Metabolic Pathways
advertisement

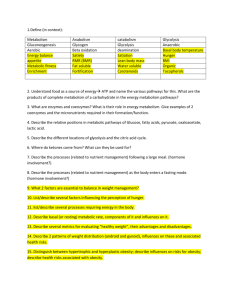
Metabolic Pathways What is metabolism? Metabolism encompasses the integrated and controlled pathways of enzymecatalysed reactions within a cell. Metabolic pathways refer to reactions in the body that are linked together. What are the two types of enzymecatalysed reaction? • Biosynthetic reactions (you probably called them synthesis reactions previously), which are also referred to as anabolism. • Breakdown reactions, which are also referred to as catabolism. Synthetic reactions Example: glucose-1-phosphate phosphorylase starch This reaction requires the input of energy to proceed (anabolic reaction). Breakdown reactions Example: starch amylase maltose This reaction releases energy (catabolic reaction). What else do you need to know? • Metabolic pathways can have reversible and irreversible steps. • Alternative pathways may exist that can bypass steps in a pathway.