TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED
advertisement
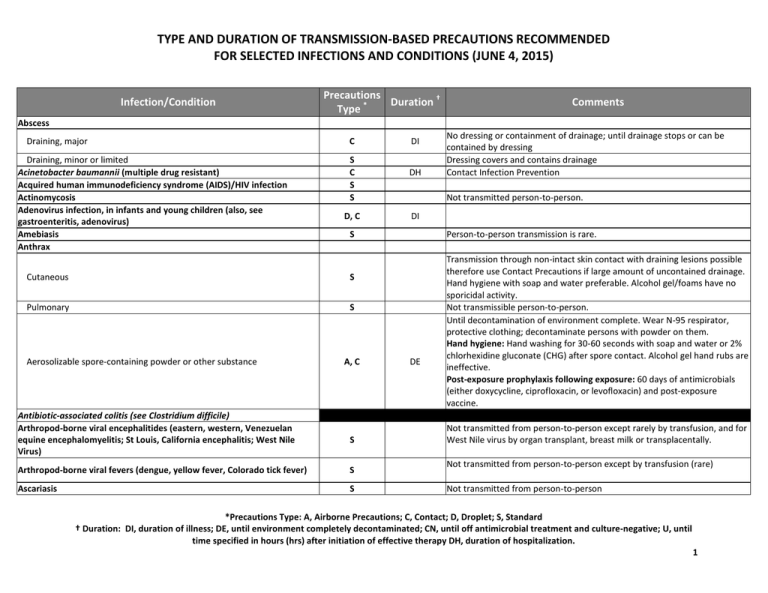
TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Precautions Duration † * Type Comments Abscess Draining, major Draining, minor or limited Acinetobacter baumannii (multiple drug resistant) Acquired human immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)/HIV infection Actinomycosis Adenovirus infection, in infants and young children (also, see gastroenteritis, adenovirus) Amebiasis Anthrax C S C S S D, C S Pulmonary S Antibiotic-associated colitis (see Clostridium difficile) Arthropod-borne viral encephalitides (eastern, western, Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis; St Louis, California encephalitis; West Nile Virus) DH A, C S Arthropod-borne viral fevers (dengue, yellow fever, Colorado tick fever) S Ascariasis S No dressing or containment of drainage; until drainage stops or can be contained by dressing Dressing covers and contains drainage Contact Infection Prevention Not transmitted person-to-person. DI S Cutaneous Aerosolizable spore-containing powder or other substance DI Person-to-person transmission is rare. DE Transmission through non-intact skin contact with draining lesions possible therefore use Contact Precautions if large amount of uncontained drainage. Hand hygiene with soap and water preferable. Alcohol gel/foams have no sporicidal activity. Not transmissible person-to-person. Until decontamination of environment complete. Wear N-95 respirator, protective clothing; decontaminate persons with powder on them. Hand hygiene: Hand washing for 30-60 seconds with soap and water or 2% chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) after spore contact. Alcohol gel hand rubs are ineffective. Post-exposure prophylaxis following exposure: 60 days of antimicrobials (either doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, or levofloxacin) and post-exposure vaccine. Not transmitted from person-to-person except rarely by transfusion, and for West Nile virus by organ transplant, breast milk or transplacentally. Not transmitted from person-to-person except by transfusion (rare) Not transmitted from person-to-person *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 1 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Aspergillosis Precautions Duration † * Type Contact Precautions and Airborne Precautions if massive soft tissue infection with copious drainage and repeated irrigations required S Avian influenza (see influenza, avian below) A, D, C Babesiosis Blastomycosis, cutaneous or pulmonary Botulism Bronchiolitis (see Respiratory infections in infants and young children) S S S C Brucellosis S Campylobacter gastroenteritis (see Gastroenteritis) Candidiasis, all forms Cat-scratch fever S S Cellulitis S Chancroid (soft chancre) Chickenpox (see varicella) Chlamydia trachomatis Conjunctivitis Genital Pneumonia (infants <3 mos of age) Chlamydia pneumoniae Cholera (see gastroenteritis) Closed-cavity infection Open drain in place; limited or minor drainage No drain or closed drainage system in place Clostridium C. botulinum S Comments 7 days after onset of symptoms DI Not transmitted from person-to-person except rarely by transfusion, Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person Use mask according to Standard Precautions Not transmitted from person-to-person except rarely via banked spermatozoa and sexual contact. Provide antimicrobial prophylaxis during lab exposure. Notify Infection Prevention. Notify laboratory personnel before sending specimens if disease is suspected. Not transmitted from person-to-person S S S S S S Contact Precautions if there is copious uncontained drainage S Not transmitted from person-to-person *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 2 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition C. difficile (see Gastroenteritis, C. difficile) C. perfringens Food poisoning Gas gangrene Coccidioidomycosis (valley fever) Precautions Duration † * Type C S Pneumonia S Colorado tick fever S Congenital rubella C Conjunctivitis Acute bacterial Chlamydia Gonococcal S S S Acute viral (acute hemorrhagic) Coronavirus associated w/ SARS or MERS (see Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome or Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome) Coxsackie virus disease (see enteroviral infection) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (including variant CJD) CJD, vCJD See IP website S S Draining lesions C S Comments Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person except under extraordinary circumstances because the infectious arthroconidial