Lesson Plan

Lesson Plan
Course Title: Construction Technology
Session Title: Types and Uses of Fasteners
Lesson Duration:
3 hours (depending on class size: two 1.5 hour blocks)
[Lesson length is subjective and will vary from instructor to instructor]
Performance Objective:
Upon completion of this assignment, the student will be able to identify different types of fasteners used throughout the construction industry. The student will also be able to use each of the fasteners viewed and discussed during this lesson .
Specific Objectives:
Upon completion of this lesson, the learner will be able to:
Identify the general types of fasteners.
Explain and show proper use of general fasteners.
Identify specialty types of bolts, nuts and washers.
Explain and show proper use of specialty products.
Identify nails and tell how they are sized.
Explain and show proper use of different nails.
Identify different types of screws.
Explain and show proper use of different types of screws.
Preparation
TEKS Correlations:
This lesson, as published, correlates to the following TEKS. Any changes/alterations to the activities may result in the elimination of any or all of the TEKS listed.
130.54. Building Maintenance Technology
(c) Knowledge and skills.
(3) Students select and install common roofing materials for residential and light commercial projects and are expected to:
(i) demonstrate the techniques for installing other selected types of roofing materials.
(5) Students will install various exterior siding materials, including wood, metal, vinyl, and cement board siding; and
(b) identify various fasteners used to install siding, including nails, screws, and adhesives.
(6) Student will gain knowledge of the types and grades of steel framing materials and the process for installation of metal framing for interior walls, exterior nonbearing walls, and partitions; and
(b) identify the fastening methods used for steel frame systems.
(7) Students will demonstrate knowledge of various types of gypsum drywall and the fastening devices and methods used to install them; as well as
(c) explain the fastener schedules for different types of drywall installations.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 1
(11) Students will know the various types of trim used in finish work and the proper methods for selecting, cutting, and fastening trim; as well as
(d) properly use fasteners to install trim, including door trim, window trim, base trim, and ceiling trim.
130.51. Construction Technology
(c) Knowledge and skills.
(2) Students will gain knowledge about building materials used in the construction industry; and
(g) describe the fasteners, anchors, and adhesives used in construction work and explain their uses.
Interdisciplinary Correlations:
This lesson, as published, correlates to the following TEKS. Any changes/alterations to the activities may result in the elimination of any or all of the TEKS listed.
English:
110.xx(6)
– Reading/word identification/vocabulary development
110.xx(6)(A)
...expand vocabulary through...listening and discussing
110.xx(6)(B)
...rely on context to determine meanings of words and phrases such as figurative language, idioms, multiple meaning of words, and technical vocabulary...
110.xx(15)
– Listening/speaking/critical listening
110.xx(6)(B)
...rely on context to determine meanings of words and phrases such as figurative language, idioms, multiple meaning of words, and technical vocabulary...
Instructor/Trainer
References:
1.
NCCER “Wheels of Learning” core curricula © 1992
2. http://www.fastenersforconstruction.com/ConstSpecs/welcome.html
3. http://www.industrial-fasteners.org/
Instructional Aids:
Types and Uses of Fasteners PowerPoint.
Chalkboard or dry erase board.
Materials Needed:
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 2
Equipment Needed:
Hammers
Wrenches
Screwdrivers
Socket Wrenches
Learner
Must complete the safety portion of the course before proceeding to this section.
Be furnished a Rubric for this lesson. ( See Formal Assessment section for the
Rubric.)
Introduction
Introduction (LSI Quadrant I):
ASK: Why do we need fasteners in construction? List responses on board and discuss.
ASK: Name some fasteners. List and discuss.
Explain history of fasteners. Show some old fasteners.
Outline
Outline (LSI Quadrant II):
Complete Introduction
Start PowerPoint Frame 1
Frame 2
– Importance of Fasteners
Frame 3 – Importance of Fasteners continued
Frame 4 – They Provide Safety
Frame 5 – General Types of Fasteners
Frame 6 – Specific Types and Uses of Fasteners
Instructor Notes:
The PowerPoint presentation, Types and
Uses of Fasteners, will be used throughout the lesson.
