Making the most of Earth System Data Keith Haines and
advertisement

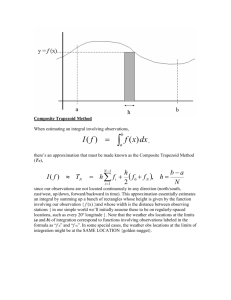
Making the most of Earth System Data Keith Haines and Jon Blower, Dan Bretherton, Alastair Gemmell, Adit Santokhee Reading e-Science Centre Different vertical coords too, eg. terrain following, or entropy following Balaji and Zhiang, http://www.gfdl.noaa.gov/~vb/gridstd/gridstd.html Calibrating observations + = Validating models HadCM3 SSM/I Low res. Climate GCM Satellite HadCM3 ERA-40 HiGEM Hi-res Climate GCM, New physics Re-analysis product Snow water equivalent 0 300mm Putt, Gurney and Haines Key challenges • Data integration – Ability to bring different datasets together • Interactivity – Ability to explore data graphically and quickly (contrast with existing batch-mode methods) • These are the two challenges that ReSC is aiming at – There are many others, notably trustworthiness Data integration Data Assimilation Black line: control run Green stars: observations Red line: assimilation run time Observation v. Background • Background: – Statistical prior eg. climatology or model product – Gridded fields (space-time) – Not what is being measured: eg satellite radiance • “Forward model” or “Observation Operator” – Converts Background to Equivalent Observation • Compare Obs with Equiv Obs either visually or statistically • Run Observation Operator within interactive viewer?: – Can do if only space/time projection – Observations, Background model remain in normal storage formats • Obs. v. Background comparison 1st step in Data Assimilation “Dataset” != “collection of files” • For Discovering and Accessing data, like to move away from file-based metaphors – File formats very diverse and idiosyncratic • We need a higher-level semantic view of the data – Provided by Climate and Forecast conventions and CSML – These are converging • And services for exchanging data and metadata across the internet – Access is based on semantic, not syntactic view of data • (Note: general-purpose e-Infrastructures tend to be based on files.) – Lowest-common-denominator approach – Impedance mismatch? CSML • Met-Ocean community is converging on CSML as an abstract data model for many kinds of environmental data • Based on ISO and Open Geospatial Consortium standards • CSML holds actual data, plus enough metadata needed to produce an accurate plot – Spatial/temporal referencing • Does not attempt to encode everything – E.g. provenance is out of scope Climate Science Modelling Language (CSML): selected “Feature Types” PointSeriesFeature (timeseries at a point) ProfileFeature (vertical profile at a point) GridSeriesFeature (series of multidimension grids) SwathFeature (single satellite sweep) SectionFeature (vertical section) Feature Types classified by their geometry Interactivity • Datasets very large • Need means to explore the data, performing simple intercomparison tasks – Not recreating Matlab! • Usability of client tools is very important • Doing this at speeds that support interactivity is challenging • Data must be online • Slowest step is often reading data from disk – Strong technology challenge to speed up low-level data access Services and access mechanisms • ncWMS ReSC Web Map Service: (http://ncwms.sf.net) for visualising CFNetCDF file data – Java application using Java NetCDF libraries with OGC standards plus geospatial add ons – Very fast visualisation – Developments:- point data, satellite data, i.e. CSML features • OpenDAP • – Exposes data arrays as URL with subsetting and aggregation capabilities – Identical to reading local file => no changing of complex codes THematic Realtime Environmental Distributed Data Services THREDDS (www.unidata.ucar.edu/projects/THREDDS/) – Very popular community software for data-serving – Catalogue Service + OpenDAP – Now has a version of ncWMS in stack • PostGres – Used currently for in situ data management in house eg. World Ocean DB (9m or so ocean profiles (T,S), using PostGIS geospatial extension Godiva2: interactive visualization of environmental data http://www.reading.ac.uk/godiva2 http://ncwms.sf.net Complex grids and reprojection Model-satellite intercomparison Compatibility with other GIS tools NASA World Wind Cadcorp SIS Google Earth GMES : European Marine Core Service 20 real-time data servers throughout Europe No images for ROMS (offline at time of these screenshots) Model v. Obs. Comparison • ncWMS modified to allow Clickable Point Features => Models and Observations • EU FP7 Coastal Oceanography project “ECOOP” • Click on observation for model-obs timeseries… QC checks on rogue obs. Compare QC decisions: Operational Agencies (real time) v. Delayed mode evaluation N Atl 07-08: Delayed mode QC vs BMRC QC 114 (accepted 10533) Ongoing • Combining remote data with client data (NERC POC project MashMyData) – Using “e-Science Central” technology from Newcastle to manage users and workflows • Interacting with data visualisations and commenting on them (JISC project BlogMyData) – Using blog technology developed for chemists! • GIS services in the cloud – For achieving necessary scalability and reliability – http://code.google.com/p/gae-wms/ Challenges/Wish List • More Services/tools => encourage standards • Ensembles of model data (eg for climate) – How to store, how to visualise • Very large files (online storage may involve file compression) • Scalability – Interactive access to data by multiple users • Getting Data Centres to buy into interactivity with data outside their own centre, community • Simplifying access control mechanisms – Complex security is a great way to kill a project Finish