Reclosers Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions
advertisement
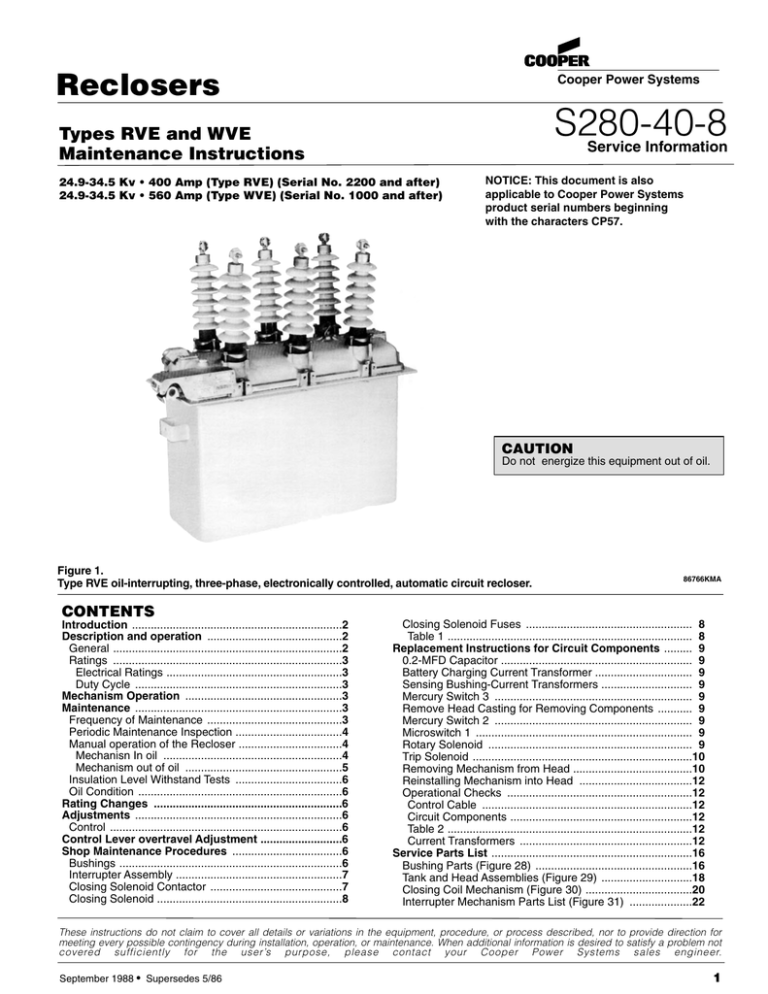
Reclosers Cooper Power Systems S280-40-8 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions Service Information 24.9-34.5 Kv • 400 Amp (Type RVE) (Serial No. 2200 and after) 24.9-34.5 Kv • 560 Amp (Type WVE) (Serial No. 1000 and after) NOTICE: This document is also applicable to Cooper Power Systems product serial numbers beginning with the characters CP57. CAUTION Do not energize this equipment out of oil. Figure 1. Type RVE oil-interrupting, three-phase, electronically controlled, automatic circuit recloser. 86766KMA CONTENTS Introduction ...................................................................2 Description and operation ...........................................2 General .........................................................................2 Ratings .........................................................................3 Electrical Ratings ........................................................3 Duty Cycle ..................................................................3 Mechanism Operation ..................................................3 Maintenance ..................................................................3 Frequency of Maintenance ...........................................3 Periodic Maintenance Inspection ..................................4 Manual operation of the Recloser .................................4 Mechanisn In oil .........................................................4 Mechanism out of oil ..................................................5 Insulation Level Withstand Tests ..................................6 Oil Condition .................................................................6 Rating Changes ............................................................6 Adjustments ..................................................................6 Control ..........................................................................6 Control Lever overtravel Adjustment ..........................6 Shop Maintenance Procedures ...................................6 Bushings .......................................................................6 Interrupter Assembly .....................................................7 Closing Solenoid Contactor ..........................................7 Closing Solenoid ...........................................................8 Closing Solenoid Fuses ..................................................... 8 Table 1 .............................................................................. 8 Replacement Instructions for Circuit Components ......... 9 0.2-MFD Capacitor ............................................................. 9 Battery Charging Current Transformer ............................... 9 Sensing Bushing-Current Transformers ............................. 9 Mercury Switch 3 ............................................................... 9 Remove Head Casting for Removing Components ........... 9 Mercury Switch 2 ............................................................... 9 Microswitch 1 ..................................................................... 9 Rotary Solenoid ................................................................. 9 Trip Solenoid ......................................................................10 Removing Mechanism from Head ......................................10 Reinstalling Mechanism into Head ....................................12 Operational Checks ...........................................................12 Control Cable ...................................................................12 Circuit Components ..........................................................12 Table 2 ..............................................................................12 Current Transformers .......................................................12 Service Parts List ................................................................16 Bushing Parts (Figure 28) ..................................................16 Tank and Head Assemblies (Figure 29) .............................18 Closing Coil Mechanism (Figure 30) ..................................20 Interrupter Mechanism Parts List (Figure 31) ....................22 These instructions do not claim to cover all details or variations in the equipment, procedure, or process described, nor to provide direction for meeting every possible contingency during installation, operation, or maintenance. When additional information is desired to satisfy a problem not covered sufficiently for the user’s purpose, please contact your Cooper Power Systems sales engineer. September 1988 ● Supersedes 5/86 1 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions INTRODUCTION Service Information S28O-4O-8 provides the maintenance instructions for Type RVE and WVE three-phase, electronically controlled, oil reclosers. Included is a general description of the recloser and its operation, instructions for periodic inspection and routine maintenance, testing procedures, and instructions for shop repairs. A service parts list, keyed to explodedview drawings of the recloser is included at the back of the manual. Procedures for testing the recloser and control together are found in the control installation manual S280-75-1. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION General The Type RVE and WVE reclosers, are self-controlled devices that protect distribution lines and equipment. A complete unit consists of the recloser, a Type ME electronic control, and an interconnecting cable. Fault current sensing is provided by the control which actuates the recloser. Circuit interruption is provided by the recloser. The Type RVE and WVE reclosers trip open an overcurrent (either phase or ground faults) and then reclose automatically. If the overcurrent is temporary the automatic recloser restores normal service. If the fault is permanent a preset number of trip and reclose operations are performed to lockout. All three phases of the RVE and WVE reclosers open, reclose and lockout simultaneously. Opening sequences can be all fast, all delayed, or any combination of fast operations followed by delayed operations up to a Figure 2. Untanked TypeRVE recvloser. 2 total of four. Fast operations clear temporary faults before branch-line fuses can be damaged. Delayed operations allow time for fuses or other downline protective devices to clear so that permanent faults can be confined to smaller sections of line. Fast arc interruption is provided by bridge-type contacts which provide two breaks in series per phase. Each current break has a self-generating type arc interrupting structure with a series of vented chambers. As the contacts open, the arc generates gas pressure within the interrupting chamber which blasts oil across the arc and out through the vents. The moving bridge-type contacts are driven by the release of opening springs that are loaded when the recloser mechanism is closed. Closing energy, as well as energy to charge the opening springs, is supplied by a high-voltage closing solenoid momentarily connected phase-to-phase through a high-voltage contactor. The contactor is mechanically closed by a rotary solenoid actuated by a signal from the electronic control. A trip-free, yellow operating handle located under the sleet hood will manually lock open the recloser. It cannot manually close the recloser but must be in the CLOSED position for the rotary close solenoid to operate. A red contact position indicator linked to the recloser mechanism, but independent of the operating handle, is also located under the sleet hood. The location of the major operation components of the RVE recloser is shown in Figure 2. They are similar for the WVE recloser. Being aware of the location of these components and their part in the operation of the recloser will give a quicker and clearer understanding of the recloser maintenance and repair procedures that follow. 