form of Coccidoides immitus is not produced in humans. Notify laboratory personnel prior to specimen submission if disease is suspected. Not transmitted from person-to-person except under extraordinary circumstances (e.g., inhalation of aerosolized tissue phase endospores during necropsy, transplantation of infected lung) because the infectious arthroconidial form of Coccidiodes immitus is not produced in humans. Not transmitted from person-to-person Until 1 yr. of Standard Precautions if nasopharyngeal and urine cultures repeatedly neg. age after 3 mos. of age DI Adenovirus most common; enterovirus 70, Coxsackie virus A24 also associated with outbreaks in eye clinics, pediatric and neonatal settings, institutional settings reported. Eye clinics follow Standard Precautions when handling patients with conjunctivitis. Routine use of infection control measures when handling instruments and equipment prevents occurrence of outbreaks in this and other settings. Use disposable instruments or special sterilization/disinfection for surfaces, objects contaminated with neural tissue if CJD or vCJD suspected and has *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 3 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Precautions Duration † * Type Comments not been R/O; No special burial procedures. Croup (see respiratory infections in infants and young children) Crimean-Congo Fever (see Viral Hemorrhagic Fever) Cryptococcosis Cryptosporidiosis (see gastroenteritis) Cysticercosis Cytomegalovirus infection, neonatal or immunosuppressed Decubitus ulcer (see Pressure ulcer) Dengue fever Diarrhea, acute-infective etiology suspected (see gastroenteritis) Diphtheria Cutaneous Pharyngeal Ebola virus (see viral hemorrhagic fevers) Echinococcosis (hydatidosis) Echovirus (see enteroviral infection) Encephalitis or encephalomyelitis (see specific etiologic agents) Endometritis (endomyometritis) Enterobiasis (pinworm disease, oxyuriasis) Enterococcus species (see multidrug-resistant organisms if epidemiologically significant or vancomycin resistant) Enterocolitis, C. difficile (see C. difficile, gastroenteritis) S Not transmitted from person-to-person, except rarely via tissue and corneal transplant. S S Not transmitted from person-to-person No additional precautions for pregnant HCWs S Not transmitted from person-to-person C D CN CN S Until 2 cultures taken 24 hrs. apart negative Until 2 cultures taken 24 hrs. apart negative Not transmitted from person-to-person S S Enteroviral infections S Epiglottitis, due to Haemophilus influenzae type b Epstein-Barr virus infection, including infectious mononucleosis Erythema infectiosum (also see Parvovirus B19) Escherichia coli gastroenteritis (see gastroenteritis) Food poisoning Botulism D S S S U 24 hrs Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent children for duration of illness and to control institutional outbreaks See specific disease agents for epiglottitis due to other etiologies Not transmitted from person-to-person *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 4 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition C. perfringens or welchii Staphylococcal Precautions Duration † * Type Comments S S Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person Furunculosis, staphylococcal S Contact if drainage not controlled or MRSA Infants and young children Gangrene (gas gangrene) C S Gastroenteritis S Adenovirus S Campylobacter species S Cholera S C. difficile (suspected or confirmed) C Cryptosporidium species S E. coli Enteropathogenic O157:H7 and other shiga toxin-producing Strains S Other species S Giardia lamblia S Noroviruses S DI DI Not transmitted from person-to-person Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks for gastroenteritis caused by all of the agents below Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Do not share electronic thermometers; ensure consistent environmental cleaning and disinfection. Bleach solutions is required for cleaning. Hand hygiene with soap and water preferred because of the absence of sporicidal activity of alcohol in waterless antiseptic hand rubs. Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks. Persons who clean areas heavily contaminated with feces or vomitus may benefit from wearing masks since virus can be aerosolized from vomitus and feces; ensure *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 5 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Precautions Duration † * Type Rotavirus C Salmonella species (including S. typhi) S Shigella species S Vibrio parahaemolyticus S Viral (if not covered elsewhere) S Yersinia enterocolitica S German measles (see rubella; see congenital rubella) Giardiasis (see gastroenteritis) Gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum (gonorrheal ophthalmia, acute conjunctivitis of newborn) Gonorrhea Granuloma inguinale (Donovanosis, granuloma venereum) Guillain-Barré’ syndrome Hand, foot, and mouth disease (see enteroviral infection) Hansen’s Disease (see Leprosy) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome Helicobacter pylori Hepatitis, viral Type A Diapered or incontinent patients DI Comments consistent environmental cleaning and disinfection. Bleach solutions may be required when continued transmission. Alcohol less active, but there is not evidence that alcohol antiseptic hand rubs are not effective for hand decontamination. Cohorting of affected patients to private rooms may interrupt transmission. Ensure consistent environmental cleaning and disinfection; prolonged shedding may occur in the immunocompromised Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness or to control institutional outbreaks S S S S S S Not transmitted from person-to-person S Provide hepatitis A vaccine post exposure as recommended Maintain Contact Precautions in infants and children <3 years of age for duration of hospitalization; for children 3-14 yrs. of age for 2 weeks after C *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 6 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Precautions Duration † * Type Type B-HbsAg positive; acute or chronic Type C and other unspecified non-A, non-B Type D (seen only with hepatitis B) S S S Type E S Type G Herpangina (see enteroviral infection) Herpes simplex (Herpesvirus hominis) Encephalitis Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent persons for the duration of illness S C Mucocutaneous, recurrent (skin, oral, genital) S C Herpes zoster (varicella-zoster, shingles) Disseminated disease in any patient Localized disease in immunocompromised patient Localized in patient with intact immune system with lesions that can be contained/covered Histoplasmosis Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) onset of symptoms; >14 yrs. of age for 1 week after onset of symptoms. Specific recommendations for care of patients in hemodialysis centers Specific recommendations for care of patients in hemodialysis centers S Mucocutaneous, disseminated or primary, severe Neonatal Comments Until lesions dry and crusted Also, for asymptomatic, exposed infants delivered vaginally or by C-section Until lesions and if mother has active infection and membranes have been ruptured for dry and more than 4 to 6 hours until infant surface cultures obtained at 24-36 hrs. of crusted age negative after 48 hours incubation A,C DI S DI S S Susceptible HCWs are reassigned if immune caregivers are available Susceptible HCWs are reassigned if immune caregivers are available. Not transmitted from person-to-person Human metapneumovirus C DI Impetigo Infectious mononucleosis C U 24 hrs Assumed to be Contact transmission as for RSV since the viruses are closely related and have similar clinical manifestations and epidemiology. S Influenza *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 7 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Human (seasonal influenza) Precautions Duration † * Type D Avian (e.g., H5N1, H7, H9 strains) Consult Infection Prevention Pandemic Influenza Consult Infection Prevention Kawasaki syndrome Lassa fever (see viral hemorrhagic fevers) Legionnaires’ disease Leprosy Leptospirosis Lice Head (pediculosis) D S Private room when available or cohort; avoid placement with high-risk patients; mask patient when transported out of room; 7 days except chemoprophylaxis/vaccine to control/prevent outbreaks. Use gown and DI in immuno gloves according to Standard Precautions especially in Pediatric settings. compromised Duration of precautions for immunocompromised patients cannot be defined; prolonged duration of viral shedding (i.e. for several weeks) has persons been reported. Use N95 respirator when performing aerosol-generating procedures. 