Sentencing Guidelines
advertisement

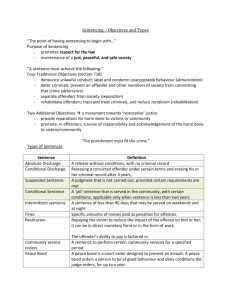
Sentencing Guidelines Course Principles of LPSCS Unit III Court Roles, Processes and Procedures Essential Question What are the sentencing and alternative sentencing guidelines in Texas? TEKS §130.292(c) (9)(E) Prior Student Learning Identify the role and function of the court system Estimated Time 2 hours Rationale Sentencing is a very important phase of the court process. Judges and juries must follow the guidelines set forth by law and precedent to ensure that due process is served on those convicted of crimes. Objectives The student will be able to: Identify types of sentencing and sentencing rules Research types of alternative sentencing Engage Do an Internet search for the following: Judge Refuses to Reduce Benson in Fatal Crash. Read and discuss the article to determine if the sentence given was adequate for the crime committed. Conduct a class discussion on the sentence that should be given, if it differs from the one assessed. Based on Texas’ sentencing guidelines, what sentence would he face? Review the statutes at http://www.statutes.legis.state.tx.us/Docs/PE/htm/PE.49.htm#49.08. Use the Discussion Rubric for assessment. Key Points Types of Sentencing o Concurrent: runs the same duration as another sentence o Consecutive: sentences run one after another o Deferred: the sentence is postponed until a later date o Determinate: the sentence lasts a specific amount of time o Indeterminate: a period of time to serve “not less than” and “not to exceed” a range of punishment o Life: the convicted person spends the remainder of his or her natural life in prison o Mandatory: the sentence is imposed from a statute that gives no room for discretion. A judge may not suspend or give probation o Maximum: the longest amount of time that can be given for an offense o Straight or flat: a fixed sentence without a maximum or a minimum o Suspended: withholding or postponing the pronouncement of a sentence or its execution Sentencing Rules in Texas o Misdemeanors Class C: Fine not to exceed $500 Class B: Fine not to exceed $2,000 and up to 180 days in jail, or both 1 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Class A: Fine not to exceed $4,000 and up to 1 year in jail, or both o Felony State Jail felony (SJF): not less than 180 days or more than 2 years, and a $10,000 fine 3rd Degree felony: not less than 2 years or more than 10 years, and a $10,000 fine 2nd Degree felony: not less than 2 years or more than 20 years, and a $10,000 fine 1st Degree felony: not less than 5 years and up to 99 years, and a $10,000 fine Capital: life without parole, or death Alternative Sentencing o Shock probation: a short amount of incarceration in addition to a period of probation o Work release: offenders report to jail during non-work hours o Weekend sentencing: offenders report to jail only for a weekend or another designated time o House arrest: offender is monitored by electronic means and may not leave the house except for certain reasons o Community service: required work for a government or nonprofit agency without pay o Probation: serves sentence in the community; offenders must abide by special guidelines o Boot camps: highly regimented program styled after the military to instill discipline and hold youths accountable o Fines: monetary amounts paid to the court in lieu of confinement o Restitution: money paid to the victim for damages and suffering o “Scarlet Letter” punishments: punishment by shaming (example: a judge requires a child molester to put a sign in his front yard stating that he is a sex offender) o Asset forfeiture: seizure of personal assets, used in or obtained from illegal activity, by the government o Incarceration: a period of confinement to either jail or prison o Diversion: charges are dropped after the person completes a condition such as a treatment program Activities Group Discussion. Have the students review news stories and videos about the alternate sentencing programs. To find some sample news stories and videos (prior to class) do an Internet search for the following: Concurrent or Consecutive Sentence (LawWebTV) Taylor Thompson gets shock probation Man Escapes from Work Release Program, Arrested in Montgomery Lindsay Lohan Turns Herself in for House Arrest After dirty drug test, suspect gets probation 2 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Then have the students discuss the pros and cons of each alternative. Here are some sample questions: What problems arise from the work release program and weekend sentencing? What are the benefits of these programs to the community or to the offender? Which of the programs do the students feel would be most beneficial? Use the Discussion Rubric to assess student understanding. Research Alternative Sentencing Options. Have the students research some forms of alternative sentencing. Students should research the effectiveness of each of the programs and look for news articles of cases where judges have imposed these and other forms of alternative sentencing. Use the Sentencing Guidelines Research Rubric for assessment. Another option for this activity is to assign each student an imaginary offender. Based on the profile of the offender, have the student create probation guidelines that fit the assigned offender. You may also choose to have the students create a form