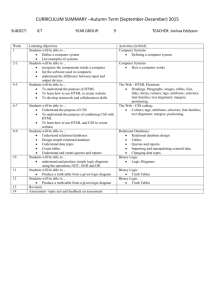
Lecture 5
advertisement

Lecture 5
●
Log into Linux client or into csserver directly
●
Webspace (www_home) should be set up
●
●
●
●
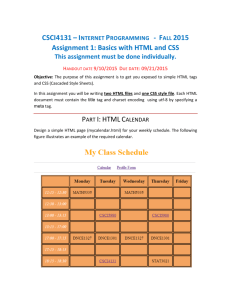
Create subdirectory cs350/pizza in webspace
and change to it
cp ~hwang/cs350/lecture06/*.* .
Load pizza­v1.html and pizza­v1.css into a
text editor
Browse to
http://csserver.evansville.edu/~username/cs350/pizza­
v1.html
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
1
Outline
●
●
HTML5
–
HTML
–
CSS
–
JavaScript - next class
References: HW3S, HNTU, CSW3
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
2
HTML5
●
●
HTML5 is the current proposed standardization
of basic web technology
Integrates previous technologies and defines
clean distinction of roles
–
–
–
●
H(yper)T(ext) M(arkup) L(anguage): structural
semantics
C(ascading) S(tyle) S(heets): presentation
JavaScript: dynamic behavior
Interactions are done by manipulating the
styling of document structures
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
3
HTML
●
●
The HTML portion basically is the union of
HTML4 and XHTML, so syntax is fairly lax.
Most of the deprecated tags and attributes are
related to presentation now handled by CSS.
The HTML5 standard for HTML is mostly
supported by most major browsers (Firefox,
Chrome, IE10, Opera, Safari).
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
4
HTML Tags
●
●
Most tags are pairs, <tag>...</tag>, and
must be properly nested, but some are selfclosing, <tag />
Tags can have attributes that provide
information. E.g. the URL for a link.
<a href="URL">A link to URL</a>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
5
HTML Document
●
All documents have following format
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!­­ This is a comment ­­> <!­­ Meta­data ­­>
</head>
<body>
<!­­ Content ­­>
</body>
</html>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
6
HTML Meta-Data Tags
●
The meta-data includes
<title></title>
<link rel="..." type="..." href="..." />
–
E.g. favicon symbol, square image in browser heading and
tabs, see HICO reference for details
<link rel="icon" type="image/png" href="pizza­icon.png" />
<style></style>
<script></script>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
7
HTML Body Tags
●
HTML5 introduced new structural elements to
better identify document contents, especially for
accessibility software.
<header>, <footer>, <nav>, <section>,
<label>, ...
●
Removed presentation elements
<font>, <center>, <tt>, ...
●
Removed presentation attributes
align, background, cellpadding, ...
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
8
HTML Body Tags
●
●
See reference HTRF for complete list
Here are some common tags that are used to
structure document content.
<h1></h1> for major headings
<h2></h2> to <h6></h6> for subheadings
<p></p> for paragraphs
<ul></ul> for unordered (bulleted) lists
<ol></ol> for ordered (numbered) lists
<li></li> for list items
<img src="..." /> for images
<a href="..."></a> for links
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
9
HTML Body Tags
●
Here are some tags for grouping items:
<div></div> for structural grouping
<span></span> mostly used for style grouping
<table></table> for tables
<tr></tr> for table rows
<th></th> for table headings
<td></td> for table data
●
Use <table> only for actual tables, not for
organizing content into presentation order.
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
10
HTML Body Tags
●
Here are a few leftover mostly presentation
tags:
<strong></strong> usually bold text
<em></em> usually italic text
<br /> for newlines
<hr /> for horizontal rule (line)
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
11
HTML Forms
●
Syntax is the same
<form action="URL" method="post">
<!­­ form elements can only appear in a form ­­>
</form>
where URL is the location of the CGI script to
run when the form is submitted. (More on CGI
next class.)
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
12
Form Elements: Input
●
<input /> has a type attribute
–
One line of text input
<input type="text" name="name" size="65" />
–
Submit button
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
●
name is associated with the input value
●
value is text label for button type inputs
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
13
Form Elements: Input
●
New HTML5 <input> types that restrict format
of text input
email, url, tel, time, number, ...
●
New HTML5 <input> attributes
required, autofocus, placeholder, pattern, ...