86767KMA S280-40-8 Ratings ELECTRICAL RATINGS Type RVE TypeWVE 24.9-34.5 38 24.9-34.5 38 150 150 70 60 70 60 400 560 Nominal system voltage, kv Maximum rated voltage, kv Rated impulse withstand voltage (BIL) kv crest 60-Hertz withstand voltage, kv Dry, one minute Wet, ten seconds Rated maximum continuous current, amps MAINTENANCE Frequency of Maintenance DUTY CYCLE % of Maximum Interrupting Circuit Rating X/R Value 15-20 45-55 90-100 reset trip lever, which releases the reset lever. The reset lever is rotated by a spring and snaps the toggle closed. This motion of the reset lever also pulls the plunger out of the closing coil. At this point the contacts are completely open. The closing coil is energized by a signal to the rotary solenoid on the side of the mechanism. The solenoid closes the closing solenoid contactor, which energizes the coil. The plunger is drawn into the coil and the reset lever is pulled back (d) to its original position, at the same time closing the contacts. The mechanism is then ready for another cycle. 4 8 15 Number of Unit Operations Type RVE 28 24 10 Total 62 Type VWV27 28 20 10 Total 58 MECHANISM OPERATION The head mechanism performs the actual opening and closing operations in response to signals from the electronic control. Contact opening is initiated by a trip coil. Contact closing is performed by the closing coil, mounted below the mechanism. The basic operation of lever arrangement is shown in Figure 3. With the contacts closed (a) the opening springs are fully extended. The trip coil push rod rests up against the toggle latch and when the trip coil is energized, the toggle opens (b). The contact-and-toggle-support assembly and the contact-and-trip-arm assembly rotate on their shafts and begin to push the contacts open. As the opening springs rotate the contact-and-trip-arm assembly past this point (c), the trip arm moves the Because reclosers are applied under widely varying operating and climatic conditions, maintenance intervals are best determined by the user based on actual operating experience. To assure proper operation, reclosers must be maintained when they have operated the equivalent of a complete duty cycle and before the dielectric strength has deteriorated below prescribed levels. In the absence of specific operating experience, the following procedures are recommended. • When Type RVE and WVE reclosers are operated under usual service conditions as defined in ANSI (American National Standards Institute) C37.6O, “Standard Requirements for Automatic Circuit Reclosers for Alternating Current Systems,” it is recommended that the following maintenance procedures be performed at the completion of an equivalent duty cycle. NOTE: ANSI C37.61, “Guide for the Application, Operation and Maintenance of Automatic Circuit Reclosers” gives a procedure for converting the standard duty cycle, as shown on page 3 of these instructions into an equivalent duty cycle based on the actual operating duty of the recloser. Figure 3. Head mechanism lever arrangement. 3 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions • However, if the recloser has not completed an equivalen duty cycle within three years, it is recommended that an external inspection, oil-level check, and a check of the dielectric strength of the oil be made at that time. (See steps 1, 2, and 8 of “Maintenance Procedure” below.) Periodic Maintenance Inspection Each periodic maintenance inspection done at the completion of an equivalent duty cycle, should include: 1. Bypass and remove the recloser from service. 2. Inspect external components. A. Check for broken or cracked bushings. Replace as necessary (see page 6 for procedure). B. Check for scratched paint, repaint as needed. C. Note counter reading and enter in the record log. 3. Perform an insulation level withstand test (see page 6 for procedure). 4. Raise head mechanism assembly from tank to expose internal components. CAUTION Be sure the recloser is open (yellow operating handle down) before raising the head mechanism assembly so the mechanism can not be accidentally tripped while out of oil. Tripping the mechanism out of oil can damage it. CAUTION Arc interruption in oil under normal operating conditions may cause an accumulation of volatile gases under the head of the recloser. Untank the recloser in a well-ventilated area away from open flames, sparks, or lighted smoking materials. Be sure to ventilate the recloser thoroughly. 5. Clean all internal components. A. Remove all traces of carbon by wiping with a clean, lint-free cloth. B. Flush the mechanism with clean transformer oil. CAUTION Never use volatile solutions, detergents, or water-soluble cleaners. 6. Remove the moving contact assembly from the bottom of the contact lift rod to check the erosion of the contacts. A. Arcing tips of the moving contacts can experience considerable erosion before replacement is necessary. Slight pitting and discoloration can be dressed with a piece of crocus cloth. B. However, erosion of the load current carrying contact surfaces requires replacement of the entire internal structure before its effectiveness is impaired. C. Figure 4 shows a moving contact after it has experienced severe interrupting duty and a new one for comparison. The used contact has reached the condition where it should be replaced. 7. Check circuit components attached to the recloser head, frame and operating mechanism. A. Check condition of the wiring to the terminal strip and make sure all connections are tight. B. Make sure that the rotary solenoid and the trip solenoid are firmly attached to the recloser frame. C. Check that the two mercury switches are securely held in place by the nylon mounting straps. D. Check condition of microswitch mounted above main shaft. 4 Figure 4. 85693KMA Left: new moving contact; right: contact after one full duty E. Check condition of the bushing current transformers and the associated wiring. F. Check the control cable receptacle. If circuit component malfunction is suspected, see page 12 for an operational check procedure. 8. Check the dielectric strength of the insulating oil. A. An oil sample taken near the bottom of the tank should have a dielectric strength of not less than 22 kv rms. B. Low dielectric strength indicates the presence of water or carbon deposits. Replace the oil as necessary. 9. If oil must be replaced. A. Drain the tank, and clean out all sludge and carbon deposits. B. Fill with new, clean, insulating oil up to 2-1/4 inches below the top of the tank flange. Tank capacity is approximately 41 U.S. gallons. See Oil Condition on page 6. 10. Clean and examine the head gasket. Replace if it is cracked, cut, or otherwise damaged, or if it has been permanently deformed. 11. Clean the head gasket seat and retank the recloser. A. Move the yellow operating handle to the up position to avoid any possible binding while retanking. B. Replace the head bolts and tighten to 35-55 ft-lbs. torque. Apply clamping force gradually and equally, in rotation, to each bolt to achieve an evenly distributed gasket sealing pressure. 