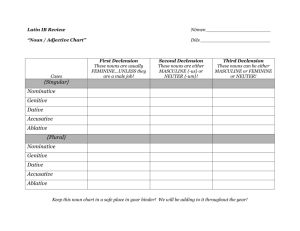
Evening Courses Latin Level 4 Prerequisite for entry:
advertisement
UCL CENTRE FOR LANGUAGES & INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION Evening Courses Latin Level 4 Prerequisite for entry: The course is appropriate for those who have attended Latin Level 3+ or have a GCSE. Term duration: 10 x 2-hour classes Aims and Objectives: The course aims to develop students’ knowledge of Classical Latin from a level comparable to that achieved at the end of Latin 3+ to a point where they will have mastered the Latin grammar and several of the regular syntactic constructions and be able to read continuous texts written in Latin. By the end of the course, the students are expected to have reached a level equivalent to the end of chapter 30 of Lingua Latina Pars 1, Familia Romana. Material to be covered: GRAMMAR: 1|Page Nouns: a. First Declension (terra, -ae) b. Second Declension (dominus, -i, puer, -i, ager, -i, donum, -i, vir, -i, deus, -i) c. Third Declension (ovis, -is, pastor, -is, corpus, corporis, mare, -is, animal, -is) d. Fourth Declension (exercitus, -us, cornu, -us) e. Fifth Declension (res, -ei) Adjectives: a. First-Second Declension (bonus, -a, -um, liber, -a, -um, niger, nigra, nigrum) b. Third Declension (brevis, -is, -e, celer, -is, -re, acer, acris, acre, audax, audacis) c. Possessive Adjectives d. Comparative & Superlative Degrees of the Adjectives Numerals: unus, una, unum, duo, duae, duo, tres, tria Pronouns: a. the personal pronoun: ego, tu, se b. the demonstrative pronouns is, ea, id, hic haec, hoc, ille, illa, illud, and ipse, ipsa, ipsum c. the interrogative (indefinite) pronoun quis, quis, quid and the interrogative (indefinite) adjective qui, quae, quod d. the relative pronoun qui, quae, quod Special Pronoun-Adjectives: alius, alia, aliud, nullus, -a, -um, alter, -a, um, uter, utra, utrum, uterque, utraque, utrumque, and neuter, neutra, neutrum Verbs: a. The tenses of the active indicative of all conjugations: present, imperfect, future, perfect, pluperfect, future perfect b. The tenses of the passive indicative of all conjugations: present, imperfect, future, perfect, pluperfect, future perfect 2|Page c. The active and passive imperative of all conjugations d. The active infinitives of all conjugations, passive present infinitive of all conjugations e. The active and passive participles of all conjugations f. The supine of all conjugations g. The gerund of all conjugations h. The deponent verbs: present indicative, imperative, infinitive, and participle i. The verbs sum, possum and eo: all tenses of the present active indicative and their infinitives SYNTAX: The prepositions included in chapters 1-30. Basic Grammatical Constructions: a. Subject – Verb – Predicate Nominative/ Adjective b. Subject – Verb – Direct Object c. Subject – Verb – Direct Object (Accusative) – Indirect Object (Dative) d. Noun-Adjective Agreement e. Object Infinitive f. Complementary Infinitive g. Subject Infinitive h. Impersonal Verbs and their grammatical structure Ablative of Cause Ablative of Manner Ablative of Means Ablative of Measure of Difference Ablative of Price Ablative of Personal Agent Ablative of Respect 3|Page Dative of Reference Predicative Dative Genitive of Possession & Dative of Possessor Genitive of Value Partitive Genitive Specific Verbs followed by the Genitive, Dative or Ablative Expressions of Time and Place Participles: Ablative Absolute Final Clauses How to express location when using the names of cities Num and none tantus…quantus = tam magnus…quam __________________________________________________________________________________________ Learning Resources: Coursebook: Hans Ørberg (2006) Lingua Latina Per Se Illustrata, Pars I Familia Romana Workbook: Hans Ørberg (2005) Lingua Latina Per Se Illustrata, Pars I Exercitia Latina I, Newburyport Handouts Note: There is a wide range of Latin language learning materials in the SelfAccess Centre: http://www.ucl.ac.uk/clie/learning-resources/sac. 4|Page 5|Page