–
E.g. email input
<input type="email" name="email" placeholder="user@domain.com">
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
14
Form Elements:
Radio Buttons, Check Boxes
●
Radio buttons
<input type="radio" name="size"
value="Small" />Small
<input type="radio" name="size"
value="Large" checked="checked"
/>Large
●
Check boxes
<input type="checkbox name="toppings[]" value="Pepperoni"
/>Pepperoni
●
name attribute ties the elements together
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
15
Form Elements: Select Boxes
●
Pull-down menu
<select name="size">
<option value="Large"
selected="selected">Large</option>
</select>
●
Multi-selection
<select name="toppings[]"
multiple="multiple">
<!­­ options the same as above ­­>
</select>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
16
Form Elements: Textarea
●
<textarea> element is used to process multiline text input:
<textarea cols="80" rows="3"
name="address">
<!­­ Default value ­­>
</textarea>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
17
CSS Rules: Elements
●
CSS rule is a collection of property values with
syntax:
property: value1 value2 ...;
●
Element rule - applied to all instances of <tag>
<h1> {
margin: 0px;
padding: 5px;
color: orange;
background­color: purple
}
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
18
CSS Rules: Classes
●
Class rule - names a type of styling. May be
applied to multiple tags on a page. Starts with
'.'
.alert {
color: red;
}
●
Applied using class attribute
<h1 class="alert">IN AN EMERGENCY</h1>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
19
CSS Rules: Ids
●
Id rule - names a unique styling. May be
applied only to one tag on a page. Starts with
'#'
#wrapper {
position: relative;
background­color: #FDF5E6;
} ●
Applied using id attribute
<div id="wrapper">...</div>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
20
CSS Stylesheets
●
●
Global CSS rules (e.g. for an entire website)
are stored in stylesheet files with extension
.css
They are associated with a webpage using the
<link> tag in the <head> section.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="pizza­v1.css">
where href gives URL of the stylesheet file.
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
21
Style Tag & Style Attribute
●
CSS rules local to a single page are declared
using the <style> tag in the <head> section.
<style>
.intro { font­style: italic; }
</style>
●
CSS rules local to an individual element are
declared using the style attribute in the tag.
<span style="color: red; font­style: italic;">...</span>
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
22
CSS Cascading
●
●
●
Most (but not all) styling cascades from outer
(parent) elements to inner (child) elements
unless overridden by child element styling.
Styling rules cascade from global stylesheet to
<style> tag in <head> section to style
attribute of an individual tag. Closest styling
applies.
Also cascades from tags to classes to ids.
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
23
CSS Properties
●
●
See reference CSRF for complete list
Styling properties for spacing
margin: w x y z for space between elements
padding: w x y z for space around contents
within an element
–
–
–
values are for top, right, bottom, left, or use margin­top,
padding­right, etc.
values in length units px (pixels), pt (points), cm, in, etc., or
% percentage of enclosing element
values may be negative
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
24
CSS Properties
●
Styling properties for appearance
border: width style color
–
–
–
default width is medium, also thin, thick, length units
default style is none, also dotted, dashed, solid,
double
default color is element color, can be any defined HTML
color name, hexidecimal RGB code, or rgb(red,green,blue)
with decimal arguments
color for foreground (text) color
background for setting background properties
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
25
CSS Properties
●
Text and font properties
text­align for horizontal alignment. Default is left for most
browsers. Also right, center, justify
font­family for font family for text. Can be family name like
"Times New Roman" or generic name like sans­serif
font­size for size of font. Default is medium. Also small,
large, etc., or fixed length units, or % of parent font size
font­style for style of font. Default is normal. Also
italic, oblique
font­weight for weight of font. Default is normal. Also
bold, bolder, lighter
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
26
CSS Properties
●
Other common styling properties:
display for controlling layout
–
Default depends on element. E.g. <span> is inline, <p>
is block
float for arranging elements relative to each other
–
Default is none, element is rendered as placed in the text.
Also left, right. Usually used with <div>.
clear for making elements start after floating elements
–
Default is none, elements may float on both sides. Also
left, right, both
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
27
In-class Exercise
●
●
Experiment with adding content to the PPP
webpage. E.g., add more size or topping
choices, or other information fields to the order
form.
Experiment with changing different properties,
adding new CSS classes and ids.
September 11, 2014
CS 350 - Computer/Human Interaction
28




![[#PFR-664] [ACCESS] Using em, percent, named for font sizes and](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008524257_1-e1b711369b412e0cc1e52963d3e370f9-300x300.png)
