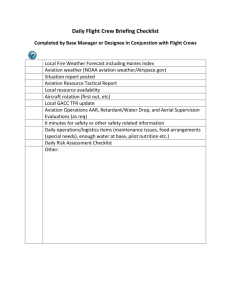
An Analysis of Resource Rationing Methods for Collaborative Decision Making NEXTOR
advertisement

NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH An Analysis of Resource Rationing Methods for Collaborative Decision Making Michael Ball and Thomas Vossen R.H. Smith School of Business & Institute for Systems Research University of Maryland & Robert Hoffman Metron Aviation 1 NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Ground Delay Programs delayed departures delayed departures delayed arrivals/ no airborne holding delayed departures NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH GDPs under CDM Resource Allocation Process: • FAA: initial “fair” slot allocation [Ration-by-schedule] • Airlines: flight-slot assignments/reassignments [Cancellations and substitutions] • FAA: periodic reallocation to maximize slot utilization [Compression] Note: - reduced capacity is partitioned into sequence of arrival slots - ground delays are derived from delays in arrival time NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Allocating Slots under CDM Ration-By-Schedule: Step 1: Order flights by their original scheduled time of arrival Step 2: Select the first flight that has not been assigned an arrival slot. – assign the selected flight to the earliest unassigned slot – repeat step 2. The resulting allocation is independent of current status of flights and is not affected by status information given by airlines!! NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Slot Reallocation under CDM Need for Inter-airline slot exchange: slots made available through flight cancellations and delays Compression Algorithm Initial AAL1:1200 AAL2:1201 UAL1:1202 USA1:1203 UAL2:1204 COA1:1205 USA2:1206 AAL3:1207 S1200 S1202 CNX S1204 S1206 S1208 S1210 S1212 S1214 Final AAL1:1200 AAL2:1201 UAL1:1202 USA1:1203 UAL2:1204 COA1:1205 USA2:1206 AAL3:1207 S1200 S1202 S1204 S1206 S1208 S1210 S1212 S1214 NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Generalizations and Extensions of CDM Procedures • • • View RBS as Process for Achieving Equitable Allocation of Time Slots – extend to insure better equity during dynamic GDP operation Extension of RBS to Enroute Airspace: Priority based on accrued delay Interpret Compression as slot trading process: extend from 1-for-1 trades to 2-for-2 trades NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH #1. GDPs as Balanced Just-in-Time Scheduling Problem flts Possible deviation measures “ideal” nb production rate Xb Cumulative production na time • Airlines = products, flights = product quantities • Minimize deviation between “ideal” rate and actual production NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH GDP Situation flts “Release times” defined by scheduled arrivals na Xa slots Questions: • What are appropriate “production rates” ? • How to minimize deviations ? • Managing program dynamics NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR What is an appropriate production rate/ideal allocation?? AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Answer: RBS!! It can be shown that RBS lexicographically minimizes the maximum delay assigned to each flight. General Principles of equity applied to a set of claimants; equity defined relative to pair-wise comparisons: in an equitable solution it should not be possible to improve the allocation to a claimant at performance level p without moving another claimant to a performance level of p or worse. For the mini-max (RBS) solution: if flight f has been assigned t* units of delay, it is impossible to reduce the delay assigned to f without increasing the delay assigned to another flight a value of t* or higher. It can be shown that RBS satisfies some very fundamental axioms for consistent, fair allocation process (there are other alternatives that we are now investigating) NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Models and Algorithms for Minimizing Deviation from Ideal Allocation • General class of problems: minimize deviation between actual slot allocation and ideal slot allocation Variants based on: – Objective function (deviation measures) – Constraints on feasible allocations • Minimize cumulative/maximum deviation: – complex network flow model (based on JIT scheduling models) can solve most variants • Minimize sum of deviations between jth slot allocated to airline a and ideal location for airline a’s jth slot: – Assignment model – Greedy algorithm for several cases NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH GDPs and Flight Exemptions • GDPs are applied to an “included set” of flights • Two significant classes of flights destined for the airport during the GDP time period are exempted: – Flights in the air – Flights originating at airports greater than a certain distance away from the GDP airport • Question: Do exemptions induce a systematic bias in the relative treatment of airlines during a GDP?? NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Analysis of Flight Exemptions (Logan Airport) 4/ 21 /0 1 AAL 4/ 14 /0 1 4/ 7/ 01 USA 3/ 31 /0 1 DAL 3/ 24 /0 1 3/ 17 /0 1 UCA 3/ 10 /0 1 3/ 3/ 01 UAL 2/ 24 /0 1 2/ 17 /0 1 COA 2/ 10 /0 1 CJC 2/ 3/ 01 1/ 27 /0 1 1/ 13 /0 1 1/ 20 /0 1 TWA 40 30 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 1/ 6/ 01 Minutes/Flight Deviation RBS (standard) vs RBS (+exemptions), Boston GDPs Flight exemptions introduce systematic biases: • USA (11m/flt), UCA (18m/flt) “lose” under exemptions NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Reducing Exemption Bias Objective : • Use deviation model to mitigate exemption bias – i.e. “inverse” compression Approach: • RBS applied to all flights whose arrival times fall within GDP time window Î ideal allocation • Set of exempted flights are defined as before (there are good reasons they are exempted) • Time slots given to exempted flights “count against” allocation • Delays allocated to non-exempted flights so as to minimize overall deviation from ideal allocation NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Flight Exemptions USA AAL 4/ 21 /0 1 DAL 4/ 14 /0 1 UCA 4/ 7/ 01 UAL 3/ 31 /0 1 COA 3/ 24 /0 1 -40 1/ 6/ 01 -40 4/ 21 /0 1 -30 4/ 14 /0 1 -30 4/ 7/ 01 -20 3/ 31 /0 1 -20 3/ 24 /0 1 -10 3/ 17 /0 1 -10 3/ 10 /0 1 0 3/ 3/ 01 0 2/ 24 /0 1 10 2/ 17 /0 1 10 2/ 10 /0 1 20 2/ 3/ 01 20 1/ 27 /0 1 30 1/ 20 /0 1 30 1/ 13 /0 1 40 1/ 6/ 01 40 CJC 3/ 17 /0 1 TWA 3/ 10 /0 1 AAL 3/ 3/ 01 USA 2/ 24 /0 1 DAL 2/ 17 /0 1 UCA 2/ 10 /0 1 UAL 1/ 27 /0 1 COA 1/ 20 /0 1 CJC 1/ 13 /0 1 TWA Deviation RBS ideal-Opt. model 2/ 3/ 01 Deviation RBS ideal-RBS actual • Minimize deviations using optimization model that incorporates exemptions • reduces systematic biases, e.g. USA from 11m/flt to 2m/flt, UCA from 18m/flt to 5m/flt NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Discussion Approach yields system where: • airlines are assigned priority lists – based on sched. arr. times, constant during GDP • dynamic changes (capacity, airline data) initiate (re)rationing – ration according to airline priorities (compression) • priority scheme cannot (completely) be maintained with flight exemptions – deviation model shows potential to reduce exemption bias NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH #2. Extension of RBS to Enroute Airspace: Priority Based on Accrued Delay Priority given to flight with largest accrued delay; accrued delay (downstream) defined as difference between ETA and scheduled arrival time. NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Scenario Scenario: flights in air and on the ground; need to reroute flights around flow constrained area: Which flights are rerouted?? Which flights are delayed on ground?? Flow Constrained Area (FCA) Targeted Region (NY area) ??? NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Impact on Allocated Delay Motivation for Priority Based on Accrued Delay: • Generalization of RBS – equivalent relative to equity principles • Implicitly coordinates multiple initiatives since previously delayed flights are given priority. 