12. Check the oil level with the dipstick in the head and adjust the level to the upper line on the dipstick. NOTE: If the recloser is equipped with an oil-sight gage, the oil level should be above the sight gage. If the oil surface line is visible in the window, add oil to raise the level to the upper line on the dipstick 13. Repeat the high voltage dielectric withstand test (Step 3) to make sure the dielectric clearances within the tank have not been compromised. Manual Operation of the Recloser The recloser may be closed and opened manually while the mechanism is either in or out of oil. MECHANISM IN OlL For a tanked recloser (mechanism immersed in oil) use the following manual operating procedure. 1. To close the recloser. S280-40-8 A. Remove the closing tool port cover and gasket from the side of the head casting. (See Figure 2 for location.) B. Insert the KA90R T-handle closing tool (furnished as an accessory) into the closing tool port (Figure 5) and engage the pin on the closing shaft. C. Lift up the yellow operating handle under the sleet hood to reset the mechanism. D. Turn the closing tool one-quarter turn clockwise to close the main contacts. CAUTION Never use the KA90R closing tool to close an energized recloser. Forcing the tool beyond the mechanism stop may shear the pin on the closing shaft. TRIP-RESET SHAFT 2. To open the recloser. A. Pull down the yellow operating handle to trip open the recloser. 86769KMA Figure 6. Location of trip-reset shaft. 2. To open the recloser. To open the contacts while the mechanism is out of oil, proceed as follows: A. Using the T-handle closing tool turn the closing shaft clockwise and hold against the stop. B. Release the trip lever (Figure 7) by moving it to the right. C. Then slowly allow the closing tool to rotate counterclockwise to open the main contacts. NOTE: This procedure requires two people; one to operate the closing tool, the other to operate the trip lever. Figure 5. Manually closing the recloser with KA90R tool. 86768KMA MECHANISM OUT OF OIL To operate the mechanism out of oil, proceed as follows 1. To close the recloser. A. If the mechanism is still mounted in the head use the procedure for a tanked recloser above (Mechanism in oil) B If the mechanism is removed from the head turn the trip-reset shaft (Figure 6) with a pair of needlenose pl ers to reset the mechanism, then turn the closing shaft clockwise with the closing tool to close the main contacts. Trip Lever CAUTION The mechanism may be damaged if it is "quick-tripped" with the yellow operating handle while out of oil. 86770KMA Figure 7. Trip lever releases mechanism when opening recloser out of oil. 5 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions Insulation Level Withstands Tests High-potential withstand tests provide information on the dielectric condition of the recloser. Testing is performed at 75% of the rated low-frequency withstand voltage 52.5 kv. TEST 1: Proceed as follows: 1. Manually close main contacts of recloser (see page 5 for procedure). 2. Ground recloser tank and head. 3. Connect all three source-side bushings (1, 3, 5) together. 4. Apply proper test voltage to source-side bushings. 5. The recloser should withstand the test voltage for 60 seconds. TEST 2: Proceed as follows: 1. Manually close main contacts of the recloser (see page 5 for procedure). 2. Ground recloser tank and head. 3. Ground Phase A (bushing 2) and Phase C (bushing 6). 4. Apply proper test voltage to Phase B (bushing 3). 5. The recloser should withstand the test voltage for 60 seconds. TEST 3: Proceed as follows: 1. Open main contacts of recloser (see page 5 for procedure). 2. Ground recloser tank and head. 3. Connect and ground all three load-side bushings (2, 4, 6). 4. Connect all three source-side bushings (1, 3, 5). 5. Apply proper test voltage to source-side bushings. 6. The recloser shouId withstand the test voltage for 60 seconds. 7. Reverse the connections: ground source-side bushings (1, 3, 5); apply test voltage to load-side bushings (2, 4, 6) for 60 seconds. 8. The recloser shouId withstand the test voltage for 60 seconds. TEST RESULTS: These high potential withstand tests provide information on the dielectric condition of the recloser and the integrity of the interrupters. A. If the recloser passes the closed-contacts tests (Tests 1 and 2) but fails the open-contacts test (Test 3) a deterioration of one or more of the interrupters is likely to be the cause. Check each interrupter individually to determine the failed phase or phases, and replace the interrupter(s). Retest to confirm the repair. B. If the recloser fails the closed-contacts tests (Test 1 and 2) the cause is likely to be adiminished electrical clearances, low oil dielectric strength or failed insulation. After correcting the problem, retest to confirm the repair. Closing coils are available in various voltage ratings from 2.4 to 34.5 kv. There are also three dc closing coils available: 48,125 and 250 vdc. No coil fuses are used with the dc closing coils. When converting a recloser from a high voltage closing coil to a low-voltage closing coil a low-voltage contactor and coil kit (KA887R) is required. ADJUSTMENTS Control Refer to the control installation manual (S280-75-1 ) for applicable procedures for adjusting operations to lockout, reclosing time, phase-trip sequence, minimum-trip values, resetting time, ground-trip sequence, phase-trip timing and ground-trip timing. CONTROL LEVER OVERTRAVEL ADJUSTMENT Check for proper adjustment of the control lever by first removing the sleet hood cover to expose the control lever. From the OPEN position, slowly push the control lever toward the CLOSED position. As the lever is pushed up, latching of the recloser will be felt. At this point the dimension between the top of the control lever and the underside of the sleet hood should be 1/4 inch (Figure 8). If the control lever is not adjusted properly, remove the C-ring and slide the control lever from the shaft. Rotate the control lever clockwise to reduce the dimension or counterclockwise to increase the dimension. Slide the control lever back onto the shaft and recheck the dimension. When the proper dimension has been obtained replace the C-ring. Oil Condition Oil provides the internal insulation barrier between phases and from phase to ground, and must be replaced before it deteriorates below a safe dielectric level. Replace the oil if its dielectric strength falls below 22 kv. New oil should always be filtered before use even though it is obtained from an approved source. Passing the oil through a blotter press will remove free water and solid contaminants such as rust, dirt, and lint. Keep aeration to a minimum during filtering to prevent moisture in the air from condensing in the oil and lowering its dielectric strength. Used oiI must be treated before reusing. FiItering may remove absorbed and free water and other contaminants to raise the dielectric strength to acceptable levels. However, filtering does not always remove water-absorbing contaminants and the dielectric strength may fall rapidly after being returned to service. Therefore the recloser should be filled with new oil, or oil that has been restored to like-new condition. oil used in these reclosers conforms to ASTM Standard D3487, Type l; its property limits are shown in Reference Data R280-90-1, “Oil Specifications and Tests.” RATING CHANGES The continuous current rating and minimum-trip values can be changed in the field, refer to the control installation manual for applicable procedures. 