Civil Law
advertisement

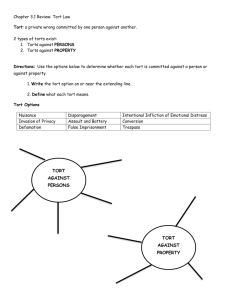
Civil Law Course Security Services Unit V Legal Issues Essential Question What is the difference between civil and criminal law? How does civil law affect security? TEKS §130.298(c) (3)(A)(B) Prior Student Learning The U.S. Constitution and Constitutional Issues Estimated Time 3 to 4 hours Rationale Responsibility is one of the key factors that affect the duties of security professionals. Not only do these professionals have to be aware of the safety of themselves and their clients, they also have a responsibility for the manner in which that they fulfill their security role. Objectives The student will be able to: 1. Differentiate between civil and criminal law. 2. Analyze the impact of legal issues relevant to security services. 3. Analyze specific federal, state, and local laws and regulations affecting government security operations. 4. Summarize specific juvenile laws affecting security operations. Engage Use the following questions for a class discussion. Use the Discussion Rubric for assessment. What constitutes a false arrest? Under what circumstances may a business detain a suspected shoplifter? When can a security officer detain an individual for arrest? If a security officer uses excessive force in detaining or arresting an individual, what offense has he or she committed? Key Points I. Key Terms A. Civil Liability – potential responsibility for payment of damages or other court-enforcement in a lawsuit, as distinguished from criminal liability which means “open to punishment for a crime” B. Tort – a civil wrong for which a private party may sue the tort feasor for restitution C. Tort Feasor – an individual who commits a tort D. Duty – the obligation not to injure another person or damage another person’s property E. Wrongful Death – a civil court action in which it is alleged that the tort feasor, by his or her actions, caused the death of a person F. Intentional torts – willful acts, even those acts that a person honestly believed he or she could lawfully commit G. Negligence Torts – require a violation of a standard of care, or the breech of a duty, proximate cause, foreseeability, and damages or injuries H. Strict Liability – liability without fault that normally does not involve security professionals I. Probable Cause – apparent facts discovered through logical inquiry that would lead a reasonably intelligent and prudent person to believe that an accused person has committed a crime, thereby warranting 1 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. his or her prosecution, or that a Cause of Action has accrued, justifying a civil lawsuit Malicious Prosecution – an action for damages brought by one against whom a civil suit or criminal proceeding has been unsuccessfully commenced without Probable Cause and for a purpose other than that of bringing the alleged offender to justice Invasion of Privacy – intrusion into the personal life of another, without just cause, which can give the person whose privacy has been invaded the right to bring a lawsuit for damages against the person or entity that intruded Assault – refers to intentionally causing fear, or imminent, harmful, or offensive touching, but without touching or physical contact Battery – intentionally harmful or otherwise offensive touching of another person. The touching does not have to be direct physical contact but may instead be through an instrument such as a cane or rock Defamation – injuring the reputation of another by publicly making untrue statements. Slander is oral defamation, while libel is defamation through written words False imprisonment – a restraint of a person in a bounded area without justification or consent. False imprisonment is a common-law felony and a tort. It applies to private as well as governmental detention Trespass – the unauthorized physical invasion of property, or remaining on the property after permission has been rescinded Intentional infliction of emotional distress (IIED) – a tort claim of recent origin for intentional conduct that results in extreme emotional distress. Some courts and commentators have substituted mental for emotional, but the tort is the same. Some jurisdictions refer to IIED as the tort of outrage II. Probable Cause A. Apparent facts B. Discovered through logical inquiry C. Would lead a reasonably intelligent and prudent person to believe that an accused person has committed a crime D. Warranting prosecution, or that a Cause of Action has accrued E. Justifying a civil lawsuit III. Criminal Law A. Crimes are generally offenses against the state B. Cases are prosecuted by the state C. The prosecutor files the case in court as a representative of the state D. Criminal cases have jail time as a potential punishment E. Crimes must generally be proven "beyond a reasonable doubt" F. Criminal cases almost always allow for a trial by jury G. A defendant in a criminal case is entitled to an attorney, and if he or she can't afford one, the state must provide an attorney H. The protections afforded to defendants under criminal law are considerable (i.e. The Bill of Rights Amendments) 2 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. IV. Civil Law A. Civil