You may use other references as needed.
Discuss.
Show examples of shear pins, driveshafts or breakaway plowshares.
Show examples of these fasteners and give a brief use of each.
Show bolts.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 3
Frame 7 – American Standard Bolts Hexagon or Square
Head
Frame 8 – Carriage Bolts
Frame 9 – Bolts
Frame 10 – Plow Bolts
Frame 11
– Nuts
Frame 12 – Castillated and Slotted Nuts
Fame 13
– Nuts
Frame 14 – Self-Locking Nuts
Frame 15 – Washers
Frame 15
– Washers
Frame 17 – Lock Washers
Review all information to this point
Divide into small groups for practice using different types of bolts and washers
Frame 18 – Nails
Frame 19
– Nail Size
Frame 20 – Penny Sizes
Frame 21 – Common Nail
Frame 22
– Common Nail
Frame 23 – Box Nails
Frame 24 – Box Nails
Show the difference.
Show bolts.
Profile of different bolts.
Show different sized nuts.
Show examples.
Profile nuts.
Show examples.
Show examples.
Profile washers.
Show examples.
(Answer questions)
Groups of 4 or 5. Have enough bolts, nuts and tools for each student. Quiz students on what type bolt, nut, etc. they are using.
Show some examples.
Show each size on chart.
Show some common nails.
Show some box nails.
Compare to common nails.
Show each nail on chart.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 4
Frame 25 – Finish Nails
Frame 26
– Finish Nails
Frame 27 – Duplex Nail
Frame 28
– Duplex Nail
Frame 29 – Roofing Nail
Frame 30 – Roofing Nail
Frame 31
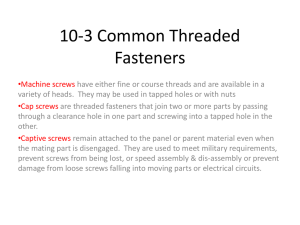
– Screws
Frame 32 – Types of Screws
Frame 33
– Screw Chart
Review all material covered on nails and screws.
Divide into small groups for practice using different types of nails and screws to fasten wood.
Additional Training aids – Build display boards or racks showing different nail types, screw types, etc. These are helpful when teaching this lesson.
Show some finish nails.
Show example.
Show example.
Show some examples.
Display on wall
(Answer questions)
Groups of 4 or 5 students.
Have plenty of scrap wood, hammers and different nails, screws, etc. Quiz students on proper nail, screw for the job and identification of nail or screw they are using.
Application
Guided Practice (LSI Quadrant III):
After covering PowerPoint frames 1-17, have students perform guided practice on that section.
After covering frames 18-33, have students perform guided practice on that section.
Independent Practice (LSI Quadrant III):
Upon completion of lesson and guided practice, student will perform independent practice.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 5
Summary
Review (LSI Quadrants I and IV):
Review at mid-point in the lesson, at the end of the lesson and before written/practical exam.
Evaluation
Informal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III):
Performed during lesson, guided practice and independent practice.
Formal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III, IV):
Develop 25 written questions using the PowerPoint presentation as a guide. Have students identify 25 nails and screws, using charts.
Guided/Independent Practice 25% 25-20% 19-15%
90-100% 80-89%
Written and/or Practical Test 75% 75-70%
90-100%
14-0%
50-79%
69-65%
80-89%
64-0%
50-79%
Extension/Enrichment (LSI Quadrant IV):
If time allows, have students build a simple box using screws and nails.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 6
Quiz on Fasteners
Name:____________________________________
1. List six types of fasteners
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
2. Which of the following is NOT TRUE of fasteners? a. They simplify the manufacture of machines and structures b. The reduce the need for large pieces c. They are cheap d. It is normally easier to make less complex components and fasten them together.
3. Give an example of how a fastener can help provide safety:
______________________________________________________________________
4. What are carriage bolts used for? a. To fasten wood parts where a smooth finish is required. b. To fasten metal parts where a smooth finish is required. c. To fasten wood to wood. d. There is no such fastener.
5. A wheel bearing spindle is a type of castellated and slotted nut. a. True b. False
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved. 7