New TB diagnostics and rollout Ruth McNerney TB Alert
advertisement

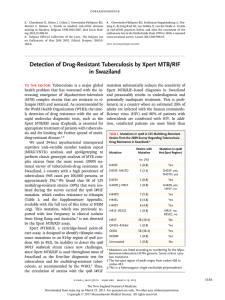
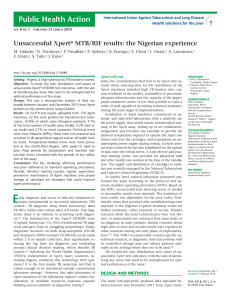
World TB Day 24th March 2015 Institute of Child Health, London New TB diagnostics and rollout Ruth McNerney TB Alert Conflict of interest statement I have no financial interest in the sale of any diagnostic test. Mention of specific companies or products does not imply endorsement or recommendation. Views expressed are my own and do not represent TB ALERT or any other organisation. TB diagnosis diagnosis is a is complicated journey TB a long journey Poverty Lack of awareness Lack of trained staff Lost results Social exclusion Cost Lack of access Stigma Delayed Dx Lack of reagents/kits Inadequate specimen Lack of robustness Poor sensitivity/ Inconvenience Confounding specificity conditions TB pathogenesis is not straight forward Infection Controlled or latent infection Infection Primary disease Post-primary disease (reactivation) Infection Disease Quiescence or cure Host response and symptoms vary by stage of disease, site of disease, bacterial lineage, preexposure and confounding conditions . . . Diagnostics Product Development Pathway Clinical performance: sensitivity/specificity Clinical trials: impact, cost effectiveness Diagnostics Product Development Pathway Clinical performance: sensitivity/specificity Clinical trials: impact, cost effectiveness GeneXpert rollout GeneXpert Rollout www.who.int/tb/laboratory/mtbrifrollout/en/ Robustness? HEAT DUST POWER GeneXpert instrument failure rates: India 18 sites: 32% of modules replaced within 10 months Nine country study: more than half of modules failed within 3 months Feasibility of decentralised deployment of Xpert MTB/RIF test at lower level of health system in India. Raizada et al PLoS One 2014; 9(2): e89301. Results from early programmatic implementation of Xpert MTB/RIF testing in 9 countries. Creswell et al. BMC Infect Dis 2014; 14: 2. Costs of installation? Nigeria: infrastructure improvements of between USD 2,622 and USD 9,716 per lab Abdurrahman et al The hidden costs of installing Xpert machines in a tuberculosis high-burden country: Experiences from Nigeria. The Pan African Medical Journal 2014, 18, 277 Published clinical trials to determine impact Sample Outcome size Indicator Study Design Setting Theron et al 2014 Randomized, parallel-group, multicentre South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe 1,502 Time to treatment Morbidity at 2 & 6m Cox et al 2014 Pragmatic prospective clusterrandomized South Africa 1,945 Confirmed cases Treatment at 3m Mortality at 6m Durovni et al 2014 Stepped-wedge Brazil cluster randomized trial 14 sites 24,227 Time to treatment TB notification rates 424 Time to treatment Mortality at 3m Mupfumi Single-centre et al pragmatic 2014 randomized controlled ART-associated TB Zimbabwe N.B Clinical trials to investigate impact on patients with drug resistant disease not available Key points • Xpert MTB/RIF detected more cases of pulmonary tuberculosis than smear microscopy • Faster access to treatment was achieved with Xpert MTB/RIF than with smear microscopy • Case notification rates were not increased by implementation of Xpert MTB/RIF when used at the point of care in health clinics. • Implementation of XpertMTB/RIF for diagnosis had no impact on patient morbidity or mortality • Further inventions are needed to control TB e.g. Community based initiatives NB Clinical trials to investigate impact on patients with drug resistant disease not available Time from sample collection to treatment initiation Study Xpert test site Theron Days to treatment (range) Xpert No Xpert Clinic 0 (0-5) 1 (0-6) Cox Clinic 4 (2-8) 8 (2-27) Durovni Clinic 8 (5-9) 11 (8-14) Mupfumi Referral lab 5 (3-13) 8 (3-23) Do high rates of empirical treatment undermine the potential effect of new diagnostic tests for tuberculosis in high burden settings? Theron et al 2014 Lancet Infect Dis 2014; 14:527–532. Suboptimal specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF among treatment-experienced patients. Metcalfe et al 2015 Eur Respir J. What next for TB diagnostics? We urgently need affordable rapid tests that can be used to screen for active TB and differentiate from latent infection. http://www.wethewomen.org We need better tests for children and nonpulmonary forms of TB. These tests do not exist for TB (yet). http://www.soulwinning.info/hm/starting.htm Novel technologies in development Several projects utilising nanotechnology POC NAAT African pouch rats Raman spectroscopy Breath analysis www.smithsdetection.com Coming soon . . . NAAT (nucleic acid amplification tests) Test XpertTB/RIF* Cepheid Inc, USA Amplification reaction Polymerase Chain Reaction Operational features EasyNAT Ustar Biotechnologies Ltd, China Cross Priming Amplification TrueNat Molbio Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd, India Polymerase Chain Reaction VerePLEX Lab-On-Chip Polymerase Chain Veredus Laboratories, Reaction Singapore Genedrive Epistem Ltd, UK Polymerase Chain Reaction * New versions in development Automated sample extraction RMP resistance Isothermal 65°C Instrument free visual output Instrument free DNA extraction Miniaturised chipbased Semi-automated DNA extraction Microarray technology RMP & INH resistance plus 9 NTMs. Paper based DNA extraction technology RMP resistance Time (min) <90 Stage of development Released to market <90 Released to market <60 Released to market <180 Released for research use 60 Field trials TB diagnosis isis a complicated journey Diagnosis a long journey Poverty Lack of awareness Lack of trained staff Lost results Social exclusion Cost Lack of access Stigma Delayed Dx Lack of reagents/kits Inadequate specimen Lack of robustness Poor sensitivity/ Inconvenience Confounding specificity conditions Thank you for your attention www.tbalert.org