HYPOTHESIS
advertisement

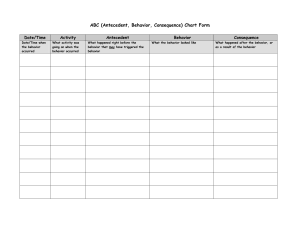
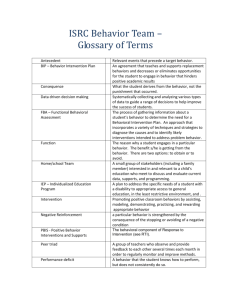
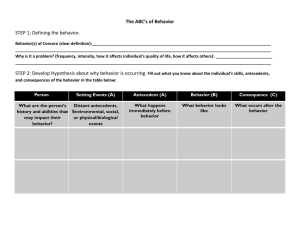
Testable Hypothesis: Summary Statement Context (Setting Event): Triggers: Positive Behavior Supports: Problem Behaviors (s): New Behavior: Get or Avoid: Consequences: HYPOTHESIS: ____________________________________ engages in ____________________________ when (Student’s Name) (Problem Behavior) _______________________________________________ occurs in order to get or avoid _______________________________. (Trigger) (Circle one) (Attention/activities/tangibles/sensory) This behavior is more likely to occur when ________________________________________________. (Context) Building a Testable Hypothesis : A guide 1. What does the problem behavior LOOK like? 2. What are the situations or events that seem to SET UP the behavior and make the problem behavior more likely to occur? 3. Are there any “triggers” that occur before the behavior, that always SET OFF the behavior? 4. What does the student “GET” or “AVOID/ESCAPE” by continuing the behavior? How is FBA information used to guide development of a behavior intervention plan? Setting Event Triggering Antecedent(s) Behavior or Response Class Maintaining Consequence(s) Add antecedent events that trigger desired behavior Remove antecedent events that trigger problem behavior Add consequence events that maintain and support desired behavior Remove consequence events that maintain problem behavior Neutralize, prevent, remove, minimize, or precorrect for influence of setting events. Teach alternative and desired behavior that is more efficient and relevant than problem behavior Function Based Intervention Planning Sandra Crosson, 2005 Interventions to change context (Positive Behavior Supports): Interventions to prevent trigger (Positive Behavior Supports): Interventions to teach new behaviors: (new/replacement behaviors): Consequent strategies (consequences/recognition & reward)