6 Figure 8. Overtravel adjustment of control lever. SHOP MAINTENANCE PRODEDURES The operations described in this section should be performed under the cleanest conditions possible. The repair work, except for bushing replacement, will be simplified if the work bench is arranged so the mechanism/head assembly can be inverted (bushings down). No special tools are required for any of the repair procedures. Bushings Bushing maintenance generally consists of a thorough cleaning and a careful examination for chips, cracks or other mechanical damage during the periodic maintenance inspection. Bushings must be replaced whenever damage is discovered. Refer to Figure 9 and proceed as follows: 1. Disconnect the bushing lead from the bottom end of the bushing rod. S280-40-8 6. Install the new bushing through the head and slide corona shield and clamp over bushing. 7. Position bushing with the stud end of the terminal pointing outward. 8. Position the clamping ring with the split centered between two clamping bolts. 9. Reassemble the bushing to the head casting. Tighten the bolts evenly, a little at a time, to a torque of 10-15 ft-lbs. NOTE: Clamping forces must be applied gradually and equally in rotation to each bolt. This results in an evenly distributed gasket sealing pressure. 10. Install corona shield O-ring into groove on bushing. 11. Slide corona shield down so inside edge is flush with mechanism frame. Position clamp approximately 1/4” above edge of the shield and secure tightly. 12. Reconnect the lead to the bushing rod. Interrupter Assembly 1. Using a 1/2-inch thin wall socket, remove the vibration-proof hex nut that secures the contact yoke to the lift rod. Gently tap contact arm to remove contacts from the lift rod. 2. Remove the terminal bolt from the top of each stationary contact assembly. 3. Remove hex nuts, flat washers, and lock washers that secure the interrupter assembly to the stringers. 4. Slide the arc interrupter assembly (Figure 11 ) off. NOTE: The arc interrupter and contact assembly and the moving contact assembly are both replaced as assemblies. They should both be replaced at the same time. Figure 9. Removing bushing. 2. Loosen the clamp securing the corona shield (Figure 10). Push shield up bushing to expose o-ring, remove o-ring. 3. Remove the three hex head capscrews and clamps that secure the bushing to the head and pull corona shield and clamp off bottom of bushing as it is lifted out. 4. Remove and discard the lower bushing gasket. 5. Twist off the split aluminum clamping ring from the old bushing and install on the new bushing, if it is in good condition—replace if damaged. 5. Place the replacement interrupter assembly into position and secure it with original hardware. 6. InstalI the terminal bolts into each stationary contact assembly. 7. Place the movable contact assembly onto the lift rod and install a new vibration-proof hex nut. NOTE: It is recommended that vibration-proof nuts not be reused. NOTE: The clamping ring cushions and distributes the pressure between the ceramic and the clamps DO NOT OMIT. MECHANISM FRAME CASTING CORONA SHIELD 85695KMA Figure 11. Trip lever releases mechanism when opening recloser out of oil. Closing Solenoid Contactor CLAMP Figure 10. Removing corona shield. 86773KMA If the contacts are badly burned or eroded, the entire contactor must be replaced. See Figure 12 and proceed as follows: 1. Unhook the two toggle openings from the pin that connects the operating shaft of the contactor to the toggle arm. 7 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions TOGGLE SPRING SOLENOID LEADS TOGGLE MECHANISM PIN C- RINGS (3) CLOSING SOLENOID COIL BASE PLATE OPERATING LINK CLOSING SOLENOID CONTACTOR Figure 12. Changing closing solenoid contactor. 83372KMA 2. Remove the three C-type retaining rings and withdraw the pin. 3. Disconnect the two coil leads from the contactor. NOTE: Reattach the lockwasher and hex nut to the contactor terminal immediately after disconnecting the coil lead to prevent loss of moving contact parts which are attached to the support plate with the same hardware. 4. Disconnect the two fuse leads from the contactor. 5. Remove three hex head capscrews and lockwasher that attach the contactor to the underside of the recloser mech nism frame and remove contactor. 6. Install the new contactor by reversing the disassembly procedure. Use new C-rings to secure the toggle-link pin. 7. Connect the solenoid coil leads to the lower terminals. 8. Connect the fuse leads to the upper terminals. NOTE: Be sure coil and fuse leads are positioned for maximum clearance to other grounded parts Closing Solenoid The closing solenoid coil is connected phase-to-phase and is rated to operate at full system voltage. It is protected with two fuses, one on either side. A data plate attached to the recloser head between source side bushings 3 and 5 provides the coil connection information. If the solenoid coil must be replaced, due to damage or change in operating voltage, refer to Figure 13 and proceed as follows: 1. Disconnect the two coil leads from the closing solenoid contactor. NOTE: Reattach the lockwashers and nut to the contactor terminal immediately after disconnecting the coil lead to prevent loss of parts of the moving contact arm assembly which is attached to the support plate with the same hardware. 2. Remove the four capscrews and lockwashers which attach the base plate to the bottom of the solenoid frame posts and lower the coil and base plate. 3. Remove the coil from the base plate and discard the coil gasket. 4. Using a new coil gasket, install the new closing coil on the base plate. NOTE: A new coil gasket is included in the closing coil replacement kit. 8 CAPSCREW AND LOCKWASHER GASKET Figure 13. Parts involved in solenoid coil replacement. 86771KMA 5. Reassemble the base plate to the solenoid frame posts and connect the coil leads to the contactor terminals. Make sure the coil leads clear the solenoid frame by at least 1/2-inch. 6. The closing coil replacement kit includes two new coil fuses which should be installed with the new coil. See Closing Solenoid Fuses, following, for fuse replacement procedure. 7. The closing coil replacement kit also includes a new voltage date plate. Replace the plate on the sleet hood of the recloser head if the operating voltage of the recloser is being changed. Closing Solenoid Fuses New fuses are provided with the closing solenoid coil replacement kit and should be installed with the replacement coil. Fuses can also be ordered separately for individual replacement if damaged. A label, attached to the closing coil, specifies the catalog number, and color band coding of the proper fuse required to protect the coil. This information is also listed in Table 1. To replace a closing solenoid fuse: 1. Disconnect the long fuse lead at the closing solenoid contactor. 