Impaired Visuospatial Processing in Young Adult Female Fragile X Trends in Children
advertisement

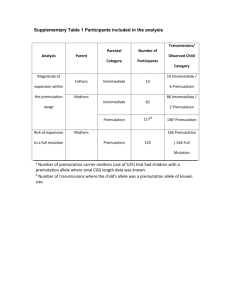
Impaired Visuospatial Processing in Young Adult Female Fragile X Premutation Carriers and Emerging Trends in Children Yingratana Bella McLennan, Ling Wong, Naomi Goodrich-Hunsaker, Danielle Harvey, Flora Tassone, Susan Rivera, Tony J. Simon 13th International Fragile X Conference, Miami 2012 July 26, 2012 FMR1 Gene Variation FMR1 gene can be found on the long arm of the X chromosome at position 27.3 Female Premutation Prevalence of premutation: • 1 in 113-259 females • 1 in 260-813 males • Female Premutation Prevalence of premutation: • 1 in 113-259 females • 1 in 260-813 males • Female Premutation Prevalence of premutation: • 1 in 113-259 females • 1 in 260-813 males • How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? How do female fragile X premutation carriers perform in visual tasks involving spatial information (visuospatial processing)? Psychomotor Speed Female Motor Reaction Times * ‣ Adult female fXPCs show faster psychomotor speed compared to HCs Female Oral Reaction Times Visuospatial Processing Tasks Magnitude Comparison Enumeration Verbal (Distance Effect Task) (Numerical Spatial Attention Task) Magnitude Comparison Magnitude Comparison Task “Which of the two blue bars is longer?” ‣ Distances between the 2 bars vary between 1-7cm in length ‣ The greater the difference in lengths, the easier it is to judge which bar is longer ‣ Performance accuracy goes down as the differences in lengths become smaller Magnitude Comparison Results * ‣ ‣ ** * Female carrier adults (20-42 years old) show significant differences in reaction times after their enhanced psychomotor speed was accounted for but had no significant difference in error rates as compared to controls However, female carrier children (7-15 years old) show no significant differences in reaction time and error rates as compared to controls Magnitude Comparison: Age and CGG Effects * * * * ‣ No significant correlations were found from age in the children or adults. ‣ However, a significant correlation was found in terms of worse performance and CGG expansion in adult female carriers but not in children. Enumeration Verbal Enumeration Verbal Task “How many green items do you see in the red square?” ‣ Small items (1-3 items) are effortless ‣ The answer can be perceived at a glance without counting ‣ Subitizing effect Enumeration Verbal Task “How many green items do you see in the red square?” ‣ ‣ ‣ Large items (5-8) are more difficult Each individual item is mentally separated out and counted Counting effect Enumeration Verbal Results ‣ Female carrier adults (21- 42 years old) show no significant differences in reaction times or error rates as compared to controls ‣ Female carrier children (7-15 years old) also show no significant differences in reaction time or error rates as compared to controls Enumeration Verbal Age and CGG Effects * * * ‣ ‣ * No significant correlations were found from age in the children or adults. However, a significant correlation was found in terms of worse performance and CGG expansion in adult female carriers but not in children for the counting range. The subitizing range showed no correlation. Summary ‣ ‣ ‣ Magnitude Comparison: As a group, adult female carriers show a significant difference in performance compared to adult female controls Results show a positive correlation indicative of poorer performance in detecting quantitative differences at higher CGG levels ‣ ‣ ‣ Enumeration Verbal: As a group, adult female carriers showed no significant differences in performance compare to adult female controls However, results show another positive correlation between poorer performance on the task and increasing CGG length ‣ Conclusion: Higher CGG repeat lengths may contribute to subtle impairments in visuospatial processing even when there are no group differences Thank you ‣ ‣ ‣ ‣ Thanks to all those that participated in our study CABIL Lab members: ‣ Naomi Goodrich-Hunsaker ‣ Ling Wong ‣ Flora Tassone ‣ Danielle Harvey Collaborators: ‣ Johnson GadElkarim ‣ Liang Zhan ‣ Olusola Ajilore ‣ Alex Leow Thanks to: ‣ Susan Rivera ‣ Paul Hagerman Funding: NIDCF UL1 DE019583, NIA ‣ Randi Hagerman RL1 AG032119, NINDS RL1 ‣ John Olichney NS062412, NIDA TL1 DA024854. ‣ The rest of the NTRI team