Document 13491298
advertisement

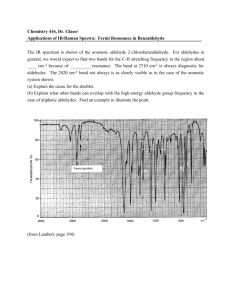
Absorption Spectroscopy Type of Radiation Energy (kcal/mol) Frequency Molecular Interaction Wavelength Translation Microwave 0.001 - 1 1 - 400 cm-1 Molecular Rotations Rotation of the molecular as a whole about its center of mass 400 - 4,000 cm-1 Molecular Vibrations Stretching and binding of bonds Infrared 1.1 - 11 Visible 50 - 75 400 - 600 nm Ultraviolet 75 - 150 200 - 400 nm Electronic Excitation Promotion of electrons to higher energy levels Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy 4000 cm-1 2000 cm-1 X-H Region 2500 - 4000 cm-1 C-H N-H O-H Stretching SP X=Y Region Region 2000 ­ 2500 cm-1 1500 2000 cm-1 C=C C=N Stretching 400 cm-1 1500 cm-1 C=C C=O C=N Stretching Fingerprint Region 400 - 1500 cm-1 Single Rond Stretching Bond Bending Polyatomic Vibrations Figure by MIT OCW. Infrared Spectra: Tables of Reference X-H Region Phenols and Alcohols ROH 3700-3500 sharp or 3200-3600 broad(H-bonded) Acids RCO2H 2800-3600 very broad Amides and Amines RCONHR R2NH 3300-3500 C-H bonds C C H C C H C C H RCHO 3100-3300 3000-3200 2850-3000 2700-2800 sp Region Acetylenes Nitriles Ketenes Allenes C C C C C N C O C C 2100 2200 2150 1950 Double Bond Region Alkenes Imines Nitro C C C N NO2 1600-1670 weak unless conjugated 1600-1700 1350-1550(two bands) Carbonyl Groups Note: subtract ca. 30 cm-1 for conjugation (e.g. with a double bond or aromatic ring) Anhydrides RC(O)OCOR Acid Chlorides RCOCI Esters Acids 1710 RCO2H 1700-1725 1740 O 1715 1780 1740 O NR O O O O 1770 O 1700 1720-1740 1680 O O 1630-1700 O O 1790-1815 1725-1755 Urethanes R2NCO2R Aldehydes RCHO O 6-membered and larger cyclic ketones 1740-1780, 1800-1840 (two bands) RCO2R Amides RCONR2 Ketones (subtract ca. 30 cm-1 for R2C O 1710 conjugation) 1690-1740 O 1730 NR 1650 Figure by MIT OCW. Regions of the 13C NMR Spectrum Aromatic 120-160 ppm Carbonyls 150-220 ppm 200 180 C-O, N 40-90 ppm Alkenyl 100-150 ppm 160 140 120 Alkynyl 70-90 ppm 100 80 Alkyl 0-50 ppm 60 40 20 0 Chemical Shift (�) Figure by MIT OCW. Characteristic Functional Group Chemical Shifts in 13C NMR (ppm) Alkanes Methyl (RCH3) Methylene (RCH2R’) Methine (RCH(R’)(R”)) Quaternary (RC(R’)(R”)(R’’’)) Alkenes Aromatic Alkynes Nitriles Alcohols, Ethers Amines 0-30 15-55 25-55 30-40 100-150 120-160 70-90 110-125 50-90 40-60 Organohalogen C–F C–Cl C–Br C–I Ketones, Aldehydes Carboxyl Derivatives Acids Esters Amides Carbamates 70-80 25-50 10-40 –20-10 185-220 150-185 155-180 150-180 150-160 1 H NMR Spectra: Tables of Reference Average Chemical Shifts (�) of �−Hydrogens in Substituted Alkanes* CH3X X RCH2X R2CHX 0.9 1.25 4.4 3.4 3.3 1.25 1.5 F Cl Br 0.233 0.9 4.26 3.05 2.68 I OH OR OAr OCOR 2.16 3.47 3.3 3.7 3.6 3.2 3.6 3.4 3.9 4.1 4.2 3.6 OCORAr SH SR SOR SO2R 3.8 2.44 2.1 2.5 4.2 2.7 2.5 5.1 2.8 2.9 3.1 NR2 2.2 2.9 2.6 2.9 H CH3 or CH2 NR-Ar NCOR NO2 CHO COR COAr COOH COOR CONH2 1 CR=CRCR Phenyl Aryl � � C CR C CN 2.8 4.28 2.20 2.1 2.6 2.07 2.1 2.02 2.0-1.6 2.3 3.0-2.5 2.0 2.0 4.0 4.1 5.0 2.8 4.4 2.3 2.4 3.0 2.3 2.3 2.2 2.3 2.7 3.2 4.7 2.4 2.5 3.4 2.6 2.6 Chemical Shifts of Hydrogens Bonded to Unsaturated Centers Unconjugated Conjugated* R2C=CH2 4.6-5.0 5.4-7.0 R2C=CHR 5.0-5.7 5.7-7.3 Aromatic 6.5-8.3 Nonbenzenoid aromatic 6.2-9.0 Acetylenic 2.3-2.7 2.7-3.2 Aldehydic 9.8-9.8 9.5-10.1 R2NCHO 7.9-8.1 ROCHO 8.0-8.2 Type * The position depends on the type of functional group in conjugation with the unsaturated group. Chemical Shifts of Hydrogen Bonded to Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfer Functional Group OH 2.6 2.9 NH2 2.3 2.7 Chemical Shift, � Alcohols 0.5 0.5-5 (Monomeric) (Associated) Phenols (Monomeric) (Associated) Enols 4.5 4.5-8 15.5 RCO2H 9-12 (Dimeric) H-bonded to C=O 13-16 Alkylamine 0.6-1.6 Arylamine 2.7-4.0 Amide 7.8 Alkylamine, 0.3-0.5 Arylamine 2.7-2.8 * The tabulated values are average values for compounds that do not contain another functional group wlthin two carbon atoms from the indicated hydrogens. NH R3NH+ Ammonium salts 7.1-7.7 (in CF3COOH) Includes polycyclic and many heterocyclic aromatics. SH Aliphatic Aromatic 1.3-1.7 2.5-4 � Figure by MIT OCW. � 1H NMR Coupling Constants (Expanded) H geminal 12-15 Hz acyclic can be 0-25 Hz in cyclic system H H 6-8 Hz vicinal (averaged by free rotation) H In rigid systems, vicinal coupling can range from 0 to 15 Hz. For example: H H ax-ax H H 6-14 Hz H ax-eq 0-5 Hz H H H eq-eq 0-5 Hz Spin-spin coupling in alkenes: H geminal 0-3-Hz H H H trans 12-18 Hz cis H 6-12 Hz allylic 0-3 Hz H Spin- spin coupling in arenes: Ha Hb Hc Hd Jab (ortho) 6-10 Hz Jac (meta) 1-3 Hz Jad (para) 0-1 Hz Note: Structures shown above represent generic coupling situations and not the specific molecules depicted (in which the labeled protons would be chemically equivalent and would not couple). Figure by MIT OCW.