2. Disconnect the lead wire from the terminal at the other end of the fuse. 3. Loosen the mounting strap and slide out the fuse. 4. Install the new fuse and reconnect the fuse leads. NOTE: Be sure the long fuse lead clears any grounded parts and insulating supports by at least 1/2-inch. TABLE 1 Closing Solenoid Fuse Data. Closing Solenoid Voltage 2.4-3.3 kv 4.16-6.0 kv 7.2-11 kv 12-14.4,17.0, 34.5 kv Fuse Catalog Number Color Band KA259R904 KA259R901 KA259R902 KA259R903 Two Red Black Yellow Red S280-40-8 REPLACEMENT INSTRUCTIONS FOR CIRCUIT COMPONENTS All circuit components associated with the recloser frame, head casting and operating mechanism except the trip solenoid, rotary solenoid, microswitch 1 and mercury switch 2 can be replaced without detaching the recloser mechanism from the head casting. Instructions for replacing bushing CT’s, mercury switch 3, and the 0.2-MFD capacitor are given first. A 100-watt soldering iron will meet all requirements for repair work. When resoldering lead connections, use only resin core solder. M-E will assume no responsibility for components having leads connected by means of acid core solder. MERCURY SWITCH 2 LEVER MOUNTING STRAPS 0.2-MFD Capacitor The 0.2-MFD capacitor is used on units supplied with the CT-Type battery charger power source. Label lead connections to the capacitor and proceed as follows: 1. Heat solder joints to disconnect leads. 2. Remove screws and bracket that secure capacitor to recloser frame. 3. Replace by reversing above procedure. Be sure to reconnect leads to proper capacitor terminals. Battery Charging Current Transformer The battery charging current transformer is used on units supplied with the CT-Type battery charger power supply. Label lead connections to the current transformer and shunt ing resistor. Then proceed as follows: 1. With diagonal cutters, clip the leads close to the current transformer. 2. Disconnect the flexible bushing lead. 3. Remove the two screws that secure the current transformer to the head casting. Bushing CT is now free to be removed. 4. Replace current transformer by reversing the above procedure. Be sure to use spacers between the transformer mounting supports. Replacement transformers are equipped with six-inch leads which can be trimmed as required. When splicing connections, be sure the proper leads are connected before soldering. Be sure to wrap all splices with electrical tape and observe soldering precautions recommended above. Sensing Bushing-Current Transformers Replacement of phase A, phase B. and phase C current transformers is identical. These transformers are installed as described above under battery-charging transformer instructions. Mercury Switch 3 Disconnect leads from terminals A and G and proceed as follows: 1. Loosen two screws that secure nylon mounting straps to lever pinned to main reclosing shaft. 2. Slip mercury switch from mounting straps when screws are loosened sufficiently. 3. Be sure to replace mercury switch so that lead wires are furthest from the rotary solenoid. If the end without lead wires is not nearest the rotary solenoid, improper operation of the recloser mechanism will result. Remove Head Casting for Removing Components To replace the following components—trip solenoid, microswitch 1, mercury switch 2 and rotary solenoid—the recloser mechanism must be removed from the head casting, as described on page 10. Mercury Switch 2 SCREWS LOOP ONCE OVER SHAFT Figure 14. Location of mercury switch 2. MANUAL LOCKOUT SHAFT 85697KMA 1. Disconnect the leads of the mercury switch from the terminal strip terminals F and G. 2. Remove the four nylon mount) ng straps that secure the sleeving to the recloser frame. 3. Remove the faulty switch from its mounting straps. With an offset screwdriver, loosen the screws that secure the nylon straps to manual-lockout shaft lever to allow removal of switch 2. 4. Pull the leads through the protective sleeving. Thread the leads of the new mercury switch through the sleeving. Thread both leads at the same time. Leads can be secured to a long wire which can draw the mercury switch leads through the sleeving. NOTE: Switch leads need only be connected between the proper terminals for correct operation. Reversing leads between switch terminals has no effect on recloser operation. 5. Pass sleeving through mounting straps and tighten to secure sleeving. Connect switch leads to proper terminals. Position switch as shown in Figure 14 and secure mounting straps to lever. If switch is positioned opposite to that illustrated in Figure 14, the recloser will operate improperly. Microswitch 1 Refer to Figure 15 and proceed as follows: 1. Disconnect the two white leads from the top of the microswitch. 2. Remove two round-head machine screws to release microswitch from mounting bracket. A hexnut and washer will be released from the threaded end of the screw. 3. Attach new microswitch to mounting bracket. Adjust microswitch so that roller lever stop just touches base of switch when roller rides on cam. When roller is off cam, it should just clear flat of cam as shown in Figure 15. Tighten machine screws. 4. Reconnect leads to two terminals nearest rotary solenoid as shown. Rotary Solenoid Refer to Figures 15 and 16 proceed as follows to replace the rotary solenoid: 1. Drive out the roll pin that secures the spring lever to the rotarysolenoid shaft. Detach retarding spring from cotter pin. Refer to Figure 14 and install new switch as follows: 9 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions MICROSWITCH 1 SPRING LEVER TERMINAL SCREWS SHAFT ROLL PIN CAM MACHINE SCREWS RETARDING SPRING HEXNUTS MOUNTING BRACKET FLAT OF CAM ROLLER ROTARY SOLENOID Figure 15. Properly installed microswitch 1. MICROSWITCH 1 85702KMA ROTARY SOLENOID MERCURY SWITCH 3 HEXNUT SPACERS 85694KMA MOUNTING BRACKET PUSH ROD STUDS HEXNUTS AND LOCKWASHERS LEADS TRIP SOLENOID MAIN SHAFT 85694KMA Figure 16. Top View of rotary solenoid and associated components. 2. Remove hexnuts and lockwashers that secure the rotary solenoid to the recloser frame. Disconnect solenoid leads from the terminal block and remove rotary solenoid. 3. Remove hexnut spacers and washers from rotary-solenoid mounting studs and attach to new solenoid. Install new rotary solenoid by reversing the foregoing procedure. Be sure solenoid leads are connected to correct terminals. Trip Solenoid The trip solenoid, Figure 17, is replaced as follows: 1. Disconnect leads from terminals A and B of the terminal block. 2. Loosen the hexnut that secures the nylon mounting strap to allow lead sleeving to slip through freely. 3. Remove two hexnuts that secure the trip solenoid to the mounting bracket. Detach trip solenoid from bracket. Two lockwashers will be released. 10 Figure 17. Properly installed trip solenoid. 85694KMA 4. Install new solenoid by reversing above procedure. Pass leads through nylon mounting strap and grommet in mechanism frame. Connect leads to terminals A and B of the terminal strip in any order. The trip solenoid is not polarity sensitive. Removing Mechanism from Head To gain access to components located in or on the main frame, the following procedure may be used to remove the mechanism from the head. NOTE: These procedures will be simplified if the untanked head and mechanism assembly can be inverted (bushings down). The unit can be supported on its bushings. 1. Disconnect all six bushing leads from the rods at the ends of the bushings. 2. Disconnect the lockout lever and contact position indicator shafts by disengaging the spring loaded couplers and locking them in the disengaged position, Figure 18. S280-40-8 ATTACHING SCREWS CAPACITOR Figure 20. Capacitor for CT-type battery charger. SHAFT COUPLERS 86773KMA TERMINAL STRIP Figure 18. Couplers locked in disconnected position. 