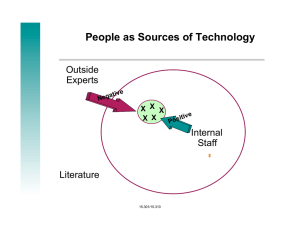
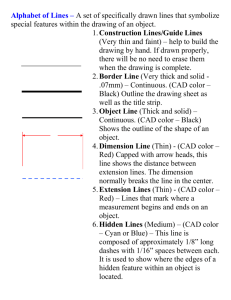
Lesson Plan CAD CAD Corrections Architectural Design
advertisement

CAD CAD Corrections Architectural Design Lesson Plan Performance Objective Students will learn how to correct simple issues within a CAD environment. Specific Objective • • • • • Demonstrate the use of commands within a CAD environment Demonstrate the terms of CAD Demonstrate CAD file organization Identify the need of CAD within a real world situation Describe the process of manipulating drawing elements within a CAD environment Terms • • • • • • • • CAD – computer aided design; using the computer software to compose drawings Move – the ability to alter the location of a drawing element Erase/Delete – the ability to remove the drawing element Cut/Trim – the ability to reduce the size of an object at a predetermined dimension Copy – the ability to replicate a drawing element Rotate/Turn – the ability to alter the angle of a drawing element Scale – the ability to alter the overall dimension of a drawing element Hatch/Pattern the command used to add a pattern to objects Time The lesson will take 35-45 minutes to complete. The independent practice can take anywhere from 25 minutes to a few days, depending on instructor resources, needs, and time frame. Please refer to the Extension/Enrichment section for explanation. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 1 Preparation TEKS Correlations: This lesson, as published, correlates to the following TEKS. Any changes/alterations to the activities may result in the elimination of any or all of the TEKS listed. Architectural Design 130.46.(c) Knowledge and skills (6) The student applies the concepts and skills of the profession to simulated or actual work situations: (B) construct points, lines, and other geometric forms using accepted computer-aided design methods; (E) use a computer system to create and modify architectural drawings; (F) plot architectural drawings for presentation. Interdisciplinary Correlations: Environmental Systems • 112.37(c)(2)(H) … use a wide variety of additional course apparatuses, equipment, techniques, materials, and procedures as appropriate such as air quality testing devices, cameras, flow meters, Global Positioning System (GPS) units, Geographic Information System (GIS) software, computer models, densitometers, clinometers, and field journals; Advanced Quantitative Reasoning • 111.37(c)(12)(A)…create and use two- and three-dimensional representations of authentic situations using paper techniques or dynamic geometric environments for computer-aided design and other applications; Occupational Correlation (O*Net – www.onetonline.org): Job Title: Architectural Drafters O*Net Number: 17-3011.01 Reported Job Titles: Drafter, Architect, Draftsman, Architectural Designer Tasks: • • • Operate computer-aided drafting (CAD) equipment or conventional drafting station to produce designs, working drawings, charts, forms and records. Lay out and plan interior room arrangements for commercial buildings using computer-assisted drafting (CAD) equipment and software. Check dimensions of materials to be used and assign numbers to lists of materials. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 2 Soft Skills: Active Listening, Mathematics, Critical Thinking Accommodations for Learning Differences It is important that lessons accommodate the needs of every learner. These lessons may be modified to accommodate students with learning differences by referring to the files found on the Special Populations page of this website (cte.unt.edu). Preparation • • • • • • • • Important – This lesson assumes you have access to a functioning computer lab with CAD software and the ability to print CAD files. Important – This lesson assumes that students have a basic introduction to CAD. Important – You may have to manipulate the given CAD file to fit your standards for class. Review and familiarize yourself with the terminology, materials, and CAD. Have computer lab ready for student use. Test and prepare CAD software. Have materials and documents ready for distribution prior to the start of the lesson. This lesson will take 35-45 minutes to complete. The Extension/Enrichment section of this lesson contains some ideas that can extend the lesson. The extent of the time frame given to this lesson can vary depending on your resources and needs. References Shumaker, T. M., Madsen, D. A., & Madsen, D. P. (2012). AutoCAD and its applications basics 2013. Hoboken, NJ: Goodheart-Willcox. Instructional Aids • • • • • Reference Book Sample CAD drawings and images Lesson Software Presentation Projection/Control software for computer lab Instructor Computer/Projection Unit Materials Needed • Presentation boards (if needed) Equipment Needed • • Computer lab with CAD software Surface to hang presentations (if needed) Learner Preparation Discuss rules and guidelines for use of computers. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 3 Introduction The main purposes of this lesson are to help students: • • • Understand CAD as a method for creating and manipulating architectural drawings (past) Understand and use CAD as a communication tool (present) Use CAD for architectural projects (future) Show examples of architectural CAD drawings. Allow students to ask questions and discuss pictures if students are unclear or curious. Ask students if they have ever heard of CAD. What does it stand for? Tell students that CAD stands for computer aided design. You use computer software to create architectural drawings. This has become the most popular method around the world for creating architectural blueprints in architecture as well as in many other industries. Ask students if they have ever heard of any CAD software. Tell students that there are many types of CAD software used throughout the world. CAD as a method has been around for many years and has become very advanced over the years. There are many different CAD programs and some have specific uses for specific industries. Ask students if they have ever used a CAD program. Tell students that the class is going to investigate how to use a CAD program to manipulate a drawing file and print the results. