Chem 102H - Spring 2016
advertisement

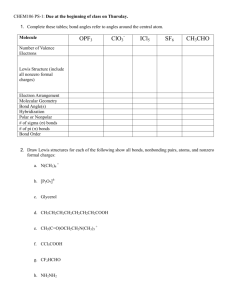
Chem 102H - Spring 2016 Equations You Should Know Gases Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT Thermodynamics Pressure-Volume Work w = !PÄV (w = P-V work) First Law ÄU = q + w (U = internal energy, q = heat, w = work) Enthalpy ÄH = ÄU + PÄV (H = enthalpy; at constant P, q = H) Second Law ÄS = (S = entropy) Heat Capacities ÄU = nCv ÄT (Cv = heat capacity at constant volume) ÄH = nCp ÄT (Cp = heat capacity at constant pressure) ÄG = ÄH ! TÄS (G = Gibbs energy; constant T and P) Gibbs Energy Equilibrium Equilibrium Constant For the reaction: aA + bB W cC + dD (Än = change in number of moles of gas during rexn.) Relationship of K to Gibbs Energy: ÄGE = !RT ln K p Acids, Bases and Solution Equilibria Autoionization of Water Kw = [H3O+] [OH!] = 1 x 10!14 pH Scale Weak Acids and Bases For: HA (aq) + H2O (l) W H3O+ (aq) + A! (aq) For: B (aq) + H2O (l) W HB+ (aq) + OH! (aq) Buffer Solutions Solubility Product (weak acid/conjugate base buffers) For dissolution reaction: AxBy (s) W xAm+ (aq) + yBn! (aq) Ksp = [Am+]x[Bn-]y Electrochemistry Free Energy ÄGE = !nFEE and ÄG = !nFE (where F = Faraday’s Constant = 96,485 C/mol e!’s) Faraday’s Laws Nernst Equation At 25EC, Kinetics Rate Laws Arrhenius Equation For reaction: aA + bB + ... 6 Products