Document 13478228
advertisement

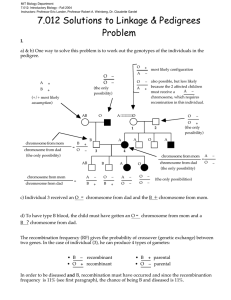
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.013 Solutions to Linkage & Pedigrees Problem I. a) & b) One way to solve this problem is to work out the genotypes of the individuals in the pedigree. O A + B + O – O – (the only possibility) (+/+ most likely assumption) AB A + most likely configuration – O – A + also possible, but less likely because the 2 affected children A – must receive a chromosome, which requires recomination in this individual. A AO O O chromosome from mom chromosome from dad (the only possibility) = B B + O − 3 O A 4 chromosome from mom AB chromosome from mom chromosome from dad A A O + (the only possibility) 2 1 – = c) Individual 3 received an O B A chromosome from dad (the only possibility) O A – O – A – O – B + B + O – O – = A – O − (the only possibilities) - chromosome from dad and the B + chromosome from mom. d) To have type B blood, the child must have gotten an O B ? chromosome from dad. - chromosome from mom and a The recombination frequency (RF) gives the probability of crossover (genetic exchange) between two genes. In the case of individual (3), he can produce 4 types of gametes: • B – recombinant • O + recombinant • B + parental • O – parental In order to be diseased and B, recombination must have occurred and since the recombinantion frequency is 11% (see first paragraph), the chance of being B and diseased is 11%. II. a) What are the genotypes of Phil and Ryan with respect to these two genes. Use the letter E for ear wiggling and the letter R for tongue rolling. Phil E + + R Ryan + + + + b) How do you account for the fact that Ryan is unable to roll his tongue or wiggle his ears? During meiosis in Phil, there was recombination between the chromosome carrying the ability to wiggle gene and the one carrying the ability to roll gene. E + + R --> E R and + + Ryan received the wildtype chromosome from his mother and the recombined completely wildtype chromosome from his father.