Energy & the Environment The Story of an Addict
advertisement

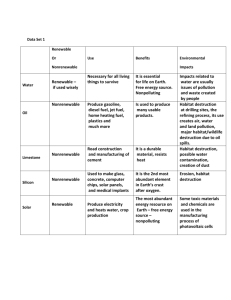
Energy & the Environment The Story of an Addict Energy & Environmental Politics • Energy consumption is a primary source of pollution • Energy production is a primary source of habitat destruction • Patterns of Energy Consumption & Production • Economic Implications • Stability of supply & price • Industry sensitivities • Regional/geographic sensitivities Clash of Values • Unfettered economic growth v environmental regulation • Pollution control v. pollution avoidance • Conservation v supply • land use values: economic exploitation v preservation • government v market • liberty v government social regulation Consumption & Production Patterns How Do We Use Energy? • Residential/Commercial = 35% • Industrial = 37% • Transportation = 28% U.S. Domestic Energy Consumption by Source 100 80 60 40 20 0 19 50 19 54 19 58 19 62 19 66 19 70 19 74 19 78 19 82 19 86 19 90 19 94 19 98 Quadrillion BTUs 120 Solar Biofuels Geothermal Hydroelectric Nuclear Coal Natural gas Petroleum Comparative Consumption per Capita (1997) million Btu/pop 350 300 250 200 France Germany Japan 150 Switzerland 100 UK 50 0 US Comparative Consumption per GDP(1997) 1000 Btus/$ GDP 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 France Germany Japan Switzerland UK US What do we Pay for Energy? What Difference Does it Make? Comparison of Fuel Prices per Gallon ($1999) US Canada Mexico Germany UK Japan Korea Gasoline Diesel 1.47 2.04 1.92 3.78 5.13 3.65 4.09 1.36 1.68 1.36 2.90 4.77 2.89 1.95 Industrial Heavy Oil 36.33 36.67 40.48 39.81 43.65 Sources of Electricity % Generation 60 50 40 30 Coal Oil Gas 20 Nuclear 10 Hydro 0 Price of Electricity Cents per KWh (constant $) 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 6 19 0 65 9 1 7 19 0 75 9 1 8 19 0 85 9 1 90 9 1 95 9 1 Impact of Cheap Energy • wasteful use of energy resources • ignoring conservation & energy efficiency • Increases pollution • blocks entry of alternative, non-fossil fuel • decreases US production (where extraction costs are high) • increase is dependence on foreign suppliers Pollution Impact Particulate Emissions by Energy Source 500 400 300 200 100 0 Electrical Utilities Other Industrial Motor Vehicles Residential Off Highway Vehicles SO2 Emissions by Energy Source 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 0 Electrical Utilities Other Industrial Motor Vehicles Residential Off Highway Vehicles NOx Emissions by Energy Source 8,000 7,000 6,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 Electrical Utilities Other Industrial Motor Vehicles Residential Off Highway Vehicles VOC Emissions by Energy Source 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 Electrical Utilities Other Industrial Motor Vehicles Residential Off Highway Vehicles CO Emissions by Energy Source 60000 50000 40000 30000 20000 10000 0 Electrical Utilities Other Industrial Motor Vehicles Residential Off Highway Vehicles Coal • Extraction • Habitat destruction • Spoils • acid leaching • landscape leveling • hydrological disruption • Processing & Use • Air Pollution • Water pollution • Climate Change Oil & Gas • Extraction • Habitat destruction • drilling structures, pipelines, & access roads • Processing & Use • • • • Air Pollutants Water Pollution Climate Change Oil Spills Nuclear • Extraction • Habitat destruction • Spoils • radioactive • Processing & Use • radioactive waste • radiation • thermal pollution Hydro Power • Extraction • Habitat destruction • Water Pollution • Processing & Use • Habitat/ecologic al destruction • hydrologic disruption • Landscape change Wind • Extraction • Habitat destruction • Water Pollution • Processing & Use • Habitat/ecologic al destruction • Wildlife kills Autos US Vehicles Miles per capita Vehicle Miles per Capita 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 1900 1920 1940 1960 Year 1980 2000 Auto Fuel Efficiency 25 Miles per Gallon 20 15 Cars Light Trucks 10 5 0 7 19 0 7 19 5 8 19 0 8 19 5 9 19 0 9 19 5 0 20 0 0 20 5 Environmental Impact of Cars & Trucks • Air Pollution • 20% Greenhouse Gases • 1 mpg increase in efficiency • Î 6400 pound reduction in GHG • Î $300 increase in car cost for fuel − USPIRG Report • soil & water pollution from fueling stations, lubricants, etc. Environmental Impact of Cars & Trucks • Fossil fuel demand • 10 mpg increase in fuel efficiency Î 7 bb oil reduction over ten years • ANWR = ~ 7-14 bb oil • 10 mpg increase in fuel efficiency Î 380 million ton annual decrease in CO2 emissions • ~ 7 % of US total • Roadways (> 6 million miles) • Use up land • Fragment landscape Energy Resource Politics U.S. Oil Fields U.S. Coal Mines U.S. Nuclear Fuel Storage