Questions on Art & HIV prevention in Botswana Mead Over Senior Fellow
advertisement

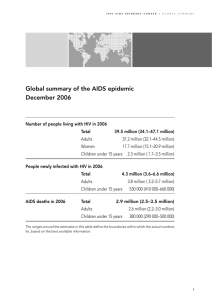
Questions on Art & HIV prevention in Botswana Mead Over Senior Fellow Center for Global Development June 6, 2007 Direct benefits of anti-retroviral (ART) Treatment - - Health benefits: Life saved, quality of life. Fewer orphans. Economic benefits: labor force participation, children going back to school, less child labor Fraction participating in labor force .7 .8 .9 Labor force participation before and after treatment in Kenya .6 Has Botswana documented similar benefits? -8 0 8 16 24 Weeks on ARVs 32 40 Source: Goldstein, Graff Zivin and Thirumurthy 2005 48 56 The objective: An “AIDS Transition” Death rate from AIDS permanently reduced Rate of new infections permanently reduced even lower The number of people living with AIDS would then eventually decline Classic analysis of the demographic transition Rate per 1000 people Rate of population growth Births Deaths Time Source: Over (2004a) “Population explosion” A successful “AIDS Transition” Rate per 1000 people Rate of growth of people living with HIV/AIDS New infections AIDS Deaths Time Source: Over (2004a) “Explosion of ART patients” Botswana: Fall in death rate & explosion of people on ART Fall in death rate Explosion of people on ART Source: WHO (2007) As patients move to 2nd line ART, fiscal burden grows more rapidly than the number of patients Millions Total Cost of Public ART (NAPHA) $500 $450 Botswana is $400 now about here $350 In Thailand expenditures will triple before they level off $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 $50 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 $0 Cost of Public ART_1 line_asy Cost of Public ART_1 line_sym Cost of Public ART_2 line_asy Cost of Public ART_2 line_sym Source: Revenga et al (2006) Transition might fail because treatment stops working … Rate per 1000 people New infections AIDS Deaths Rate of growth of people living with HIV/AIDS Time Source: Over (2004a) “Boom” of ART patients Botswana: How long will patients survive on ART? About 10% of ART patients die each year Source: WHO (2007) … or because the rate of new infections never declines. Rate of growth of people living with HIV/AIDS Rate per 1000 people New infections AIDS Deaths Time Source: Over (2004a) “Explosion of ART patients” ART can affect HIV prevention Biological Effects which might slow Transmission • Reduces viral load Effects which might speed Transmission • Lengthens duration • Selects for resistance Behavioral • Motivates testing • Reduces perceived • Promotes risk of unsafe behavior solidarity Source: Over et al (2004b) Suppose ART increases HIV transmission New infections Rate per 1000 people Rate of growth of people living with HIV/AIDS AIDS Deaths Time Source: Over (2004a) “Explosion of ART patients” Questions posed to Dr. Moeti Does Botswana have a back-up plan to pay for AIDS treatment in case aid from outside is not enough? In Botswana, has treatment success reduced or increased risky behavior? Has Botswana found a way to use treatment as a tool for prevention? References Over, Mead. 2004a. Impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic on the health sectors of developing countries. In The macroeconomics of HIV/AIDS. Edited by Markus Haacker. Washington, D.C.: International Monetary Fund. Over, Mead et al., "Antiretroviral therapy and HIV prevention in India: modeling costs and consequences of policy options," Sex Transm.Dis. 33 (10 Suppl): S145S152 (2006). Thirumurthy, Harsha, Johsua Graff-Zivin, and Markus Goldstein, "The economic impact of AIDS treatment on labor supply in western Kenya," NBER Working Paper No.11871:47, December 2005 (2005). Over, Mead. et al. 2004b. HIV/AIDS Prevention and Treatment in India: Modeling the Costs and Consequences. Washington: World Bank. Revenga, Ana et al. 2006. The economics of effective AIDS treatment: Evaluating policy options for Thailand. Washington, DC: World Bank. WHO, UNAIDS, and UNICEF. Towards Universal Access: Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector, Progress Report, April 2007. 2007. Geneva, Switzerland, World Health Organization. 6-8-2007.