cases are typically disputes between individuals regarding the legal duties and responsibilities they owe one another B. In civil cases, the wronged party files the case C. Civil cases generally only result in monetary damages D. Civil cases are proved by lower standards of proof such as "the preponderance of the evidence" E. Many civil cases will be decided by a judge F. A defendant in a civil case is not given an attorney and must pay for one, or else defend himself or herself V. Categories of Civil Liability A. Intentional Tort 1. The defendant, or tort feasor, committed an intentional act 2. The act was wrong 3. The plaintiff suffered injuries or damages B. Negligence Tort 1. Existence of a duty 2. Foreseeability of the likelihood of the injury occurring 3. Failure to meet a reasonable standard of care 4. Proximate results of the injury 5. Injury or damages C. Strict Liability 1. Held liable without the need to prove an intentional act or negligence 2. High standard of care 3. Dangerous activity VI. Civil Liability Examples A. Assault (Texas Penal Code Section 22.01) 1. Intentionally causes fear of imminently harmful or offensive touching 2. Without touching or physical contact B. Battery (Texas Penal Code Section 22.01) 1. Intentionally harmful 2. Offensive touching 3. Of another person 4. Touching does not have to be direct physical contact 5. May be through an instrument such as a cane or rock C. Trespass (Texas Penal Code Section 30.05) 1. Unauthorized physical invasion of property 2. Remaining on the property after permission has been rescinded D. False Imprisonment and Kidnapping (Texas Code of Criminal Procedures Article 13.12) 1. Restraint of a person 2. In a bounded area 3. Without justification 4. Without consent E. Invasion of Privacy (Texas Civil Practices and Remedies Code Section 15.017) 1. Intrusion into the personal life of another 3 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 2. Without just cause 3. Gives the person whose privacy has been invaded the right to bring a lawsuit 4. Damages against the person or entity that intruded F. Malicious Prosecution (Texas Civil Practices and Remedies Code Section 16.002) 1. An action for damages 2. Brought by one against whom a civil suit or criminal proceeding has been unsuccessfully commenced 3. Without probable cause 4. Purpose other than that of bringing the alleged offender to justice 5. Institution of original judicial proceedings by or at the encouragement of the defendant 6. Termination in the plaintiff’s favor 7. Malice 8. Lack of probable cause 9. Damage G. Defamation (Texas Civil Practices and Remedies Code Section 73.001) 1. Injuring the reputation of another 2. Publicly making untrue statements 3. Slander is oral defamation 4. Libel is defamation through written words H. Intentional infliction of emotional distress (IIED) [Civil Tort Claim] 1. Intentional conduct 2. Results in extreme emotional distress 3. Some courts and commentators have substituted mental for emotional 4. Some jurisdictions refer to IIED as the tort of outrage Activities 1. Have the class work in small groups to brainstorm and develop guidelines or procedures as to when a security officer may detain a customer on the grounds of shoplifting, illegal skateboarding, trespassing, etc. Afterwards, have the groups present and discuss their guidelines and/or procedures. Make sure to inform the students of situations where security observed the incident occurring vs. not observing the incident occurring. Also, alert students to issues that involve when a security officer can or cannot detain a customer, which connects with observing and not observing the incident. Use the Presentation Rubric and/or the Discussion Rubric as needed for assessment. 2. Have students role play incidents (based on Activity 1). Have several students act out a situation in which a “customer” commits an illegal activity on private property or in a store (example – shoplifting, skateboarding, trespassing), and have other students act as security officers. Afterward discuss the incidents as a class. Use the Role Play Rubric and/or the Discussion Rubric as needed for assessment. 3. Have the class complete the Legal Issues: Civil Law Crossword Puzzle to 4 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. become familiar with the key terms from this unit. Use the Civil Law Crossword Puzzle Key for assessment. Assessments Civil Law in Security Services Exam and Key Discussion Rubric Individual Work Rubric Presentation Rubric Research Rubric Role Play Rubric Materials Civil Law in Security Services computer-based presentation Civil Law in Security Services Key Terms Civil Law Crossword Puzzle Civil Law Crossword Puzzle Key Civil Law Venn Diagram handout Civil Law Venn Diagram with possible answers White board/chalk board Resources Texas Commission on Private Security http://www.txdps.state.tx.us/psb Introduction to Private Security: Theory Meets Practice, Cliff Roberson & Michael L. Birzer Introduction to Security (6th Edition), Robert J. Fischer & Gion Green Investigator/Officer’s Personal Experience The Texas Criminal Code of Procedure http://www.statutes.legis.state.tx.us/ Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, the students