7 days from See (www.pandemicflu.gov ) for current pandemic influenza guidance onset of symptoms Not an infectious condition S S S Not transmitted person-to-person See http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/lice/index.html C Body S Pubic S Listeriosis S Lyme disease Lymphocytic choriomeningitis Lymphogranuloma venereum S S S Malaria S Marburg virus disease (see viral hemorrhagic fevers) Comments U 24 hrs Transmitted person-to-person through infested clothing. Wear gown and gloves when removing clothing; bag and wash clothes according to CDC guidance above. Transmitted person-to-person through sexual contact Person-to-person transmission rare; Cross transmission in neonatal settings reported Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person except through transfusion rarely and through failure to follow Standard Precautions during patient care *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 8 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Precautions Duration † * Type Measles (rubeola) A Melioidosis, all forms Meningitis Aseptic (nonbacterial or viral; also see enteroviral infections) Bacterial, gram-negative enteric, in neonates Fungal Haemophilus influenzae, type b known or suspected Listeria monocytogenes Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcal) known or suspected Streptococcus pneumoniae S S S S D S D S M. tuberculosis S Other diagnosed bacterial S Meningococcal disease: sepsis, pneumonia, meningitis Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) D A, D, C 4 days after onset of rash; DI in immune compromised Comments Susceptible HCWs are reassigned if immune care providers are available; For exposed susceptible persons, post-exposure vaccine within 72 hrs. or immune globulin within 6 days when available. Place exposed susceptible patients on Airborne precautions and exclude susceptible HCW from duty from day 5 after first exposure to day 21 after last exposure regardless of post exposure vaccine. Not transmitted from person-to-person Contact for infants and young children U 24 hrs U 24 hrs Not transmitted from person-to-person See meningococcal disease below Concurrent, active pulmonary disease or draining cutaneous lesions necessitate addition of Airborne Precautions For children, Airborne Precautions until active pulmonary tuberculosis in visiting family members can be ruled out Post exposure chemoprophylaxis for household contacts, HCWs exposed to respiratory secretions. Contact Infection Prevention; post exposure vaccine only if outbreak DI plus 10 days Enhanced precautions with N95 or higher respiratory protection; surgical after mask if N95 unavailable; eye protection (goggles, face shield); gowns and resolution of gloves; aerosol-generating procedures and “supershedders” highest risk for transmission via small droplet nuclei and large droplets. Vigilant fever, provided environmental disinfection. Contact Infection Prevention. respiratory sxs are absent or improving U 24 hrs *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 9 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Molluscum contagiosum Monkeypox Precautions Duration † * Type S A,C Mucormycosis Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs), infection or colonization (e.g., MRSA, VRE, VISA/VRSA, Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, ESBLs) Mumps (infectious parotitis) Mycobacteria, nontuberculosis (atypical) Pulmonary Wound Mycoplasma pneumonia Necrotizing enterocolitis Nocardiosis, draining lesions, or other presentations Norovirus (see gastroenteritis) Norwalk agent gastroenteritis (see gastroenteritis) Orf Comments Until See www.cdc.gov/ncidod/monkeypox for most current recommendations. monkeypox Transmission in hospital settings unlikely confirmed and Pre- and post-exposure smallpox vaccine recommended for exposed HCWs smallpox excluded, lesions crusted S S/C D S S D S S MDROs – see Isolation Policy for specific MDROs and Isolation type After onset of swelling; susceptible HCWs are reassigned if immune U 5 days after caregivers are available. Contact Infection Prevention for advice on infected parotitis onset HCW or immunocompromised patients. Not transmitted person-to-person DI Contact Precautions when cases temporally clustered S Parainfluenza virus infection, respiratory C Parvovirus B19 D Pediculosis (lice) C DI Viral shedding may be prolonged in immunosuppressed patients. Reliability of antigen testing to determine when to remove patients with prolonged hospitalizations from Contact Precautions is uncertain. Consult Infection Prevention. Maintain precautions for duration of hospitalization when chronic disease occurs in an immunocompromised patient. For patients with transient aplastic crisis or red-cell crisis, maintain precautions for 7 days. Duration of precautions for immunosuppressed patients with persistently positive PCR not defined, but transmission has occurred. U 24 hrs of tx *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 10 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Precautions Duration † * Type U 5 days Post-exposure chemoprophylaxis for household contacts and HCWs with prolonged exposure to respiratory secretions. S D U 48 hrs Antimicrobial prophylaxis for exposed HCW. D, C