4/12/2016
advertisement

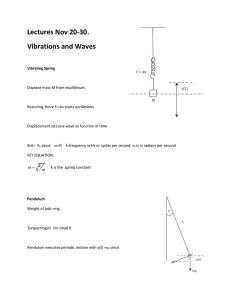
4/12/2016 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Wave definition, types of waves, orbital waves Why study waves? Wave parts, anatomy of a wave How waves begin, generating force, restoring force Wave Speed: R=D/T or C=L/T, Celerity Water motion in waves Wave base, L/2 Deep water waves, intermediate and shallow water waves Wind generated waves, H dependent on WfD Wave types: Sea, Swell and Surf Waves as they approach the shore: refraction, diffraction and reflection Canyon divergence and headland convergence Sea caves, arches and sea stacks Wave generated currents: longshore and rip Standing waves: nodes and antinodes, seiches Catostrophic waves: storm surges and tsunamis Mega tsunamis: know H, L and P of a typical seismic sea wave! Internal waves 1 4/12/2016 2 4/12/2016 Fig. 19‐8, p.571 3 4/12/2016 Standing Waves • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Wave definition, types of waves, orbital waves Why study waves? Wave parts, anatomy of a wave How waves begin, generating force, restoring force Wave Speed: R=D/T or C=L/T, Celerity Water motion in waves Wave base, L/2 Deep water waves, intermediate and shallow water waves Wind generated waves, H dependent on WfD Wave types: Sea, Swell and Surf Waves as they approach the shore: refraction, diffraction and reflection Canyon divergence and headland convergence Sea caves, arches and sea stacks Wave generated currents: longshore and rip Standing waves: nodes and antinodes, seiches Catostrophic waves: storm surges and tsunamis Mega tsunamis: know H, L and P of a typical seismic sea wave! Internal waves Hurricanes cyclones and storms bring waves and coastal flooding Hurricane Andrew https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bYI1zIjJr4g STORM SURGES 4 4/12/2016 Hurricane Katrina 8/28/05 Storm in Bangladesh in April 1991 ~138,000 killed, 10 million left homeless, 6 meter storm surge goes inland, 1.5 billion in damage Superstorm Sandy 10/28/12 Typhhon Haiyan 11/8/13 5 4/12/2016 http://ulithimarineconservation.ucsc.edu/ Tsunami reporting stations and subduction zones Tsunamis DART: Deep‐Ocean Assessment and Reporting of Tsunamis 6 4/12/2016 9.1 – 9.3 Magnitude Sumatran Earthquake Dec. 26, 2004 Areas at Risk Hawaii Alaska California East Coast US? – Gulf Coast US? – – – – • Plates‐Boundary Type • Depth: 30km • Rupture Length and shaking duration: ~1,300Km (810mi), over 4 min in 1 area, up to 10min total • Displacement: lateral ~20m, vertical 2‐5m • Energy Released: ~475 megatons of TNT or 23,000 A‐Bombs Earthquake activity in Japan from 1990 to 2011 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=Yl08jK4 ci2g&feature=relmfu 7 4/12/2016 Capitola California March 11, 2011 Reducing Tsunami Hazards • Warning system in all major oceans • Local gov’t evacuation routes and procedures • Education about warning signs – Ground‐shaking in coastal areas – Unusual disturbance of ocean – Move to high ground (several hours‐days) – First wave generally not largest – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qFKgQwou7ls Surfing calving glaciers • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Wave definition, types of waves, orbital waves Why study waves? Wave parts, anatomy of a wave How waves begin, generating force, restoring force Wave Speed: R=D/T or C=L/T, Celerity Water motion in waves Wave base, L/2 Deep water waves, intermediate and shallow water waves Wind generated waves, H dependent on WfD Wave types: Sea, Swell and Surf Waves as they approach the shore: refraction, diffraction and reflection Canyon divergence and headland convergence Sea caves, arches and sea stacks Wave generated currents: longshore and rip Standing waves: nodes and antinodes, seiches Catostrophic waves: storm surges and tsunamis Mega tsunamis: know H, L and P of a typical seismic sea wave! • Internal waves 8 4/12/2016 Small Internal Wave in Monterey Bay, 2008 Figure 10_28 Internal Waves: can have L of 100’s of Ms to 10’s of Kms H often >50m, T could be from 20 min to a few hrs. Fig. 10.26 9