will create a Venn Diagram illustrating the similarities and differences between civil and criminal law using the Civil Law Venn Diagram handout. Use the Civil Law Venn Diagram with possible answers and the Individual Work Rubric for assessment. For enrichment, the students will write a research paper about specific cases regarding civil law and civil rights violations. The following website may be used to spark research. Use the Research Rubric for assessment. http://library.thinkquest.org/11572/cc/ State Education Standards Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Career and Technical Education §130.298. Security Services (One to Two Credits). (3) The student analyzes the impact of ethical and legal responsibilities relevant to security services. The student is expected to: (A) differentiate between civil and criminal law; (B) analyze the impact of legal issues relevant to security services; College and Career Readiness Standards Cross-Disciplinary Standards 5 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. I. Key Cognitive Skills C. Problem solving 1. Analyze a situation to identify a problem to be solved. 2. Develop and apply multiple strategies to solve a problem. 6 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Civil Law in Security Services Key Terms Civil Liability – potential responsibility for payment of damages or other court-enforcement in a lawsuit, as distinguished from criminal liability, which means “open to punishment for a crime” Tort – a civil wrong for which a private party may sue the tort feasor for restitution Tort Feasor – an individual who commits a tort Duty – the obligation not to injure another person or damage another person’s property Wrongful Death – a civil court action in which it is alleged that the tort feasor, by his or her actions, caused the death of a person Intentional torts – willful acts, even those acts that a person honestly believed that he or she could lawfully commit Negligence Torts – require a violation of a standard of care, or the breech of a duty, proximate cause, foreseeability, and damages or injuries Strict Liability – refers to liability without fault and normally does not involve security professionals Probable Cause – apparent facts discovered through logical inquiry that would lead a reasonably intelligent and prudent person to believe that an accused person has committed a crime, thereby warranting his or her prosecution, or that a Cause of Action has accrued, justifying a civil lawsuit Malicious Prosecution – an action for damages brought by one against whom a civil suit or criminal proceeding has been unsuccessfully commenced without probable cause, and for a purpose other than that of bringing the alleged offender to justice Invasion of Privacy – intrusion into the personal life of another, without just cause, which can give the person whose privacy has been invaded the right to bring a lawsuit for damages against the person or entity that intruded Assault –intentionally causing fear or imminent, harmful, or offensive touching, but without touching or physical contact Battery – intentionally harmful or otherwise offensive touching of another person. The touching does not have to be direct physical contact but may instead be through an instrument such as a cane or rock Defamation – injuring the reputation of another by publicly making untrue statements. Slander is oral defamation, while libel is defamation through written words False imprisonment – restraint of a person in a bounded area without justification or consent. False imprisonment is a common-law felony and a tort. It applies to private as well as governmental detention Trespass – the unauthorized physical invasion of property, or remaining on the property after permission has been rescinded Intentional infliction of emotional distress (IIED) – tort claim of recent origin for intentional conduct that results in extreme emotional distress. Some courts and commentators have substituted mental for emotional, but the tort is the same. Some jurisdictions refer to IIED as the tort of outrage 7 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name:_________________________ Date:______________________ Civil Law in Security Services Exam Answer the following multiple choice questions. 1. _____ The obligation not to injure another person or damage another person’s property. a. Civil Liability b. Strict Liability c. Duty d. Malicious Prosecution 2. _____ Potential responsibility for payment of damages or other court-enforcement in a lawsuit, as distinguished from criminal liability, which means “open to punishment for a crime.” a. Civil Liability b. Strict Liability c. Duty d. Malicious Prosecution 3. _____ An action for damages brought by one against whom a civil suit or criminal proceeding has been unsuccessfully commenced without Probable Cause and for a purpose other than that of bringing the alleged offender to justice. a. Civil Liability b. Strict Liability c. Duty d. Malicious Prosecution 4. _____ Liability without fault that normally does not involve security professionals. a. Civil Liability b. Strict Liability c. Duty d. Malicious Prosecution 5. _____ Willful acts, even those acts that a person honestly