Prevention of Illicit Discharge Within Manhattan, Kansas Ellen Calhoun, Ryan Flickner,
advertisement

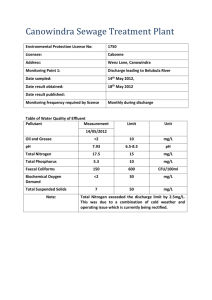
Prevention of Illicit Discharge Within Manhattan, Kansas Ellen Calhoun, Ryan Flickner, A. Meredith Smythe, Kelsi Steele Outline Project Overview Project Objectives National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Illicit Discharge Common Illicit Discharges Clean-Up Procedure Environmental Impact Employee Training Emergency Procedure Haz-Mat Conclusions and Recommendations Project Overview Our Service Learning project was to assist the City of Manhattan in establishing an illicit discharge prevention plan that fulfills a minimum control measure established through NPDES. Project Objectives Define regulations presented in NPDES Develop a plan for the prevention of illicit discharges into the stormwater sewer Formulate a list of potential contaminants, the actions required, and the environmental impact of the contaminants. Formulate a spill prevention and spill clean-up procedures. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Established by Federal Water Pollution Control Act (FWPCA) Amendments of 1972 Requires that facilities that release pollutants into waters of the US to obtain a permit Has 4 goals… National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Goal 1 Eliminate the discharge of pollutants into navigable waters of the United States National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Goal 2 Protect fish, shellfish and wildlife National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Goal 3 Provide safe water for recreational purposes National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Goal 4 Prohibit the release of toxic discharges National Discharge Pollutant Elimination System (NPDES) Permit (EPA definition) “a license for a facility to discharge a specified amount of a pollutant into a Office of Wastewater Management - Water Permitting receiving water under certain conditions; however, permits may also authorize facilities to process, incinerate, landfill, or beneficially use sewage sludge.” National Discharge Pollutant Elimination System (NPDES) Types of Permits Individual Customized to the specific facility General Envelop multiple facilities within a specific category Currently Manhattan, Kansas has neither type of permit on record with the EPA website Illicit Discharge Any discharge into a storm water drain or treatment plant that is not composed entirely of storm water Exempt items: wetlands, diverted stream flows, springs Exempt under certain conditions: foundation drains, landscape irrigation, individual residential care washing, sidewalk washing, as well as flows from emergency fire fighting activities Common Illicit Discharges Our focus: oil, grease, gasoline, paints, yard wastes, garbage, household chemicals, and pesticides Cause for concern: chlorinated pool water, cigarette butts, sanitary sewer flows, commercial car wash wastewater, construction debris, and food wastes Clean-Up Procedure Yard Waste – Compost Pile Garbage Paper Litter – Recycle Plastic Bottles – Recycle Source: http://www.bidisposal.com/images/YARDWASTE.jpg Clean-Up Procedure Motor Oil, Gasoline, Source: http://www.homedepot.co m/cmc_upload/HDUS/E N_US/asset/images/eplus/ 130232_3.jpg Grease, Paint Shut off all possible ignition sources Transfer excess pollutant into spill proof container. Remove remaining residue use an absorbent such as earth, sand, or vermiculite. Source: http://www.phasmidsincyb erspace.com/Pictures/Verm iculite.JPG Clean-Up Procedure Acid/Base Neutralize an acid with soda ash, sodium bicarbonate, or lime Neutralize a base with citric acid or dilute hydrochloric acid Liquid Detergent Transfer into another container Remove residue with absorbents Flush with water Safety Equipment Source: http://www.dickblick.com/items/329/07/32907 -OA2ww.jpg Safety Goggles Rubber or Nitrile Gloves Source: http://www.ritop.com/informa tion/images/ya127c.jpg Respirator Protective Clothing Source:http://www.ritop.com/inf ormation/images/glass1bk.jpg Environmental Impact If any discharge enters the stormwater sewer contact the National Emergency Response Center Absorbent pillow can be used to contain the pollutant until remediation can occur It is important to act quickly to prevent substantial damage to the ecosystem. Employee Training Employee training is crucial in pollution prevention The EPA recommends at a minimum the following in a program Maintenance training Maintenance schedules Long-term inspection training Procedure for properly disposing of waste when removed from storm sewers Ability to transfer knowledge through public education Finance planning for enough funding Employee Training Options for training procedures: Visual: posters, bulletin boards Verbal: employee meetings, courses Field training: hands-on demonstrations Employee Training Record process of training programs Senior management involvement is vital Employee Training Advantages Cost effective Easily implement able Able to be Duplicate/ can be standardized Disadvantages Senior management apathy Employee lack of motivation Lack of Incentives to become involved Prioritization List all illicit disposal incidents that have been reported but not yet investigated and place in one of the following categories: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Hazardous, affecting public health and safety Hazardous, affecting the environment (receiving waters, air, etc…) Hazardous, affecting property Hazardous, other Non-hazardous, affecting public health and safety Non-hazardous, affecting the environment (receiving waters, air, etc…) Non-hazardous, affecting property Remaining incidents Emergency Procedure Contact the Fire Department immediately with information Type/cause of incident Types of chemicals involved Resources available on site Possible injured personnel Source: http://www.ecy.wa.gov/programs/spills/incidents/willapa/willapaphoto s/willabase.jpg Haz-Mat Hazardous Materials Division Within the Kansas State Fire Marshal’s Office Supports local first responders by isolating hazardous materials Accidents and/or Acts of Terrorism Haz-Mat Kansas Haz-Mat Response Team Within the state boundaries, regardless of local government jurisdiction Haz-Mat Regional Response Teams Coffeyville Colby Emporia Ford County Hays Manhattan Newton Overland Park Salina Sedgwick County Seward County Topeka Wellington Haz-Mat Kansas State Fire Marshal’s Office Teams can respond to most areas in Kansas within an hour or less Can haz-mat incidents and accidents as well as terrorist events Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear (CBRN) Haz-Mat To Request a Response Team Call the toll-free hotline Call the group pager (1-866-KHAZMAT) (785-357-3261) website (www.myairmail.com) Both hotline and website forward to the group pager Conclusions Manhattan has accomplished two out of the six minimum control measures. Public education and outreach Public participation and involvement Recommendations to accomplish next minimum control measure Two or more city workers become trained in hazardous materials protocol Obtain a MSDS database Keep on hand absorbents such as: sand, earth and vermiculite. Acknowledgements Dr. Alok Bhandari, Team Advisor Steve Hampton, Assistant City Engineer Questions?