1. What is your gender? 1 2 61 %
advertisement
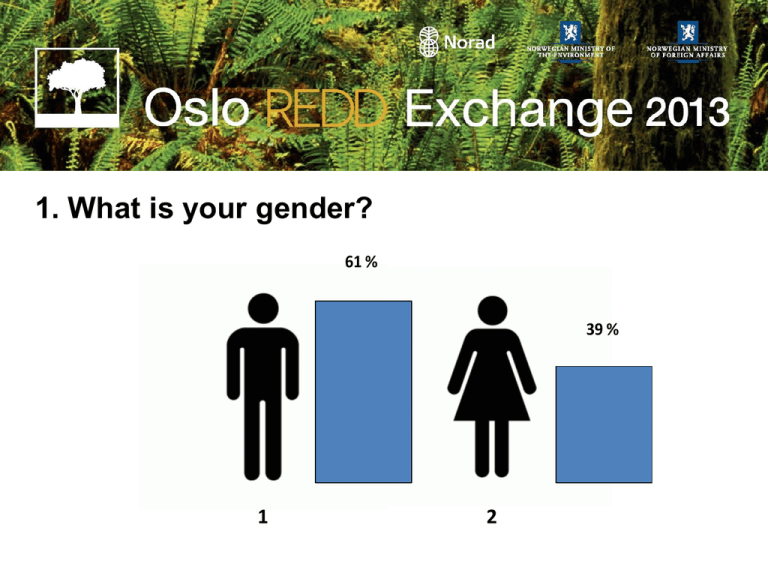
1. What is your gender? 61 % 39 % 1 2 2. What is your primary regional perspective? 1. Africa 24 % 2. Asia 22 % 3. Latin America 25 % 4. Europe/ North America/ Australia 29 % 3. What is your primary professional affiliation? 1. Government/Multilateral Organization 40 % 2. Private Sector 8% 3. Civil Society 29 % 4. Research 23 % 4. Which is the most urgent area for agreement in REDD+ negotiations – finance or rules? 1. Mainly finance 15 % 2. Both, but agreement on finance is more urgent 34 % 3. Equally urgent 19 % 4. Both, but agreement on rules is more urgent 26 % 5. Mainly rules 6% 5. What should be the criteria for allocating international funding – emission reductions or non-carbon benefits? 1. Mainly based on emission reductions 22 % 2. Both, but with emphasis on emissions reductions 30 % 3. Equally important 19 % 4. Both, but with emphasis on non-carbon benefits 24 % 5. Mainly based on non-carbon benefits 5% 6. What is the most important domestic constraint on REDD+? 1. Lack of clear forest tenure 15 % 2. Lack of institutions for coordination across sectors 20 % 3. Lack of institutions and capacity for MRV 10 % 4. Lack of political will or motivation for action 42 % 5. Lack of institutions for REDD+ finance and benefit-sharing 13 % 6. What is the most important domestic constraint on REDD+? Lack of clear forest tenure Lack of institutions for coordination across sectors Africa Lack of institutions and capacity for MRV Lack of political will or motivation for action 0% 10 % 20 % 30 % 40 % Lack of institutions for REDD+ finance and benefit-sharing 6. What is the most important domestic constraint on REDD+? Lack of clear forest tenure Lack of institutions for coordination across sectors Asia Lack of institutions and capacity for MRV Lack of political will or motivation for action 0% 20 % 40 % 60 % Lack of institutions for REDD+ finance and benefit-sharing 6. What is the most important domestic constraint on REDD+? Lack of clear forest tenure Lack of institutions for coordination across sectors Latin America Lack of institutions and capacity for MRV Lack of political will or motivation for action 0% 10 % 20 % 30 % 40 % Lack of institutions for REDD+ finance and benefit-sharing 6. What is the most important domestic constraint on REDD+? Lack of clear forest tenure Lack of institutions for coordination across sectors Europe/ North America/ Australia Lack of institutions and capacity for MRV Lack of political will or motivation for action 0% 20 % 40 % 60 % 80 % Lack of institutions for REDD+ finance and benefit-sharing 7. What is the most important international constraint on REDD+? 1. demand for commodities that convert or degrade forests 21 % 2. insufficient North-South financial transfers 11 % 3. lack of an overall climate agreement and rules for REDD+ 44 % 4. availability of finance for activities that convert or degrade forests 10 % 5. lack of a market for forest carbon credits 14 % 8. At what level is increased attention and investment most urgent and important? 1. national level 26 % 2. jurisdictional level 25 % 3. landscape level 19 % 4. community level 27 % 5. the current allocation is appropriate. 3% 8. At what level is increased attention and investment most urgent and important? Government/Multilateral Organization 0% national level landscape level the current allocation is appropriate. 10 % 20 % jurisdictional level community level 30 % 40 % 8. At what level is increased attention and investment most urgent and important? Private Sector 0% 10 % 20 % national level landscape level the current allocation is appropriate. 30 % 40 % jurisdictional level community level 50 % 60 % 8. At what level is increased attention and investment most urgent and important? Civil Society 0% 5% 10 % national level landscape level the current allocation is appropriate. 15 % 20 % 25 % jurisdictional level community level 30 % 35 % 8. At what level is increased attention and investment most urgent and important? Research 0% 5% 10 % national level landscape level the current allocation is appropriate. 15 % 20 % jurisdictional level community level 25 % 30 % 9. What is the highest priority for attention to REDD+ safeguards and synergies? 1. Land tenure and rights 51 % 2. Poverty 26 % 3. Gender equality 3% 4. Biodiversity 8% 5. Food security 12 % 9. What is the highest priority for attention to REDD+ safeguards and synergies? land tenure and rights poverty Male gender equality biodiversity Female food security 0% 20 % 40 % 60 % 10. What is the highest priority for addressing commodity supply chain impacts? 1. Link to sustainable jurisdictions in forest countries 27 % 2. Commodity-specific roundtables and voluntary certification 10 % 3. Voluntary corporate commitments to responsible sourcing 8% 4. Financiers sensitized to deforestation risk 18 % 5. Demand-side policies in consumer countries 37 % 11. What is the highest priority for action in forest countries? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Link REDD+ to poverty reduction, food security, and adaptation to climate change Strengthen transparency of forest-related information and accountability 18 % Link REDD+ to transformational change with respect to tenure, community rights, and gender 22 % Strengthen rules for benefit-sharing 4% Link supply chain and REDD+ metrics at jurisdictional levels 13 % 43 % 12. What is the highest priority for international action? 1. Commit significant payment-for-performance funding 26 % 2. Accelerate negotiations toward an overall climate agreement 40 % 3. Remove deforestation from global commodity supply chains 21 % 4. Make remotely-sensed data on forests more accessible 3% 5. Create markets for forest carbon credits 10 %