believed that he or she could lawfully commit. a. Tort b. Tort Feasor c. Intentional Torts d. Negligence Torts 6. _____ An individual who commits a tort. a. Tort b. Tort Feasor c. Intentional Torts d. Negligence Torts 8 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 7. _____ A civil wrong for which a private party may sue the tort feasor for restitution. a. Tort b. Tort Feasor c. Intentional Torts d. Negligence Torts 8. _____ Require a violation of a standard of care, or the breech of a duty, proximate cause, foreseeability, and damages or injuries. a. Tort b. Tort Feasor c. Intentional Torts d. Negligence Torts 9. _____ Intentionally harmful or otherwise offensive touching of another person. The touching does not have to be direct physical contact but may instead be through an instrument such as a cane or rock. a. Assault b. Battery c. Defamation d. False Imprisonment e. Trespass 10. _____ Intentionally causing fear, or imminent, harmful, or offensive touching, but without touching or physical contact. a. Assault b. Battery c. Defamation d. False Imprisonment e. Trespass 11. _____ Restraint of a person in a bounded area without justification or consent. a. Assault b. Battery c. Defamation d. False Imprisonment e. Trespass 12. _____ Injuring the reputation of another by publicly making untrue statements. a. Assault b. Battery c. Defamation d. False Imprisonment e. Trespass 13. _____ Unauthorized physical invasion of property, or remaining on the property after permission has been rescinded. a. Assault b. Battery c. Defamation d. False Imprisonment e. Trespass 9 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Answer the following True/False Questions 14. _____ Required elements of Probable Cause are the apparent facts that are discovered through logical inquiry that would lead a reasonable person to believe that an a person has committed a crime. a. True b. False 15. _____ Invasion of Privacy is the intrusion into the personal life of another, with just cause, which can give the person whose privacy has been invaded the right to bring a lawsuit. a. True b. False 16. _____ Intentional infliction of emotional distress (IIED) is a claim that requires proof of physical trauma. a. True b. False 17. _____ The Categories of Civil Liability include Intentional Tort, Negligence Tort, Strict Liability, and Probable Cause. a. True b. False 18. _____ The Elements of a Negligent Tort include the existence of a duty, the foreseeability of the likelihood of injury occurring, the failure to meet a reasonable standard of care, and proximate results of the injury and Injury or damages. a. True b. False 19. _____ Malicious Prosecution is brought by one against whom a civil suit or criminal proceeding has been successfully commenced with probable cause. a. True b. False 20. _____ Battery is an intentionally harmful act that includes the offensive touching of another person. a. True b. False 10 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Civil Law in Security Services Exam Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. c a d b c b a d b a d c e a b b b a b a 11 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name:_____________________________________Date:_____________________________ Civil Law in Security Crossword Puzzle 4 6 5 10 14 7 11 3 2 8 1 12 9 15 13 16 Across: Down: 1. Potential responsibility for payment of damages or other courtenforcement in a lawsuit. 2. The obligation not to injure another person or damage another person’s property. 3. A civil court action in which it is alleged that the tort feasor, by his or 4. Injuring the reputation of another by publicly making untrue her actions, caused the death of a person. statements. 5. The intrusion into the personal life of another without just cause. 6. A civil wrong for which a private party may sue for restitution. 7. Intentionally harmful or otherwise offensive touching of another person. 8. The unauthorized physical invasion of property or remaining on the property after permission has been rescinded. 9. Intentionally causing fear, or imminent, harmful, or offensive touching, but without touching or physical contact. 10. Require a violation of a standard of care, the breech of a duty, foreseeability, and damages or injuries. 12. Willful acts, even those acts that a person honestly believed he or she could lawfully commit. 11. Liability without fault. 13. An individual who commits a tort. 14. A restraint of a person in a bounded area without justification or consent. 15. Apparent facts discovered through logical inquiry that would lead a reasonably intelligent person to believe that an accused person has committed a crime, thereby warranting his or her prosecution. 16. An action for damages brought by one against whom a civil suit or criminal proceeding has been unsuccessfully commenced without probable cause and for a purpose other than that of bringing the alleged offender to justice. 