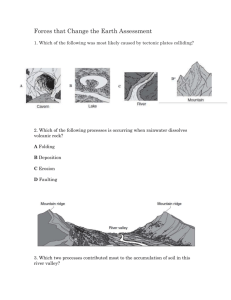
Document 13418218

Water Erosion and Deposition
Background & Overview
Water plays an important role in the changing of the Earth’s surface over time. Because of the water cycle , water is constantly on the move on Earth.
It evaporates from the oceans to form clouds, rains down over land to form rivers and lakes, which eventually drain back into the ocean. Along the way water picks up rocks and other minerals, causing erosion and forming canyons and valleys. The water eventually drops these rocks and minerals in other places in a process called deposition .
The size and other characteristics of the minerals involved in erosion and deposition depend on how fast the water moves. By learning about different types of deposition and observing the landscape, you can find clues about what types of water processes have been involved.
Materials
•
Trough
•
Bucket or deep tray
•
Mixture of rocks, sand, and silt
•
Watering can
Activity
1.
Place the trough on an angle so that it drains into the bucket.
2.
Fill the trough with the mixture of rocks, sand, and silt. Pile it up on the high end as tall as you can without spilling it over the sides.
3.
Fill the watering can with water, and pour over the pile.
4.
Stop pouring water on the pile and allow the water to drain into the bucket.
5.
Repeat if necessary, until the pile erodes away.
Discussion
1.
What did you observe as the water flowed from the pile into the bucket? How is this similar to the water cycle in nature? How is it different?
2.
What natural landforms are represented by this exercise? In other words, what natural landforms are similar in formation and appearance to what you see in the demonstration?
3.
What do you notice about the distribution of the rocks, sand and silt after pouring the water? Is it different than before?
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Yosemite Falls, CA 1
1 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Yosemite_falls_winter_2010.JPG
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Alluvial fan above Lake Louise
Alberta, CA 2
2 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:AlluvialFanLakeLouiseBC.jpg
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Rocky Mountain National Park, CO 3
3 http://www.rmnp.com/RMNP-‐Areas-‐HorseshoePark-‐AlluvialFan.html
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Eroded glaciofluvial deposits.
Matanuska River, AK 4
4 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Matanuska_River_8727.JPG
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Grand Canyon, AZ 5
5 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Grand_canyon_hermits_rest_2010.JPG
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Alluvial Fans
Death Valley, CA 6
6 http://marlimillerphoto.com/alluvialfans.html
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Great Salt Lake, UT 7
7
©
John Bush, 2006
Water Erosion and Deposition
Pictures
Black Rock Desert, NV 8
8 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Kluft-‐photo-‐Black-‐Rock-‐Desert-‐Aug-‐2005-‐
Img_5081.jpg
© 2010 John Bush, Colorado School of Mines GK-12 Learning Partnership, http://inside.mines.edu/~jobush/gk12
Support for this work is provided by the National Science Foundation’s Graduate Education, NSF, DGE-0638719
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free
Documentation License, Version 1.3 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no
Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts.
[GFDL (www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC-BY-SA-3.0 (www.creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)]