DI Pertussis (whooping cough) D Pinworm infection Plague (Yersinia pestis) Bubonic Pneumonic Pneumonia S Adenovirus Bacterial not listed elsewhere (including gram-negative bacterial) B. cepacia in patients with CF, including respiratory tract colonization B. cepacia in patients without CF(see Multidrug-resistant organisms) Chlamydia Fungal Haemophilus influenzae, type b Adults Infants and children Legionella spp. Meningococcal Multidrug-resistant bacterial (see multidrug-resistant organisms) Mycoplasma (primary atypical pneumonia) Pneumococcal pneumonia Pneumocystis jiroveci (Pneumocystis carinii ) Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus, group A Adults Infants and young children Varicella-zoster (See Varicella-Zoster) Comments For immunocompromised patients, extend duration of isolation due to prolonged viral shedding. S C While Avoid exposure to other persons with CF; private room preferred. Criteria hospitalized for D/C precautions not established. See CF foundation guideline S S S D S D U 24 hrs U 24 hrs D S S S DI D U 24 hrs D U 24 hrs See meningococcal disease above Avoid placement in the same room with an immunocompromised patient For MRSA, see MDRO section. See streptococcal disease (group A streptococcus) below Contact precautions if skin lesions present Contact Precautions if skin lesions present *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 11 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Viral Adults Infants and young children (see respiratory infectious disease, acute) Poliomyelitis Pressure ulcer (decubitus ulcer, pressure sore) infected Major Minor or limited Prion disease (See Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease) Psittacosis (ornithosis) Q fever Rabies Precautions Duration † * Type S C DI C DI S S S S Rat-bite fever (Streptobacillus moniliformis disease, Spirillum minus disease) Relapsing fever Resistant bacterial infection or colonization (see multidrug-resistant organisms) Respiratory infectious disease, acute (if not covered elsewhere) Adults Infants and young children Comments If no dressing or containment of drainage; until drainage stops or can be contained by dressing. If dressing covers and contains drainage Not transmitted from person-to-person DI Person-to-person transmission is rare; transmission via corneal, tissue, and organ transplants has occurred. If patient has bitten another individual or saliva has contaminated an open wound or mucous membrane, wash exposed area thoroughly and administer post exposure prophylaxis. S S S C Respiratory syncytial virus infection, in infants, young children and immunocompromised adults C Reye's syndrome Rheumatic fever S S Rhinovirus D DI DI DI In immunocompromised patients, extend the duration of Contact Precautions due to prolonged shedding. Reliability of antigen testing to determine when to remove patients with prolonged hospitalization from Contact Precautions is uncertain. Contact Infection Prevention. Not an infectious condition Not an infectious condition Add Contact Precautions if copious moist secretions and close contact likely to occur (e.g., young infants.) *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 12 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Rickettsial fevers, tickborne (Rocky Mountain spotted fever, tickborne typhus fever) Rickettsialpox (vesicular rickettsiosis) Precautions Duration † * Type S S Ritter's disease (staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome) Rocky Mountain spotted fever Roseola infantum (exanthem subitum; caused by HHV-6) Rotavirus infection (see gastroenteritis) C S S Rubella (German measles, also see congenital rubella) Salmonellosis (see gastroenteritis) Scabies Scalded skin syndrome, staphylococcal Schistosomiasis (bilharziasis) Shigellosis (see gastroenteritis) Smallpox (variola; see vaccinia for management of vaccinated persons) DI Not transmitted person-to-person Rarely outbreaks have occurred in healthcare settings, (e.g., NICU, rehab hospitals). Use Contact Precautions for outbreaks. See staphylococcal disease, scalded skin syndrome below Not transmitted from person-to-person except through transfusion, rarely D Susceptible HCWs are reassigned if immune caregivers are available. Pregnant women who are not immune are not assigned to these patients. U 7 days after Administer vaccine within 3 days of exposure to non-pregnant susceptible onset of rash persons. Place exposed susceptible patients on Droplet Precautions; exclude exposed susceptible HCW from duty from day 5 after first exposure to day 21 after last exposure, regardless of post-exposure vaccine. A, D,C DI plus 10 days Enhanced