86772KMA 3. If the recloser is equipped with the auxiliary switch accessory, remove the C or E-ring and washer, Figure 19, and disconnect the operating lever of the switch from the recloser mechanism. BUNDLE STRAP 86774KMA Figure 21. Connections to terminal strip attached to reclose mechanism frame. E-RING NOTE: By temporarily substituting eye-bolts for two of the hex head bolts in the bottom of the closing solenoid frame, the mechanism can be easily lifted and handled with a hoist (Figure 22). OPERATING LEVER 83375kma Figure 19. Remove E-ring to disconnect auxiliary switch operating 4. If the recloser is equipped with the CT-type battery charger power source, remove the screws that secure the 0.2 mfd bathtub capacitor to the recloser frame, Figure 20. 5. Disconnect the seven leads connected to the bottom of the terminal block attached to the recloser frame, Figure 21. Be sure all leads are labeled before removing. With the unit inverted as shown in Figure 21, the leads are labeled A, B. C, D, E, F and N from left to right. 6. The lead bundle is secured with a nylon strap attached to the mechanism frame, Figure 21. Remove the attaching screw to free the strap from the mechanism. 7. Remove the six socket head bolts and lockwashers that secure the frame to the head casting and carefully lift the mechanism from the head. Six long pipe spacers will be released when the mechanism is lifted. Figure 22. Lifting mechanism in and out of the head. 86775KMA 11 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions 8. Remove the two spring-loaded couplers disengaged in Step 2 for safekeeping. The components remaining in the head are shown in Figure 23. tronic control cable and for discontinuity between unlike pins and pin sockets to determine the condition of the control cable. NOTE: Pins or pin sockets N and P on either plug are not connected. Repair or replace the control cable if defective. FAULT-SENSING BUSHINGCURRENT TRANSFORMERS CIRCUIT COMPONENTS All measurements are made at the pin sockets of the control cable receptacle on the recloser head. A reading within + 15 percent of the specified value indicates components are opera tional. Any component failing to meet the specified checks should be replaced. Figure 26 identifies the various circuit components. NOTE: If the electronic control battery is used to supply the 25 vdc power, connect as directed for only as long as necessary to perform the specified action to prevent excessive battery drain. Trip-Solenoid THESE WIRES CONNECTED TO TERMINAL STRIP RECEPTACLE ON HEAD CASTING 83379KMA Figure 23. Head casting detached from operating mechanism. Hex socket-head bolts have been attached to head casting for illustrative purposes. 1. Connect an ohmmeter between pin sockets A and B. • The meter should read approximately 9.5 ohms. 2. Lift up the yellow manual operating handle under the sleet hood and manually close the recloser with the T-handle closing tool as described on page 5. 3. Momentarily apply 25 vdc to pin sockets A (+) and B (-). . The recloser should trip. Rotary Solenoid and Closing Solenoid Contactor Reinstalling Mechanism into Head To reinstall the recloser mechanism assembly into the head, the following procedure may be used. 1. Install the couplers on the lockout lever and contact position indicator shafts of the mechanism and lock them in the disengaged position. 2. Carefully lower the mechanism assembly onto the six pipe spacers which have been positioned over the attaching holes in the casting (Figure 23). 3. Install the six attaching socket head bolts and tighten evenly to avoid any binding of the mechanism. NOTE: Replace the hex head bolts in tne bottom of the closing solenoid frame if eye-bolts were used for handling the recloser mechanism. 4. Re-engage the lockout lever and contact position indicator shaft by releasing the shaft couplers. 5. Reconnect the operating lever of the auxiIiary switch (if used ) to the mechanism and secure with the washer and E-ring (Figure 19). 6. Attach the 0.2 mfd bathtub capacitor (if present) to the mechanism frame (Figure 20). 7. Reconnect the leads to the respective terminals on the terminal block, and reattach the nylon strap to the frame to secure the lead bundle (Figure 21). 8. Reconnect the bushing leads to their respective bushings. Operational Checks An internal connection diagram of the recloser circuits is shown in Figure 24. The operating sequence for the various circuit components is diagrammed in Figure 25. These components should provide trouble-free operation with little or no maintenance. However, if the recloser does not operate properly, the following checks can be made to trouble-shoot the recloser circuits. NOTE: Procedures for checking, testing and troubleshooting the electronic control are provided in a separate manual (S28O-75-1). The recloser need not be untanked to perform these checks. CONTROL CABLE Using an ohmmeter, check the continuity between like pins and pin sockets of the connector plugs on either end of the elec- 12 1. Connect an ohmmeter between pin sockets E and F. The meter should read approximately 19 ohms. 2. With the yellow manual operating handle in the up position and the recloser contacts open, momentariIy apply 25 vdc to pin sockets F (+) and E (-). • The rotary solenoid should operate producing an easily distinguishable sound. Repeat two or three times. 3. Connect the ohmmeter across source side B and C phase bushings, or from source side C bushing to recloser ground (depending upon the recloser coil connection) and again energize the rotary solenoid. • The meter should indicate closing coil continuity (read the effective dc resistance of the closing coil) confirming that the closing solenoid contactor is closed. 4. With the rotary solenoid still energized, manually close the recloser with the closing tool. • The ohmmeter should indicate loss of continuity indicating that the closing solenoid contactor has opened. Switches (SW1, SW2, SW3) Table 2 shows switch for manual operating lever/recloser contact combinations. An ohmmeter connected across the designated pin sockets of the control cable receptacle will indicate zero for a closed contact and infinity for an open contact. TABLE 2 Switch Status. Recloser Contacts Manual Operating Lever SW1 Pin Sockets C&D SW2SW3 Pin Sockets F&N Pin Sockets A&N OPEN OPEN CLOSED DOWN UP UP OPEN OPEN CLOSED OPEN CLOSED CLOSED CLOSED CLOSED OPEN CURRENT TRANSFORMERS The current sensing transformers are mounted on the source side bushings underneath the head casting. The battery charger CT power source (if applicable) is mounted on the load side center bushing. S280-40-8 SW1 - MlCROSWITCH ON MAINSHAFT—CLOSED WHEN CLOSING SOLENOlD PLUNGER IS DOWN SW2 - MERCURY SWITCH ON MANUAL OPERATING HANDLE—CLOSED WHEN HANDLE IS UP ON “CLOSED” POSITlON. SW3 - MERCURY SWITCH *ON MAIN SHAFT—OPEN WHEN CLOSING SOLENOlD PLUNGER IS DOWN PLUNGER IS DOWN WHEN RECLOSER IS CLOSED NOTE 1: BATTERY CHARGING TRANSFORMER IS AN ACCESSORY. Figure 24. Internal connection diagram. 13 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions Figure 25. Sequential operation of contacts. 14 S280-40-8 SW2 SW1 SW3 TERMINAL BOARD ROTARY SOLENOID Figure 26. Location of circuit components on mechanism frame. 85696KMA 83379KMA Continuity Check 1. Connect an ohmmeter, in turn, to pin sockets K and N. K and H. and K and J to check the continuity of the three current sensing transformers. • The meter should read approximately 7 ohms, the d.c. resistance of each winding. 2. Connect the ohmmeter to pin sockets K and L to check the continuity of the battery charger CT winding, if used. • The meter should read approximately 1000 ohms. A zero ohms reading indicates the 0.2 mfd capacitor may be short circuited. Readings deviating more than + 20% from 1000 ohms indicates a damaged resistor or transformer winding. 