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 4 Outline Outline (LSI Quadrant II): Instructors can use the software presentation and slides in conjunction with the following outline. MI OUTLINE I. NOTES TO INSTRUCTOR Prior knowledge of the concept of CAD II. III. Use software presentation slides 3-5 to introduce CAD concepts. Introduction of CAD Vocabulary and terms for CAD IV. Demonstrate how to properly edit CAD drawings V. Show how to use the computer lab and access the CAD software VI. Begin discussion over CAD and discover students’ prior knowledge. Use images from web sites, magazines, etc. Independent Practice Use software presentation slides 6-10 to introduce CAD concepts. Demonstrate CAD editing software, or available means. Show the CAD software to students for editing CAD files Students will correctly edit the CAD file Multiple Intelligences Guide Existentialist Interpersonal Intrapersonal Kinesthetic/ Bodily Logical/ Mathematical Musical/Rhythmic Naturalist Verbal/Linguistic Visual/Spatial Application Guided Practice (LSI Quadrant III): Demonstrate to the students how to open CAD drawings, access files, and manipulate the drawing elements within them. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 5 Model the proper techniques, safety, guidelines, and rules for using the computer lab. Independent Practice (LSI Quadrant III): • Have students manipulate the CAD file into a correct format. Summary Review (LSI Quadrants I and IV): • Have students present their corrected printed CAD file. • Ask students to reflect on their knowledge and recall where else they can use CAD in their lives and at school. Evaluation Informal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III): Any of the following can be used as informal assessments : • Spot check for vocabulary terms • Check progress on CAD project • Participate actively in computer lab • Present CAD project Formal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III, IV): • CAD project file using grading rubric Enrichment Extension/Enrichment (LSI Quadrant IV): • Have students develop designated additional drawing elements. • Have students create and develop their own additional drawing elements. • Have students significantly manipulate the drawing file. • Have students re-create the drawing without the initial CAD file. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 6 Architectural Design CAD Correction Handout Concepts: CAD: computer aided design; the process of using computer software to draft and/or design architectural projects CAD Commands: the various program commands that allow the user to operate within the CAD environment Selection: Modification: the process of choosing objects for modification the process of altering existing objects Dimensioning: the process of adding dimensions indicating sizes on objects CAD Vocabulary: Crosshairs: the cursor used for selection Line: the command used to create a line Cut/Trim: the command used to “delete” a portion of a line Erase/Delete: the command used to remove an object or objects from a drawing Rotate/Turn: the command used to alter the angle of an object’s position in the plane Copy: the ability to replicate a drawing element Scale: the command used to proportionately resize an object Hatch/Pattern: the command used to add a pattern to objects Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 7 Architectural Design CAD Corrections Test/Project Project: Students will use the given CAD file and correct the indicated errors on the drawing. Students will then print and present their adjusted CAD drawing. Test: Student files will be graded using the rubric. Extension: Students can add given elements to the layout. Students can develop their own elements to add to the layout. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 8 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 9 Rubric Template Task Statement: CAD Task Assignment: CAD Corrections Criteria Concepts/Skills to be Assessed Followed directions (Possible 4 points) Vocabulary usage Novice 1 Criteria Categories (Novice to Exemplary) Developing Accomplished 2 3 Demonstrated no understanding and did not follow directions for lesson Understood and followed some directions for lesson Understood and followed most directions for lesson Understood and followed all directions for lesson Did not use proper vocabulary Used some vocabulary Properly used most vocabulary Accurately and thoroughly used vocabulary Incorrect layers, colors, and/or placement of elements Some correct layers, colors, and/or placement of elements Mostly correct layers, colors, and/or placement of elements Accurate layers, colors, and placement of elements Elements improperly located and/or missing Some elements properly located Most elements properly located All elements accurately located File unorganized, improperly named, contains additional unnecessary elements File unorganized and improperly named File mainly organized File accurate, well organized, and properly stored; includes all elements (Possible 4 points) Drawing Format (Possible 4 points) Element Location (Possible 4 points) CAD File (Possible 4 points) Exemplary 4 A = 20 – 17 points Total Points: 20 B = 16 – 13 points C = 12 – 9 points D = 8 – 5 points F = 4 – 1 points Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 10 Points Earned