precautions with N95 or higher respiratory protection; surgical after mask if N95 unavailable; eye protection (goggles, face shield); gowns and resolution of gloves; aerosol-generating procedures and “supershedders” highest risk for transmission via small droplet nuclei and large droplets. Vigilant fever, provided environmental disinfection. See http://www.cdc.gov/sars/index.html respiratory symptoms are absent or improving Rubeola (see measles) Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Not transmitted from person-to-person except through transfusion, rarely S Ringworm (dermatophytosis, dermatomycosis, tinea) Comments C C S U 24 DI A,C DI See staphylococcal disease, scalded skin syndrome below) Until all scabs have crusted and separated (3-4 weeks). Non-vaccinated HCWs do not provide care when immune HCWs are available; N95 or higher *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 13 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Sporotrichosis Spirillum minus disease (rat-bite fever) Staphylococcal disease (S aureus) Skin, wound, or burn a Major b Minor or limited Enterocolitis Multidrug-resistant (see multidrug-resistant organisms) Pneumonia Scalded skin syndrome Toxic shock syndrome Streptobacillus moniliformis disease (rat-bite fever) Streptococcal disease (group A streptococcus) Skin, wound, or burn Major Minor or limited Endometritis (puerperal sepsis) Pharyngitis in infants and young children Pneumonia Scarlet fever in infants and young children Serious invasive disease Streptococcal disease (group B streptococcus), neonatal Streptococcal disease (not group A or B) unless covered elsewhere Multidrug-resistant (see multidrug-resistant organisms) Strongyloidiasis Precautions Duration † * Type Comments respiratory protection required for susceptible and successfully vaccinated individuals; postexposure vaccine within 4 days of exposure protective S S C S DI No dressing or dressing does not contain drainage adequately Dressing covers and contains drainage adequately Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent children for duration of illness DI Consider healthcare personnel as source of nursery, NICU outbreak S S C S S C,D S S D D D D Not transmitted from person-to-person U 24 hrs No dressing or dressing does not contain drainage adequately Dressing covers and contains drainage adequately U 24 hrs U 24 hrs U 24 hrs U24 hrs Outbreaks of serious invasive disease have occurred secondary to transmission among patients and healthcare personnel Contact Precautions for draining wound as above; follow rec. for antimicrobial prophylaxis in selected conditions S S S *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 14 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Syphilis Latent (tertiary) and seropositivity without lesions Skin and mucous membrane, including congenital, primary, Secondary Tapeworm disease Hymenolepis nana Taenia solium (pork) Other Tetanus Tinea (e.g., dermatophytosis, dermatomycosis, ringworm) Precautions Duration † * Type S S S S S S S Toxoplasmosis S Toxic shock syndrome (staphylococcal disease, streptococcal disease) S Trachoma, acute Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (see Creutzfeld-Jacob disease, CJD, vCJD) Trench mouth (Vincent's angina) Trichinosis Trichomoniasis Trichuriasis (whipworm disease) Tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) S Extrapulmonary, draining lesion) Comments Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person Vertical transmission from mother to child and through transplant organs and blood transfusions. Droplet Precautions for first 24 hours after implementation of antibiotic therapy if Group A streptococcus is likely. S S S S A,C Extrapulmonary, no draining lesion, meningitis S Pulmonary or laryngeal disease, confirmed Pulmonary or laryngeal disease, suspected Skin-test positive with no evidence of current active disease A A S Discontinue precautions only when patient is improving clinically, and drainage has ceased or there are three consecutive negative cultures of continued drainage. Examine for evidence of active pulmonary tuberculosis. Examine for evidence of pulmonary tuberculosis. For infants and children, use Airborne Precautions until active pulmonary tuberculosis in visiting family members ruled out. Consult Infection Prevention to discontinue precautions. Consult Infection Prevention to discontinue isolation precautions. *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 15 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Tularemia Draining lesion Pulmonary Typhoid (Salmonella typhi) fever (see gastroenteritis) Typhus, endemic and epidemic