3. Readings within this range indicate sufficient output to maintain control battery charge. NOTE: Ratio and polarity test-circuits shown are the effective circuits that contribute to the testing. Components not having an effect on the current flow are not shown. Dotted lines in the polarity-test circuit are test leads. Ratio Test for Sensing CT's 1. Connect all three phases of the recloser in series as shown in Figure 27 and close the recloser contacts with the manual closing tool. 2. Connect a 100 ampere a-c test current to test points 1 and 2. 3. Energize the 100 ampere test source. 4. Using a 0-500 millimeter check the current output across socket pins K-G, K-H, and K-J (Figure 27A). • The output of each CT should measure 100 ma + 10%. NOTE: Be sure to allow for the tolerances of meter being used. The resistance of certain type of meters is not negligible. Use as high a scale (lower resistance) as is accurately readable. 5. A 100 ma reading verifies the 1000:1 ratio of the sensing CT’s. If the 100 ma is not attained the CT winding is probably faulty. 6. De-energize the test source. Polarity Test for Sensing CT's 1. With the phases still connected in series from the previous test, connect the secondaries of the CT’s in parallel by connecting pin socket G to H to J and measure the output between pin sockets K and J as shown in Figure 27B. 2. Energize the 100 ampere a-c test source. A. All three transformers should have the same polarity; the output should measure 300 ma. B. If one transformer has its polarity opposite of the remaining two the output will measure 100 ma. 3. De-energize the test source and remove the jumper wire from the receptacle. Output Test of Battery Charging CT, if Used 1. With the phases still connected in series, energize 100 ampere a-c source. 2. Measure the output between pin socket K and L of the control cable receptacle. • Output should measure 40-60 ma. Figure 27. Test circuit for checking bushing current transformers. 15 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions SERVICE PARTS LIST The service parts and hardware listed and illustrated include only those parts and assemblies usually furnished for repair or involved in the maintenance procedures described in this manual. Further breakdown of listed assemblies is not recommended. Dimensions of all common hardware parts have been carefully checked so that they may be locally acquired. The suffix letter of the 14 character cataIog number for common hardware parts codes the plating of the part: A—No plating; raw material H—Silver M—Black oxide Q—Cadmium + zinc + chromate Y —Zinc + chromate Z —Electro zinc + bronze irridite Figure 28. Bushing parts group. 16 A hardware kit, Catalog No. KA849R1, contains an assortment of roll pins, cotter pins, retaining rings, stop nuts, etc.—common hardware parts used in Cooper Power Systems' reclosers that may not be readily locally available. To assure correct receipt of any part order, always include recloser type and serial number. Because of Cooper Power System's continuous improvement policy, there may be instances where the parts furnished may not look exactly the same as the parts ordered. However, they will be completely interchangeable without any rework of the recloser. AlI parts carry the same warranty as any whole item of switchgear, i.e., against defects in material or workmanship within a period of one year from date of shipment. S280-40-8 Bushing Parts (Figure 28) Item No. 1 2 3 4 5 Description Bushing Assembly Type RVE Below Serial No. 4000 (includes: bushing, corona shield (10), shield clamp (9), O-ring (11) and conductive gasket (8). Standard bushing Standard bushing with BCT accy. Above Serial No. 3999 Standard bushing Standard bushing with BCT accy. Type WVE Below Serial No. 2400 (includes: bushing, corona shield (10), shield clamp (9), O-ring (11) and conductive gasket (8). Standard bushing Standard bushing with BCT accy. Above Serial No. 2399 Standard bushing Standard bushing with BCT accy. Hex jam nut, 1/2-20, brass Flat washer Split lockwasher, med. 1/2, bronze Capscrew, hex hd, 3/8-16 x 2-1/4, stl. Catalog Number Qty Per Assy. Item No. 6 7 8 9 10 11 KA899R1 6 KA899R1 6 KA56RV1 6 KAS6RV2 6 6 12 13 14 15 16 KA56RV3 KA56RV4 K880725320050H KP2028A903 18 19 20 KA841W26 6 6 12 12 K900830050000A 6 K730101137225Q 18 Bushing calmp Clamping ring Lower bushing gasket Clamp Corona shield O-ring KP1109R KP1111 R KA1193R KP109WV KP582RV900 KP2000A19 Qty. Per Assy. 18 6 6 6 6 6 The following parts are applicable to the bushing current transformer accessory. Quantities shown for one current transformer. 17 KA841W1 Description Catalog Number 21 22 Bushing spacer Capscrew, hex hd, 3/8-16 x 1-7/8, stl. Transformer clamping flange Flange gasket Replacement current transformer 600:5 multi-ratio 1200:5 multi-ratio CT washer used with plastic housing CT’s Capscrew, hex hd, 3/8-16 x 1, stl. Transformer clamping sleeve O-ring gasket used with transformer clamping sleeve that has machined groove. Old style clamping sleeve, without groove, use KP2090A66. Hex nut, 3/8-16, stl. Stud KP275W1 1 K730101137187Q KP170W1 KP2090A73 3 1 2 KA159W1S KA132W 1 1 KP312W 1 K730101137100Q KP169W1 3 1 KP2000A64 K880201116037Q KP3149A40 1 3 3 17 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions Figure 29. Head and tank parts group. 18 S280-40-8 Tank and Head Assemblies (Figure 29) Item No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3O 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Description Receptacle and wiring bundle assembly Gasket Capscrew hex hd, 1/4-20 x 3/4, stl. Split lockwasher, med., 1/4, stl. Oil level dipstick O-ring gasket Closing coil instruction plate Self-tapping screw, Type Z. #2 x 5/16, sst. Capscrew, hex hd., 1/4-20 x 5/8 st 1. Manual closing tool access cover plate Cover plate gasket Capscrew, hex hd., 5/8-11 x 1-1/2, stl. Split lockwasher, med., 5/8, stl. Lifting lug Capscrew, hex, hd, 1/4-20 x 5/8, stl Split lockwasher, med., 1/4, stl. Auxiliary switch cover plate Gasket Ground connector Head casting includes control shaft bushings Head gasket Cable clamp Cable clamp Machine screw, rd., hd., 8-32 x 5/16 stl. Split lockwasher med. #8, stl. Current transformer support Spacer Current transformer Flat washer, #14S, brass Split lockwasher, med., 1/4, stl. Machine screw, rd., hd., 1/4-20 x 2, stl. Hex nut 10-24 stl. Split lockwasher, med., #10, stl. Resistor, wirewound, 100 ohm, 25 watt Bracket Machine screw, rd., hd., 10-24 x 2-1 /4, stl. Self-tapping screw, Type Z. #4 x 3/16, sst. Voltage data plate Nameplate Type RVE Type WVE Thread cutting screw, Type T #12 x 1/2, sst. Catalog Number KA33RE1 KP611R Qty. Per Assy. 1 1 K7301001125075Q K90080l025000Z KA363R KP2000A9 KP2312R 4 4 1 1 1 K801515002031 A 2 K730101125062Q 2 KP246R1 KP2000A12 1 1 K730101162150Q K900801062000Z KP456H2 2 2 2 K730101125062Q K90080l025000Z KP609R KP611R KA392R 4 4 1 1 1 KA840R KP2103A8 KP2006A1 KP2006A2 1 1 2 4 K721501108031 Z K90080l008000Z KP145RE KP3009A38 KA86RE1 K900525026056A K900801025000A 6 6 6 6 3 12 6 K721501125200Z K881001124010Z K900801010000Z 6 3 3 KP4022A31 KP238E 3 3 K721501110225Z 3 K801515004018A KP567R 4 1 KP2RVE KP103WVE 1 1 Item No. 