: How many sides does every object have? Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 6 A: 6 Q: What 3 views do we only draw? A: Top, front, right side Q: Why do we only draw those 3? A: Because the other views are redundant since front and back are mirror images. Q: What letter should the correct layout of the views look like? A: L Q: Why do we only use pencils and not a pen? A: So you can erase Q: Why only use a triangle and not a ruler or scale to draw straight lines? A: Because it leaves bumps Q: Why do we have hidden lines? A: To show holes, parts, etc. Q: Why do we draw lines lightly and go back and darken them? A: Once done, then you darken the finished problem Q: Why do you dimension the drawing? A: So it can be built correctly Q: Why is the border the darkest lines? A: Because it makes the finished drawing stand out. Evaluation Informal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III): Teacher walks around the room and monitors students as they work on the drawings. Correct or redirect mistakes before they get too bad. If they do get too bad, give them a new piece of paper and have them try again. Formal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III, IV): Does your drawing match the example given? Use the built in rubric and have students grade themselves first. If you have to have every drawing equal 100 pts then take the points earned and multiply by 4. Recommend students do 4 drawings at 25 points each which adds up to 100. 2-3 days’ work equals 1 grade in grade book. Extension Extension/Enrichment (LSI Quadrant IV): There is a TAKS based drawing that has students draw the multiview if they have extra time, or as a pop quiz the following day. If you refer to the released TAKS test you can find even more TAKS based questions that fit in here. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 7 Introduction to Orthographic Projection or Multiview Drawings Review Questions 1. How many sides does every object have? 2. What 3 views do we only draw? 3. Why do we only draw those 3? 4. What letter should the correct layout of the views look like? 5. Why do we only use pencils and not a pen? 6. Why only use a triangle and not a ruler or scale to draw straight lines? 7. Why do we have hidden lines? 8. Why do we draw lines lightly and go back and darken them? 9. Why do you dimension the drawing? 10. Why is the border the darkest lines? Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 8 Introduction to Orthographic Projection or Multiview Drawings Review Questions and Answers 1. How many sides does every object have? Answer: 6 2. What 3 views do we only draw? Answer: Top, front, right side 3. Why do we only draw those 3? Answer: Because the other views are redundant since front and back are mirror images. 4. What letter should the correct layout of the views look like? Answer: L 5. Why do we only use pencils and not a pen? Answer: So you can erase 6. Why only use a triangle and not a ruler or scale to draw straight lines? Answer: Because it leaves bumps 7. Why do we have hidden lines? Answer: To show holes, parts, etc. 8. Why do we draw lines lightly and go back and darken them? Answer: Once done, then you darken the finished problem 9. Why do you dimension the drawing? Answer: So it can be built correctly 10. Why is the border the darkest lines? Answer: Because it makes the finished drawing stand out. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 9 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 10 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 11 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved.