Massachusetts institute of Technology Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering
advertisement

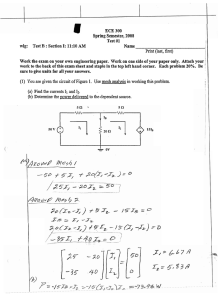
Massachusetts institute of Technology Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 22.071/6.071 - Introduction to Electronics, Signals and Measurement Spring 2006 Homework 6 Due 3/22/06 Problem 1. Calculate the currents i1(t) and i2(t) as shown on the following circuit 10 Ω vs = 5cos(628t ) i1 i2 0.01mF 2H Problem 2. Determine the voltage Vo for the following circuit. (Hint: superposition) + 2H vs = 10 cos(10t ) 6.071/22.071 Spring 2006, HW6 Vo 1Ω 0.01mF is = 4sin(7t ) Problem 3. For the circuit below, determine the Thevenin equivalent circuit seen by capacitor C. (Hint: it helps if you work out the problem symbolically and then substitute for the element values.) 0.01mF is = 2sin(1000t ) 100 Ω C 2mH 0.01uF Problem 4. Tau finds a black box with 3 terminals labeled Χ, Υ, Ζ. Tau, who took 6.071 last year, decides to make resistance measurements across the terminals at DC ( ω = 0 Hz ) and at high frequency ( ω large). She observes the following results: Resistance (Ω) at Measure resistance across Χ–Υ Υ–Ζ Χ-Ζ DC ∞ 0 ∞ High-Freq. 40 ∞ ∞ Which of the following equivalent circuits is inside Tau’s black box? x C R x y R L y L C z z Circuit A x Circuit B R y x C y L L C R z Circuit C 6.071/22.071 Spring 2006, HW6 z Circuit D Problem 5. A motor is made up of a coil which has a resistance R and an inductance L. We will set up an experiment to measure the values of R and L. The circuit is shown below. 10 Ω + motor Va R Vs + Vm - L The motor runs with 60Hz power and all measurements will be performed with the real source power connected to it and operating at a constant load (steady state). Using a voltmeter set in AC mode (i.e measure the RMS value of a sinusoidal voltage) we perform the following measurements. Vs = 220 Volts , Va = 75 Volts , Vm = 110 Volts Use these measurements to determine R and L 6.071/22.071 Spring 2006, HW6