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 Cover plate Manual operating handle assembly Spacer Retaining ring, Type C, 5/16, sst WA516 Roll pin 1/8 x 3/4 Shaft and lever assembly Spacer Flat washer, #14S, brass Cotter pin, 3/32 x 1/2, brass Roll pin, 3/32 x 1/4, stl. Link Pin Retaining ring, Type C, 3/16, sst. WA510 Groove pin Spacer Retaining ring, Type C, 3/8, sst., WA518 Spacer Indicator and support assembly Spacer Groove pin Spacer Capscrew, hex hd., 1/2-13 x 3-1/4, stl. Flat washer Pipe plug, 1-in., sq. hd. Tank liner kit Tank Pipe plug, 1/2-in., sq. hd. Oil sample and drain valve assembly Tank data plate Qty Per Assy. KP283R 1 KA477R KP3009A39 1 1 K970915312000A K970801125075C KA319R KP3007A8 K900525026056A K970525093050A K970801093050C KP137RE KP3190A11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 K970915183000A KP3126A4 KP3006A9 3 1 1 K970915375000A KP3013A93 KA19RE KP3013A38 KP3126A4 KP3013A11 2 1 1 3 1 1 K730101150325Q KP2027A23 KP2007A4 KA867R KA88W KP2007A3 10 10 1 1 1 1 KA809R KP101WE 1 1 The following parts are applicable to the CT-Type battery charger power source, if used. 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 K781515112050A Description Catalog Number Split lockwasher, med., #6, stl. Machine screw, rd., hd., 6-32 x 5/16 stl. Hex nut 10 24 stl Split lockwasher, med., #10, stl. Flat washer, #14S, brass Resistor, wirewound, 1K, 25W Bracket Machine screw, rd., hd., 10-24 x 2-1/4 stl. Current transformer support Spacer Current transformer Split lockwasher, med., 1/4, stl. Machine screw, rd., hd., 1/4-20 x 2, stl. Capacitor, 0.2 mfd, 2500 wvdc K900801006000Z 2 K721501106031 Z K881001124010Z K900801010000Z K900525026056A KP4022A36 KP238E 2 1 1 3 1 1 K721501110225Z KP145RE KP3009A38 KA86RE1 K900801025000A 1 2 2 1 2 K721501125200Z KP4004A8 2 1 5 19 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions Figure 30. Closing coil solenoid mechanism parts group. 20 S280-40-8 Closing Coil Mechanism (Figure 30) Item No. 1 2 3 4 S 6 7 8 9A 9B 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Description Capscrew skt. hd. 1/2-13 x 4-1/2, stl Split lockwasher, med., 1/2, stl. Spacer Operating lever coupler Indicator shaft coupler Contactor toggle spring Groove pin Retaining ring WA514, Type C, 1/4, stl. Closing coil contactor assembly, below 30 kv Closing coil contactor assembly above 30 kv Capscrew with preassembled split lockwasher, 1/4-20 x 1/2, stl. Machine screw, rd. hd., 1 /4-30 x 1/2 brass Split lockwasher, med., 1/4, bronze Hex nut, 1/4-20, brass Fuse retaining clip Closing coil fuse assembly (also included in closing coil replacement kit, item 27) 2.4-3.3 kv (2 red color bands) 4.15-6 kv (black color band) 7.2 to 11 kv (yellow color band) 12 to 14.4 kv 17.0 kv, 34.5 kv (red color band) Fuse mounting bracket Lead assembly Flat washer, 3/8 SAE, stl. Groove pin Retaining ring WA518, Type C, 3/8, stl. Plunger and link assembly Upper stringer assembly Hex nut, 3/8-16 stl. Split lockwasher, med. 3/8, stl. Capscrew, hex hd., 3/8-16 x 1-1/4, stl. Solenoid frame Closing coil replacement kit (includes closing coil, lower coil gasket 28, two fuse assemblies 15 and voltage data plate, 38 Figure 29) 2.4 kv 3.3 kv 4.16-4.8 kv 6.0 kv 7.2-8.32 kv 11.0 kv 12.0-13.2 kv 17.0 kv 23.0-24.9 kv 34.5 kv Reclosers with low voltage closing 48 vdc 125 vdc 250 vdc Catalog Number Qty. Per Assy. Item No. 28 29 30 31 KP2036A3 K900801050000M KP3182A1 KP1177R KP1056R1 KP141R1 KP1306R 6 6 6 1 1 2 1 KP970901250000M 4 KA430R3 1 KA1143R1 1 K830101125050A 3 K721525125050A 6 37 38 39 40 41 K900830025000A K881025120025A KP2006A16 6 8 2 42 43 44 2 KA259R904 KA259R901 45 46 47 KA259R902 48 KA259R903 KP257L KA28W1 K900201037000A KP3126A2 2 2 2 1 K970901375000M KA50R KA62R K880201116037A K900801037000Z 2 1 4 4 12 K730101137125A KP100R1 12 1 KA834R1 KA834R10 KA834R2 KA834R6 KA834R3 KA839R9 KA834R4 KA834R12 KA834R13 KA834R14 KA834R16* KA834R7* KA834R8* 32 33 34 35 36 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 Description Lower solenoid gasket Solenoid bridge plate assembly Solenoid frame post Machine screw, rd. hd., 8-32 x 3/4 stl. Cable clip Split lockwasher, med., No. 8, stl. Hex nut, 8-32, stl. Trip solenoid assembly Capscrew, hex. hd., 1/4-30 x 1/2 stl. Flat washer 1/4 SAE, stl. Hex nut, 1/4-20, stl. Insulator Terminal block Machine screw, fil. hd, 6-32 x 5/8, stl. Lead wire assembly Hex nut 6-32, brass Machine screw, rd. hd., 6-32 x 1/2 brass Mercury switch (SW 3) Mounting clip Machine screw, rd. hd., 8-32 x 7/16 stl. Machine screw, rd. hd., 6-32 x 1 brass Internal tooth lockwasher, No. 6, bronze Hex nut, 6 32, brass Microswitch (SW 1) Rotary solenoid assembly Type RVE below serial 3173 and Type WVE below serial 1839 Type RVE above serial 3251 and Type WVE above serial 1901 Hex nut 1/4-28, stl. Flat washer, No. 14S, brass Split lockwasher, med., 1/4, stl. Groove pin Retaining ring WA510, Type C, 3/16, stl. Spring Spacer Cotter pin, 3/32 x 1, brass Mercury switch assembly (SW 2) Toggle assembly Type RVE Below Serial No. 3173 Serial No. 3251 and above Type WVE Below Serial No. 1839 Catalog Number Qty. Per Assy. KP389R KA644R1 KP1669R 1 1 4 K721501108075Z KP2006A8 5 7 K900801008000Z K881001132008Z KA11RVE 4 5 1 K730101125050Y K900201025000Z K880201120025Y KP2101 A209 KP2101A9 1 2 1 1 1 K721801106062Z KA62RE K881025132006A 2 1 1 K721525106050A KP134RE1 KP2006A19 1 1 4 K721501108043Z 4 K721525106100A 2 K901032006000A K881025132006A KP2181A16 4 2 1 KA12RE1 1 KA61WE K881001328025Z K900525025056Z K900801025000Z KP3123A3 1 4 2 2 1 K970901188000M KP98L KP3007A30 K970525093100A 2 1 1 1 KA63RE1 1 KA450R3 KA166W 1 1 KA450R1 1 * No fuses are used with the low-voltage dc coils. When converting a recloser for low-voltage operation use low-voltage contactor and coil kit KA887R; specify desired operating voltage (Vdc or Vac). 21 Types RVE and WVE Maintenance Instructions Figure 31. Interrupter mechanism parts group. 22 S280-40-8 Interrupter Mechanism Parts List (Figure 31) Item No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Description Capscrew, hex hd., 3/8-24 x 7/8, silver bronze Split lockwasher med. 3/8, brz. Flat washer, #24S, brass Lead (6 per bushing) Capscrew with preassembled split lockwasher, 1/4-20 x 1/2, stl Contact rod guide Retaining ring, Type C, 5/16 st1., WA516 Flat washer, 5/16 AN, stl. Groove pin Moving contact rod assembly Type RVE, phases A & B Type RVE phase C Type WVE phases A & B Below Serial No. 1839 Serial No. 1900 and above Type WVE, phase C Below Serial No. 1839 Serial No. 1900 and above Stringer assembly Catalog Number Qty. Per Assy. K700122227087A K900830037000A K900525039087H KP3250A1 6 6 6 36 K830101125050A KP346W2 6 3 K970901312000M K900201032056Z KP3125A2 6 6 3 KA44RV2 KA44RV1 2 1 KA29WV2 KA165W2 2 2 KA29WV1 KA165W1 KA62R 1 1 9 Item No. 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Description Flat washer, 3/8, stl. Split lockwasher, med., 3/8, stl. Hex nut, 3/8-16, stl. Interrupter assembly Type RVE, phases A & B Type RVE phase C Type WVE phases A & B Below Serial No. 1839 Serial No. 1900 and above Type WVE, phase C Below Serial No. 1839 Serial No. 1900 and above Moving contact assembly Type RVE Type WVE Roll pin, 1/8 x 5/8, stl. Spacer Flat washer, 5/16, stl. Stop nut, 5/16 Lead Assembly Type RVE (4 per assembly) Type WVE (6 per assembly) Catalog Number Qty. Per Assy. K900201037000A K900801037000Z K880201116037A 9 9 9 KA49RV2 KA49RV1 2 1 KA28WV2 KA168W2 2 2 KA28WV1 KA168W1 1 1 KA46RV1 KA105DV1 K970801125062M KP1505R K900201031000Z KP2020A4 3 3 3 3 3 3 KP3250A1 KP3250A1 24 36 23 Cooper Power Systems Quality from Cooper Industries ©1991 Cooper Industries, Inc. P.O. Box 2850 • Pittsburgh, PA 15230 KDL 7/05