C R D P
advertisement

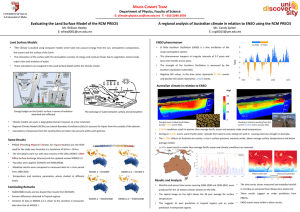
CLIMATE RESEARCH IN THE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS W. Healey, MALTA CLIMATE TEAM 14-19th March 2011 Evaluating the Land Surface Model of the Regional Climate Model PRECIS •Why the climate? -The weather patterns over a period of years. -The Impact of the climate. •How do we do it?! -Computer models running simulations of parameters -Different scales: Global, Regional and Local 300 km 50km •How do we do it?! 250 m -Computer models running simulations of parameters -Different scales: Global, Regional and Local 2 The effect of the surface on climate… 3 The effect of the surface on climate… 3 … in the climate model Dynamic Core Radiation LSM Clouds Aerosols 4 Providing REgional Climates for Impact Studies (PRECIS) 5 Providing REgional Climates for Impact Studies (PRECIS) 5 The details • A 60 year study from 1960 till 2020 • Taking parameters most affected by the land surface – temperatures and moisture levels • Comparing the LSMs with Measured Data 6 Met Office Surface Exchange Scheme – the LSM 9 different surface types: Broadleaf trees, needleleaf trees, temperate grass, tropical grass, shrubs, bare soil, Ice, Urban and lake/inland water Upgrades over the older version include: •Height of vegetation in calculations •Shortwave / longwave radiation • Soil flooding 7 Results part I MOSES 1 MOSES 2.2 Average surface temperature from 1960 to 1990 Measured 8 Results part II Temperature (˚C) Surface temperature Time (Years) 9 Results part III Relative Humidity (%) Relative Humidity Time (Years) 10 Conclusions •PRECIS is still relatively weak in predicting the measured results. • Spatial plots reveal an over prediction in tropical regions and an under prediction in temperate regions. • Time series for surface temperature shows on average an over prediction of about 0.3 ˚C in models. • Whilst an under prediction of around 3% for relative humidity. • MOSES2.2 results do not show improvement in PRECIS’ performance compared to measured data. 11 Thank you! 11