12 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Civil Law in Security Crossword Puzzle Key 4D 6T 5I N V A S I 14F O E N O F R A T M A 7B A P R I V A C Y 10N E T T E R Y G L T L S I I E 11S I T M R P 1C I V R 12I N I O N G F U L N L L I A B I L I T 2D E A T E N T I O N A L T L O I N A M B E I 16M A T L O R T S 8T H G U R E T E N Y S C P E C S N 3W R 9A S S A U L S 15P R O B A B L E C A U S T O E R T 13T O I C I O U S P R O S R T F E A S O E C U T I O N R I T Y Across: Down: 1. Potential responsibility for payment... (civil liability) 2. The obligation not to injure... (duty) 3. A civil court action in which it is... (wrongful death) 4. Injuring the reputation of another... (defamation) 5. The intrusion into the personal life... (invasion of privacy) 6. A civil wrong for which a private party may sue... (tort) 7. Intentionally harmful or otherwise offensive... (battery) 8. The unauthorized physical invasion... (trespass) 9. Intentionally causing fear, or... (assault) 10. Require a violation of a standard of care... (negligence torts) 12. Willful acts, even ones that a person... (intentional torts) 11. Liability without fault. (strict liability) 13. An individual who commits a tort... (tort feasor) 14. A restraint of a person in a bounded... (false imprisonment) 15. Apparent facts discovered through logical inquiry... (probable cause) 16. An action for damages brought by one against whom... (malicious prosecution) 13 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 14 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 15 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name_______________________________________ Date_______________________________ Discussion Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Participates in group discussion Encourages others to join the conversation Keeps the discussion progressing to achieve goals Shares thoughts actively while offering helpful recommendations to others Gives credit to others for their ideas Respects the opinions of others Involves others by asking questions or requesting input Expresses thoughts and ideas clearly and effectively Total Points (32 pts.) Comments: 16 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name______________________________________ Date_______________________________________ Individual Work Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Follows directions Student completed the work as directed, following the directions given, in order and to the level of quality indicated Time management Student used time wisely and remained on task 100% of the time Organization Student kept notes and materials in a neat, legible, and organized manner. Information was readily retrieved Evidence of learning Student documented information in his or her own words and can accurately answer questions related to the information retrieved *Research/Gathering information (if relevant) Student used a variety of methods and sources to gather information. Student took notes while gathering information Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 17 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name:____________________________________ Date:_____________________________ Presentation Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Topic/Content Topic discussed completely and in-depth Includes properly cited sources (if used) Creativity/Neatness Integrates a variety of multimedia effects to create a professional presentation (transition and graphics) or appropriate visual aid used Title slide, table of contents, bibliography are included, using acceptable format Mechanics Grammar, spelling, punctuation, and capitalization are correct Image and font size are legible to the entire audience Oral Presentation Communicates with enthusiasm and eye contact Voice delivery and projection are dynamic and audible Audience Interaction Presentation holds audience’s attention and relates a clear message Clearly and effectively communicates the content throughout the presentation Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 18 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name______________________________________ Date_______________________________________ Research Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Question/goal Student identified and communicated a question or goal of the research Research/Gathering information (if relevant) Student used a variety of methods and sources to gather information. Student took notes while gathering information Conclusion/Summary Student drew insightful conclusions and observations from the information gathered. Information is organized in a logical manner Communication Student communicated the information gathered and summary or conclusions persuasively. Student demonstrated skill in the use of media used to communicate the results of research Reflection Student reflected on the importance of the research and its potential application Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 19 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name:____________________________________ Date:_____________________________ Role Play Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Relates to the audience Provides a fluent rendition of the scenario Includes all required content Acts with feeling and expression Varies intonation Presents characters appropriately Gives the scenario its full range Breaches are easily identified Total Points (32 pts.) Comments: 20 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved.