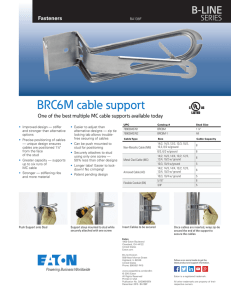
CYME
Power Engineering Software and Solutions
Real-Time Thermal Rating
Compute future cable ampacity, estimate conductor
temperature and compute emergency ratings
The CYMCAP/RTTR Real
Time Thermal cable Rating
software extends the
monitoring functionality and
forecasts the behavior of the
installation under emergency
situations. It is designed
to provide both steadystate and transient thermal
analysis. It is based on the
IEC Standards 60287©,
60853© and/or on the
finite element method
depending on the type of
installation. This function
allows the user to manage
contingency and emergency
situations more efficiently.
Numerous underground
transmission projects are
emerging worldwide. Each
project requires a substantial
investment of time and money
in an industry where lack of
reliability and blackouts are not
acceptable anymore.
It is a universal practice to use
Distributed Temperature Sensing
(DTS) systems based on fiber
optic technology to monitor
the cables temperature along
the cables run. To supplement
this technology, the CYMCAP/
RTTR Real Time Thermal cable
Rating software was designed
to extend the monitoring
functionality and predict/forecast
the behavior of the installation
under emergency situations.
The software is designed to
provide both steady-state and
transient thermal analysis. It
is based on the IEC Standards
60287© and/or 60853© or
finite elements. This function
allows managing contingency
and emergency situations more
efficiently.
Operating Modes
The Real-time Thermal Rating
software is based on the
CYMCAP software and has two
modes of operation:
•
Estimating the conductor
temperature from the fiber
optic measured temperature
•
Computing emergency ratings
with the transient engine
CYMCAP Model and results for a
multi-layer installation
Real-Time
Thermal Rating
Compute future cable
ampacity, estimate
conductor temperature and
compute emergency ratings.
Modeling Capabilities
Emergency Rating
Computational Procedures
Virtually every cable construction
available in the market can be
modeled with the CYMCAP
software: one-core, three-core,
sheathed cables, concentric
neutrals, armored cables,
screens, shields, beddings,
servings, jackets, etc. The
following installation types
can be modeled: duct banks,
backfills, directly buried, buried
ducts, buried pipes, cables in
air (including groups of cables
and riser poles) and cables in
tunnels. The CYMCAP software
is its ability to model several
materials with different thermal
resistivities, for example:
stratified soil layers, multiple
duct banks and multiple backfills.
The CYMCAP/RTTR software
provides the following
information of high importance
to the cable operator:
When there are available realtime measurements of both
the temperature at the fiber
location (cable surface, etc.)
and the current, the software
uses the IEC 60853© Standard
to conveniently compute
the temperature of the core
conductor. When only the
temperature at the location
of the fiber optic sensor is
available, the temperature of the
core can be determined from
the IEC 60287© Standard.
•
Given the emergency time
during which an emergency
overload is applied, the
CYMCAP/RTTR software
predicts the temperature of
the cable at the end of an
emergency period.
•
Given the maximum
admissible emergency
temperature and the applied
(over) load, the CYMCAP/RTTR
software gives the maximum
time the cable can be
overloaded before exceeding
the specified admissible
emergency temperature.
•
Given the maximum
admissible emergency
temperature and the time
for an emergency overload,
the software computes the
maximum current that the
circuit can carry while not
exceeding the emergency
temperature.
Transient Calculations
Cable operating temperature
very much depends on the
history of the load applied
to the cable. In other words,
the operating temperature
of a cable depends on the
intensity of the current and its
variation over time. The thermal
inertia of the cable installation
determine how far in the past
the loading history can affect
the operating temperature at
the current time or how fast the
core temperature changes in
response to the load variation.
A typical response to a step
overload of 100% lasting 12
hours is shown in the figure
below. One can appreciate
that the temperature of the
cable exponentially follows the
changes in current.
Emergency Rating options
Eaton
1000 Eaton Boulevard
Cleveland, OH 44122
United States
Eaton.com
CYME International T&D
1485 Roberval, Suite 104
St.Bruno, QC, Canada J3V 3P8
P: 450.461.3655 F: 450.461.0966
P: 800.361.3627 (Canada/USA)
CymeInfo@eaton.com
www.eaton.com/cyme
© 2015 Eaton All Rights Reserved
Printed in Canada
Publication No. BR 917 031 EN
November 2014
Eaton is a registered trademark.
All other trademarks are property
of their respective owners.
Follow us on social media to get the
latest product and support information.