LA 358: CHILD LAW: LEARNING OUTCOMES
advertisement

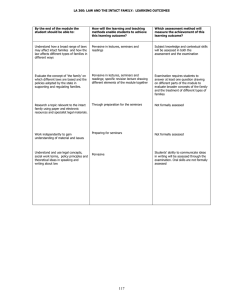
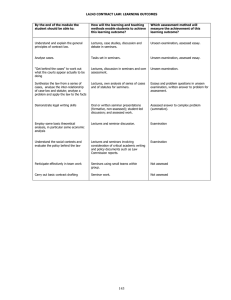
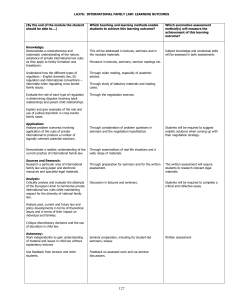
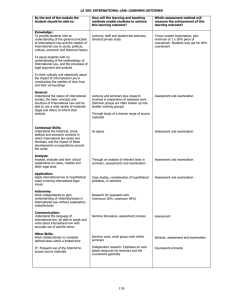
LA 358: CHILD LAW: LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of the module the student should be able to: How will the learning and teaching methods enable students to achieve this learning outcome? Which assessment method will measure the achievement of this learning outcome? Knowledge: Understand how the law defines and regulates parenthood . This will be addressed in lectures, seminars and in the module materials. Understand the concept and extent of children’s rights Pervasive in lectures, seminars, seminar readings etc. Subject knowledge and contextual skills will be assessed in both the assessment and the examination Evaluate the role of the law in regulating relationships between parent, child and the state Through wider reading, especially of academic articles Identify the relevant sources of key principles. Through study of statutory materials and reading cases. Explain and give examples of the role and use of discretion in child law. Pervasive in lectures, seminars, student-led seminar readings etc. Contextual Skills: Understand the operation of child law in society. Pervasive in lectures, seminars, seminar readings etc. Application: Apply English law to hypothetical situations involving child law issues Through consideration of problem questions in seminars and the written assessment. Students will be required to answer at least one problem question in the examination Demonstrate a realistic understanding of the current practice of family law. Through examination of real-life situations and a wide range of materials. Students will be required to suggest realistic solutions in answering problem questions Sources and Research: Research a particular area of child law using paper and electronic resources and specialist legal materials. Through preparation for seminars and research for the written assessment. The written assessment will require students to research relevant legal materials. Discussion in lectures and seminars Students will be required to answer at least one essay question in the examination. Analysis: Analyse past, current and future law and policy developments in terms of theoretical issues and in terms of their impact on individuals & families. Critique discretionary decisions and the use of discretion in child law. Autonomy: Work independently to gain understanding of material and issues in child law without explanatory lectures Seminar preparation, including for studentled seminars; essays Use feedback from lecturer and other students. Feedback on assessed work and via seminar discussions. Communication/Literacy Understand and use legal concepts, social work terms, policy principles and theoretical ideas in speaking and writing about law and family practice Written assessment Students’ ability to communicate ideas in writing will be assessed through the written assessment and the examination. Oral skills are not formally assessed Pervasive. Use correct citations and bibliographies. Element in written assessment. Other Basic Skills: Group Work: Work collaboratively to complete a defined task within a limited time Exercise in advising on parental responsibility in student-led seminar 114 Not formally assessed. Numerical: Read and understand quantitative research materials. Directed reading Not formally assessed, but incorporation of such material may be a means of demonstrating an appreciation of the context in which the law operates. IT: Use internet to access further readings on child law issues. Use learning packages (e.g.module website) for selfstudy. Word processing. Through research for seminars, directed reading and module website. 115 Research skills are assessed as part of written assessment.