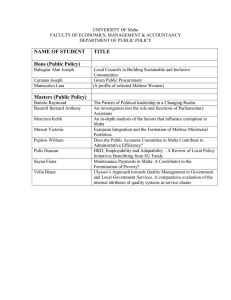
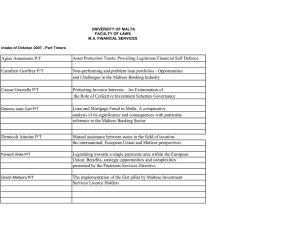
A Human Resource Development Policy and Strategy for Malta Anne Marie Thake

A Human Resource Development
Policy and Strategy for Malta
Anne Marie Thake
B.A. (Hons), M.Sc. (Manchester)
Objectives
• Prepare a strategic plan for the development of human resources in
Malta which dovetails with the National Development Plan for Malta, as well as the programming period for the European Social Fund
• guide for Government to establish its priorities and to take the corresponding decisions and actions regarding employment and training in line with the European Employment Strategy
• common framework document to guide all organisations related to workforce development through social dialogue in their planning and delivery of services and to enable coordination among the organisations
The main themes are:
1. Preliminary Considerations of HRD in Malta
2. Employment
3. Training, Development and Lifelong Learning
4. Vocational and Career Guidance
5. Women in Employment and Training
6. Focus on Specific Groups
7. Implementation
1- Preliminary considerations of HRD in Malta
• The Maltese Context
• Labour Market Trends
• Relevant Maltese Official Policies
• The Human Resource Infrastructure
• Employability and Lifelong Learning
1 - Preliminary Considerations
• Employment patterns in Malta are changing as a result of international socio-economic trends, and Maltese geo-cultural realities
• Elements of traditional Maltese culture such as multiculturalism, flexibility, networking among employers and employees, cultural and institutional resilience, are potential contributors
• Recent developments in the Maltese official foreign, economic, environmental, employment, and educational policies facilitate the development of an effective HRD Policy and Strategy
2 - Employment
Issues to be addressed include:
• Occupational preferences of the unemployed may not reflect jobs in demand in the labour market
• A need to improve skill levels
•
Insufficient involvement of social partners in VET
• Low participation rates among the LTU in training programmes
3 - Training, Development and Lifelong Learning
Issues that are being addressed include:
•
Levels of basic skills are low
• Inadequate quality of VET and certification
• Low level of VET funding by EU standards
• Bias against technical courses persists amongst students and parents
• Insufficient recognition of non-formal and informal learning
4 – Vocational and Career Guidance
Issues that are being addressed include:
• Skill shortages in particular sectors
• Career guidance services within and outside educational structures need upgrading
• More comprehensive and widespread career guidance information
5 - Women in Employment and Training
Issues that are trying to be addressed include:
• Female labour participation is low and often tied to specific sectors and levels of occupation
• Unequal working conditions between genders
• Low participation of women in CVT
• Not enough enabling measures to enhance employment rate (eg. Childcare provision)
6 - Focus on Specific Groups
A need to review mechanisms for the inclusion of the following specific groups in the labour market:
• Youths
• LTUs and VLTUs
• Disadvantaged groups (ex-substance abusers, ex-correctional inmates, persons with social problems, and persons with disabilities)
• Mid-career job seekers
• Job seekers with low literacy skills
• Job seekers coming from specific localities
7 - Implementation
There are 8 main challenges:
1. Reintegrating unemployed people into the national workforce
2. Helping people become more employable and promoting gainful employment through the development of their skills
3. Underpinning competitiveness by promoting investment in skills and knowledge of the workforce
4. Strengthening commitment to lifelong learning/VET
5. Providing comprehensive guidance and counselling services
6. Promoting equal opportunities
7. Assisting small enterprises to overcome the skill barriers to development
8. Developing a strong quality assurance system
Challenge 1 - Reintegrating unemployed people into the national workforce
Concrete strategies include the following:
• Action programmes for the unemployed are to be enhanced and given more publicity
• Standards of occupational competence and certification are to be implemented
• Assistance through financial and/or technical support to midcareer job seekers are to form cooperatives or take up selfemployment
Challenge 2 Helping people become more employable and promoting gainful employment through the development of their skills
Concrete strategies include:
• Early interventions to encourage long-term educational participation, identify and address literacy and numeracy difficulties at an early stage
• Compilation of a national skills inventory and identification of employees who need to improve their skills
• Schools and training centres to be linked to internet and developed into multi-purpose local learning centres
Challenge 3 - Underpinning competitiveness by promoting investment in the skills and knowledge of the workforce
Concrete strategies include:
• Recognition of academic knowledge and practical application through MQC and NARIC
• A programme aimed at cultivating a trust culture in the MCESD and among the social partners
• Create incentives for companies to invest more in continuing training for employees
Challenge 4 - Strengthening commitment to lifelong learning/ CVT
Concrete strategies include:
• Actions are to be taken to prevent or address the digital divide
• A language institute to be set up within MCAST to upgrade the fluency of languages in different learning settings
• A national database of providers of formal learning opportunities to be initiated, effectively managed and marketed on a wide scale
Challenge 5 - Providing comprehensive guidance and counselling services
Concrete strategies include the setting up of a
National Vocational Guidance Agency in order to:
• create policies related to vocational guidance and counselling
• coordinate career guidance services
• assess the effectiveness of existing guidance services (including staffing, access, financing, the role of key stakeholders in planning and delivering services, delivery methods)
Challenge 6 - Promoting equal opportunities
Concrete strategies include:
• Gender impact assessments
• Promote flexible work practices to increase the female participation rate
• Employment incentive schemes and training programmes for disadvantaged groups
• National Childcare Strategy
Challenge 7 - Assisting SMEs to overcome the skill barriers to development
Concrete strategies include the following incentives to assist SMEs to be set up:
• Tax credits and allowances for relevant training
• educational vouchers
• co-funding between private employers and trainees
• matching funding for innovative ideas
• national competitions to reward good practice
Challenge 8 - Developing a strong quality assurance system
Concrete strategies include the setting up of a formalised quality assurance system to:
• provide reliable information on best practices
• information on training consultants or institutions
• ensure that skills and experience acquired are certified to a standard which has widespread recognition and portability
National Commission for Higher Education
This Commission has been set up to:
• monitor and assist the implementation of the recommendations put forward by this document
• draw up and execute future policy recommendations to
Government and social partners at the national, sectoral and enterprise levels
Conclusion
• These HRD policies and strategies are acting as a catalyst for change in line with the European
Employment Strategy
• They are being used dynamically and must change and be adapted to circumstances
• All social partners should be actively involved in the training and development of Malta’s human resources
Anne Marie Thake
Resident Academic
University of Malta anne.thake@um.edu.mt