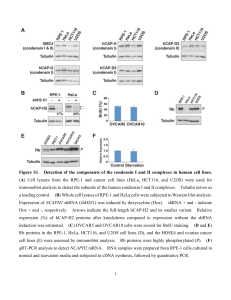
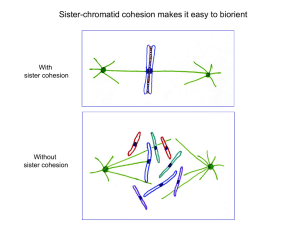
Resonant vibrations in HEAT repeats: the tune for the mitotic dance? UK
advertisement

Resonant vibrations in HEAT repeats: the tune for the mitotic dance? Nigel Dyer UK Professor Herbert Frohlich A single polarised macromolecule, e.g. a protein • Preferential excitement of large amplitude low frequency modes Multiple polarised proteins • Coherent vibrational mode through dipole-dipole interaction HEAT repeat structure – Importin beta • A ladder of helix-turn-helix motifs • Outer ‘A’ helixes and inner ‘B’ helixes surround a central importin beta alpha helix (blue) Proteins containing HEAT repeats Condensin: Compacts Chromosomes Importin: Transports cargo into the cell nucleus TOGp (XMAP215 etc): Associated with the ends of microtubules as they grow towards the chromosomes during mitosis. Others… Delangins: Locates the cohesin complex within chromosomes Huntington: The Condensin Family Prokaryotic Condensin Structured Maintainance of Chromosomes (SMC) proteins Eukaryotic Condensin ATP binding at SMC heads Proteins containing HEAT repeats Effect of disabling Condensin I and II (Ono, Losada et al. 2003) •e: Control •f: Condensin I disabled: Puffy and bent •g: Condensin II disabled: Straighter but curly Group of coherently vibrating proteins with misalignment Interaction brings proteins into alignment Mitotic chromosome: Condensins disabled • Condensin I (Green) aligned along chromosome axis Condensin I • Aligning of Condensin I straightens Chromosome arms Condensin II • Condensin II (Blue) orthogonal to main axis • Not aligned with each other because main axis is twisted Condensin II • Aligning force from condensin II removes twist from chromosome arms Condensin I and II • Both act to draw together and align chromosome arms Condensin I and II axis definition •Condensin I defines long axis of Chromosome •Condensin II defines perpendicular axis/plane through both Chromosome arms Effect of depleted Condensin I on metaphase plate • Control, with well defined metaphase plate • Depleted Condensin 1 Poorly defined metaphase plates (From Ono, Fang et al. 2004) Condensin 1 • Axis extends to span multiple chromosomes Effect of depleted Condensin II on metaphase plate •Control, with centrosomes (arrowed) symmetrically placed on either side of the metaphase plate (dotted line) • Depleted Condensin II • Centrosomes poorly positioned in relation to metaphase plate (From Ono, Fang et al. 2004) Condensin II • creates a plane that sets the location of centrosomes centrosomes HEAT repeat structure – Importin beta HEAT repeat structure • The original ‘cork and bead’ model HEAT repeat structure – A more compact form? • Rings of 5 inner (yellow) helixes around an elongated core • One helix (green) spans two rings HEAT repeat structure View along the length of Importin alpha/beta complex End on view of Importin alpha/beta complex, with no side chains on the IBB domain of importin alpha HEAT repeat vibrating in cellular matrix • Inner core and outer sheath oscillate 180° out of phase • No movement of centre of mass • Vibrations spread as evanescent wave into the surrounding substrate HEAT repeat resonant energy transfer • Energy coupled from excited structure (on right) to adjacent structure (on left) • Both structures finish in coherent synchronous oscillation HEAT repeat alignment • HEAT repeats oscillating but slightly misaligned • Non-linear interaction of evanescent waves generates forces that bring HEAT repeats into alignment. The Condensin Family Prokaryotic Condensin Structured Maintainance of Chromosomes (SMC) proteins Eukaryotic Condensin ATP binding at SMC heads Proteins containing HEAT repeats SMC proteins/Prokaryotic Condensin • Thermally induced breathing modes in long coiled coil legs • Pulls DNA together during contraction phase of oscillation SMC head binding with ATP • ATP binds heads together in Prokaryotic condensin at Walker A/B domains • Walker A/B domains in ABC transporter proteins associated with mysoin like power stroke Walker A/B domain and binding ATP The Condensin Family Prokaryotic Condensin Structured Maintainance of Chromosomes (SMC) proteins Eukaryotic Condensin ATP binding at SMC heads Proteins containing HEAT repeats HEAT repeats in TOGp/XMAP 215 • TOGp is associated with the growing ends of the microtubules as they extend towards the chromosomes in the metaphase plate TOGp (red) HEAT repeats in Importin beta • Importin beta attaches to cargos and transfers them into the nucleus Importin beta (green) Cell nucleus The Nuclear pore complex • Core of complex filled with nucleoporin proteins, a mix of multiple FG repeats and hydrophilic linkers • Pore blocked by water gell created by nucleoporin proteins? Passage of Importin through the Nuclear pore complex • Gel/water transition triggered by Importin vibrations Central formers for HEAT repeats • Importin beta: Importin alpha • Condensin: Histone H3 tails (Jager, Rauch et al. 2005) • TOGp/XMAP215 Tubulin tails Orthogonal condensin axes and orthogonal centrioles centrosomes Centriole pair Thanks to: Vermont Photonics Warwick University Lila Gierasch, Gerry Pollack, Mae-wan Ho and countless others who I have visited and emailed The creaters of Blender Biophoton emission from dividing fish egg cells • ‘Cascades’ of biophoton spikes.