1st come/ 1st served Priority Based on Accrued Delay NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Implementation Alternatives F-Based S-Based Step 1: For each unassigned flight, calculate its total accrued delay assuming it is assigned to the earliest available slot for which it is eligible. Step 2: Choose the flight with the maximum accrued delay that has not been assigned to a slot. – assign the selected flight to the earliest unassigned slot for which it is eligible – if there are remaining unassigned flights, go to step 1; otherwise stop Step 1: Choose the earliest available slot, s. Step 2: Find the set of flights, F, that can be assigned to s. For each flight in F, calculate the total accrued delay assuming the flight is assigned to s. Choose the flight in F with the maximum calculated accrued delay and assign it to s. If there are remaining unassigned flights go to step 1; otherwise stop. NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH F-Based vs S-Based: The Leap Frog Principle F-Based: • Utilization = 100% • Avg. delay = 30 min • Avg. of top 20% = 103 min • Std. Dev. = 43 min. S-Based: • Utilization = 100% • Avg. total delay = 30 min • Avg. of top 20% = 50 min • Std. Dev = 14 min. NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH #3. Compression vs Trading RBS allocates slots to airlines during a GDP Compression provides a mechanism whereby an airline gives up a slot it cannot use and get one (from another airline) that it can use … NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR An Alternate View of Compression: Inter-Airline Bartering NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH UAL AAL Mediator: FAA DAL NWA SWA NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Mediated Slot Exchange • Offer: – slot_O: slot willing to give up – slot_A1,…, slot_An: slots willing to accept in return • Each airline submits a set of offers • Mediator determines set of offers to accept and for each accepted offer, the returned slot NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Default Offers earliest time of arrival slot_An slot_A1 slot_O NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Offer Associated with Canceled or Delayed Flights time slot from canceled flight earliest time of arrival for earliest available flight occupied time slot occupied time slot slot_O slot_A1 slot_An NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH 1-for-1 trades to 2-for-2 trades • Compression ⇔ 1-for-1 trading system, i.e. offers involve giving up one slot and getting one in return (many offers processed simultaneously) • What about k-for-k or k-for-n offers, e.g. 2-for-2: Trade?? NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Initial Results • Compression Benefits – performance improvement if compression executed after flts with excessive delay (>2hrs) are canceled Compression Improvement 40 Global Max. Compression % improvement 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 bo s0 106 -0 bo 1 s0 115 -0 bo 1 s0 119 -0 bo 1 s0 130 -0 bo 1 s0 208 -0 bo 1 s0 214 -0 bo 1 s0 221 -0 bo 1 s0 226 -0 bo 1 s0 310 -0 bo 1 s0 313 -0 bo 1 s0 321 -0 bo 1 s0 323 -0 bo 1 s0 330 -0 bo 1 s0 408 -0 bo 1 s0 418 -0 1 0 GDP NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Initial Results • 2-for-2 Trading Model: – proposed offers: all at-least, at-most pairs that improve on-time performance Trading Improvement 40 Global Max Trading Model 30 25 20 15 10 5 06 -0 bo 1 s0 115 -0 bo 1 s0 119 -0 bo 1 s0 130 -0 bo 1 s0 208 -0 bo 1 s0 214 -0 bo 1 s0 221 -0 bo 1 s0 226 -0 bo 1 s0 310 -0 bo 1 s0 313 -0 bo 1 s0 321 -0 bo 1 s0 323 -0 bo 1 s0 330 -0 bo 1 s0 408 -0 bo 1 s0 418 -0 1 0 bo s0 1- %Improvement 35 GDP Computational Efficiency: • 13sec avg. • 67% solved by LP relaxation NATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR NEXTOR AVIATION OPERATIONS RESEARCH Generic View of CDM GDP Procedures • Equitable allocation among airlines • Intra-airline maximization of economic efficiency • Inter-airline resource exchange