of alternative sentencing for their offender. They must be able to justify why they chose that particular method of sentencing. Assessments Sentencing Guidelines Exam and Key Sentencing Guidelines Research Rubric Discussion Rubric Research Rubric Materials Sentencing Guidelines computer-based presentation Sentencing Guidelines Key Terms handout Computers with Internet access Resources http://www.statutes.legis.state.tx.us/Docs/PE/htm/PE.49.htm#49.08 Do an Internet search for the following: Judge refuses to reduce benson in fatal crash Findlaw sentencing Legalmatch types alternative sentencing Cliffnotes types of sentences Concurrent or Consecutive Sentence (LawWebTV) Taylor Thompson gets shock probation Man Escapes from Work Release Program, Arrested in Montgomery Lindsay Lohan Turns Herself in for House Arrest After dirty drug test, suspect gets probation Accommodations fo Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, the class will participate in a mock justice system. Allow 3 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. the class to set some simple rules such as wearing ID, dress code, bringing supplies, etc. Students that violate these rules shall be issued a “ticket” for the violation (you will need to select two students to serve as police officers). Have the students elect a judge and prosecutors. Allow the other students to serve as defense attorneys. Create a mock trial situation, trying each violation as a separate offense. Select 6 – 12 students to serve on the jury. Once both sides have presented their cases, allow the jury to deliberate and determine what sentence should be given. You may allow them to pre-set punishment ranges or allow them to be creative, as long as they are reasonable with the punishments. After the trials discuss the punishments given and determine whether or not the sentences were effective. Use the Discussion Rubric for assessment. For enrichment, have students research sentencing guidelines in other states then compare and contrast the differences between the guidelines from other states and those from Texas. Use the Research Rubric for assessment. State Education Standards Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Career and Technical Education §130.292. Principles of Law, Public Safety, Corrections, and Security (OneHalf to One Credit). (9) The student identifies the roles and functions of court systems. The student is expected to: (E) identify types of sentencing and sentencing rules College and Career Readiness Standards English/Language Arts V. Research A. Formulate topic and questions. 2. Explore a research topic. 4 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Sentencing Guidelines Key Terms Types of Sentencing 1. Concurrent – runs the same duration as another sentence 2. Consecutive – sentences run one after another 3. Deferred – sentence is postponed until a later date 4. Determinate – a specific amount of time is given for an offender to serve 5. Indeterminate – a period of time to serve “not less than” and “not to exceed” a range of punishment 6. Life – the convict spends the remainder of his or her natural life in prison 7. Mandatory – a sentence is imposed from a statute that gives no room for discretion. A judge may not suspend it or give probation 8. Maximum – the longest amount of time that can be given for an offense 9. Straight or flat – a fixed sentence without a maximum or minimum 10. Suspended – withholding or postponing of the pronouncement or execution of a sentence Sentencing Rules of Texas 1. Misdemeanors Class C – fine not to exceed $500 Class B – fine not to exceed $2,000 and up to 180 days in jail, or both Class A – fine not to exceed $4,000 and up to 1 year in jail, or both 2. Felonies State Jail felony – not less than 180 days or more than 2 years, and a $10,000 fine 3rd Degree felony – not less than 2 years or more than 10 years, and a $10,000 fine 2nd Degree felony – not less than 2 years or more than 20 years, and a $10,000 fine 1st Degree felony – not less than 5 years, up to 99 years, and a $10,000 fine Capital – life without parole, or death Alternative Sentencing 1. Shock probation – a short amount of incarceration in addition to a period of probation 2. Work release – offenders report to jail during non-work hours 3. Weekend sentencing – offenders report to jail only for a weekend or other designated time 4. House arrest – the offender is monitored by electronic means and may not leave his or her house except for certain reasons 5. Community service – required work for a government or nonprofit agency without pay 6. Probation – offenders serve sentences in the community; offenders must abide by the special guidelines 7. Boot camps – highly regimented programs styled after the military to instill discipline and hold youths accountable 8. Fines – monetary amounts paid to the court in lieu of confinement 9. Restitution – money paid to the victim for damages and suffering 10. “Scarlet letter” punishments – punishment by shaming (example: a judge requires a child molester to put a sign in his front yard stating that he is a sex offender). 11. Asset forfeiture – seizure of personal assets, used in or obtained from illegal activity, by government 12. Incarceration – a period of confinement to either jail or prison 13. Diversion – the charges are dropped after the person completes a condition such as a treatment program 5 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name: Date: _____ ____ Sentencing Guidelines Exam Match the correct Sentencing Rule with the correct punishment. 