Rickettsia prowazekii (Epidemic Louse-borne Typhus) Rickettsia typhi Urinary tract infection (including pyelonephritis), with or without urinary catheter Precautions Duration † * Type S S BSL 2 laboratory only for processing cultures Not transmitted from person-to-person Not transmitted from person-to-person S S Transmitted person-to-person through close personal or clothing contact. Not transmitted from person-to-person S Vaccinia (vaccination site, adverse events following vaccination) * Vaccination site care (including autoinoculated areas) Eczema vaccinatum Fetal vaccinia Generalized vaccinia Progressive vaccinia Postvaccinia encephalitis Blepharitis or conjunctivitis Iritis or keratitis Vaccinia-associated erythema multiforme (Stevens Johnson Syndrome) Secondary bacterial infection (e.g., S. aureus, group A beta hemolytic streptococcus Comments S C C C C S S/C S S S/C Until lesions dry and crusted, scabs separated Only vaccinated HCWs have contact with active vaccination sites and care for persons with adverse vaccination events; if unvaccinated, only HCWs without contraindications to vaccine may provide care. Vaccination recommended for vaccinators; for newly vaccinated HCWs: semi-permeable dressing over gauze until scab separates, with dressing change as fluid accumulates, ~3-5 days; gloves, hand hygiene for dressing change; vaccinated HCW or HCW without contraindication to vaccine for dressing changes For contact with virus-containing lesions and exudative material Use Contact Precautions if there is copious drainage Not an infectious condition Follow organism-specific (strep, staph most frequent) recommendations and consider magnitude of drainage *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 16 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Varicella Precautions Duration † * Type A,C Variola (see smallpox) Vibrio parahaemolyticus (see gastroenteritis) Vincent's angina (trench mouth) Viral hemorrhagic fevers due to Lassa, Ebola, Marburg, Crimean-Congo fever viruses Viral respiratory diseases (not covered elsewhere) Adults Infants and young children (see respiratory infectious disease, acute) Whooping cough (see pertussis) Wound infections Major Minor or limited Yersinia enterocolitica gastroenteritis (see gastroenteritis) Comments In immunocompromised host with varicella pneumonia, prolong duration of precautions for duration of illness. Post-exposure prophylaxis: provide postexposure vaccine ASAP but within 120 hours; for susceptible exposed persons for whom the vaccine is contraindicated, (immune compromised Until lesions persons, pregnant women, newborns whose mother’s varicella onset is < 5 dry and days before delivery or within 48 hours after delivery) provide VZIG when crusted available, within 96: if unavailable, use IVIG. Use Airborne Precautions for exposed susceptible persons and exclude susceptible exposed HCW beginning 8 days after the first exposure until 21 days after last exposure or 28 days if received VZIG regardless of post-exposure vaccine S S, A, C DI Private negative pressure room with anteroom. Emphasize: 1) use of sharps safety devices and safe work practices, 2) hand hygiene; 3) barrier protection against blood and body fluids upon room entry (double gloves and fluid resistant or impervious gown, eye/face protection with masks, goggles, or face shields); appropriate waste handling. Use Powered Air Purifying Respirator (PAPR) when performing aerosol generating procedures. Largest viral load in final stages of illness when hemorrhage may occur; additional PPE, including double gloves, neck, leg, and shoe coverings beneficial when extensive uncontrolled bleeding. Notify Infection Prevention immediately if Ebola is suspected S C S DI No dressing or dressing does not contain drainage adequately Dressing covers and contains drainage adequately *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 17 TYPE AND DURATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS RECOMMENDED FOR SELECTED INFECTIONS AND CONDITIONS (JUNE 4, 2015) Infection/Condition Zoster (varicella-zoster, see herpes zoster) Zygomycosis (phycomycosis, mucormycosis) Precautions Duration † * Type S Comments Not transmitted person-to-person http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dhqp/pdf/guidelines/Isolation2007.pdf *Precautions Type: A, Airborne Precautions; C, Contact; D, Droplet; S, Standard † Duration: DI, duration of illness; DE, until environment completely decontaminated; CN, until off antimicrobial treatment and culture-negative; U, until time specified in hours (hrs) after initiation of effective therapy DH, duration of hospitalization. 18