1) _____ Class B 2) _____ 1st degree felony a. $2000 and/or up to 180 days in jail 3) _____ Class A b. 180 days up to 2 years and $10,000 4) _____ 3rd degree felony c. $500 fine only 5) _____ Capital Felony d. Life without parole or death 6) _____ Class C e. 2-10 years and $10,000 7) _____ 2nd degree felony f. $4000 and/or up to 1 year in jail 8) _____ State Jail Felony g. 5-99 years and $10,000 h. 2-20 years and $10,000 6 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Match the correct Types of Sentencing with the correct definition. 9) _____ Determinate 10) _____ Concurrent a. Sentence is postponed until another date 12) _____ Consecutive b. Withholding or postponing of pronouncing a sentence or executing a sentence 13) _____ Mandatory c. A fixed sentence without a maximum or minimum 11) _____ Indeterminate 14) _____ Maximum 15) _____ Suspended d. Specific amount of time given for an offender to serve 16) _____ Life e. Convicted person spends the rest of his or her natural life in prison 17) _____ Deferred 18) _____ Straight/Flat f. Period of time to serve "not less than" and "not to exceed"...punishment range g. Sentences run one after another h. Sentence imposed from statute that gives no room for discretion i. Runs the same duration as another sentence j. The longest amount of time that can be given for an offense 7 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Match the correct type of Alternative Sentencing with the correct definition. 19) _____ "Scarlet Letter" punishments 20) _____ Incarceration 21) _____ Weekend sentencing 22) _____ Shock probation 23) _____ Work release 24) _____ Fines a. Seizure of personal assets, used in or obtained from illegal activity, by the government b. Highly regimented program styled after the military to instill discipline and hold youths accountable c. A period of probation along with a period of incarceration 25) _____ Asset forfeiture d. Offenders report to jail during nonwork hours 26) _____ Probation e. Monetary amount paid to the court in lieu of confinement 27) _____ Diversion 28) _____ Community Service 29) _____ Restitution 30) _____ House arrest 31) _____ Boot Camps f. Offender is monitored by electronic means and may not leave their house except for certain reasons g. Charges are dropped after the person completes a condition such as a treatment program h. Money paid to victim for damages and suffering i. Punishment through shaming, such as child molesters having to place signs in their yards stating such. j. Period of confinement to either jail or prison k. Serves sentence in the community; offenders must abide by special guidelines l. Required work for the government or a non-profit agency without pay m. Offenders report to jail only during weekends or other designated times 8 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Sentencing Guidelines Exam Key 1. A 2. G 3. F 4. E 5. D 6. C 7. H 8. B 9. D 10. I 11. F 12. G 13. H 14. J 15. B 16. E 17. A 18. C 19. I 20. J 21. M 22. C 23. D 24. E 25. A 26. K 27. G 28. L 29. H 30. F 31. B 9 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name_______________________________________ Date_______________________________ Sentencing Guidelines Research Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Program Effectiveness: Program selected has an effective rate of completion. Most offenders do not tend to reoffend. Creativity: Student was creative in selecting the appropriate sentence for his or her offender. Appropriate sentencing: Sentence was suited for the offense and was very appropriate for the offender. Total Points (12 pts.) Comments: 10 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name_______________________________________ Date_______________________________ Discussion Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Participates in group discussion Encourages others to join the conversation Keeps the discussion progressing to achieve goals Shares thoughts actively while offering helpful recommendations to others Gives credit to others for their ideas Respects the opinions of others Involves others by asking questions or requesting input Expresses thoughts and ideas clearly and effectively Total Points (32 pts.) Comments: 11 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. Name______________________________________ Date_______________________________________ Research Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Question/goal Student identified and communicated a question or goal of the research Research/Gathering information (if relevant) Student used a variety of methods and sources to gather information. Student took notes while gathering information Conclusion/Summary Student drew insightful conclusions and observations from the information gathered. Information is organized in a logical manner Communication Student communicated the information gathered and summary or conclusions persuasively. Student demonstrated skill in the use of media used to communicate the results of research Reflection Student reflected on the importance of the research and its potential application Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 12 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved.