ST PANCRAS GARDENS – ROCK TYPES
advertisement

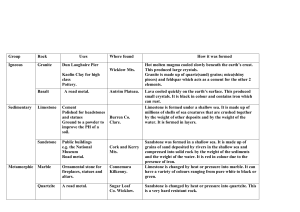
ST PANCRAS GARDENS – ROCK TYPES St Pancras Gardens is a haven for the geologist with representatives from the sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic aspects of the rock cycle. 1 LIMESTONE YOU WILL NEED: Map of St Pancras Gardens Two sheets of fossils Two colouring pencils Instructions There are two distinctly different types of limestone within the gardens – Portland Limestone and Carboniferous Limestone. Each one contains a unique group of fossils that can be used to identify it. You have been given two sheets of paper that list some of the fossils found in each. A number of unshaded gravestones, in the vicinity of St Pancras Old Church, are also marked on your map. These are made of either one of the two limestones. Locate these gravestones and try to determine their lithology (rock type) by finding as many of the listed fossils in each one as you can. Choose a different colour for each type of limestone and colour in the unshaded gravestones on your map according to your findings. Don’t forget to colour in your key too! While you are doing this: LOOK at the fossils carefully. Draw what you see and label any features you can using the sketches provided. THINK about what you are looking at… What do these fossilized creatures remind you of? Where do you think they might have lived? (answer on your notes pages) What does this tell you about how the limestones were formed? (answer on your notes pages) Notes and sketches of Portland Limestone (use extra paper if necessary) Notes and sketches of Carboniferous Limestone (use extra paper if necessary) 2 MARBLE Marbles are limestones that have been altered by high temperatures and/or pressures. This process is known as METAMORPHISM, and marble is a METAMORPHIC rock. There are a few examples of marble within St Pancras Gardens, but don’t be misled by the information plaques on some of the memorials because the word marble is used by stonemasons to mean any rock that can take a polish, which is not the same definition as a geologist would give! Compare the marble of the Tate Family Grave with the limestone of the Ann Abbey Memorial (see map). How are they similar? How are they different? Colour (try to find relatively clean surfaces) ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Fossil content (don’t try and identify anything, just look at numbers!) ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Surface weathering (which has a rougher, more eroded-looking surface?) ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Texture (are they smooth? rough? crystalline? grainy?) ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 3 GRANITE What type of rock is granite? (circle correct answer) SEDIMENTARY IGNEOUS METAMORPHIC There are two distinct types of granite in St Pancras Gardens: c A pink granite (polished) d A black and white granite (unpolished) Mineralogy The positions of some granite gravestones are marked onto your map. Make your way to ONE of them (try to avoid all going to the same one!) You should be able to see three different types of mineral in this rock: c FELDSPAR = Pink or white crystals with large rectangular outlines, often crossed by fine parallel cracks known as “cleavage”. d QUARTZ = Grey or colourless irregularly shaped crystals with a glassy appearance. e MICA = Black and/or silver flakes Black flakes – BIOTITE MICA Silver flakes – MUSCOVITE MICA (not visible in polished granites) Quartz is otherwise known as SILICON DIOXIDE. What is its chemical formula? _______________ Sketches SKETCH OF THE MINERALS IN GRANITE Quartz Feldspar Biotite mica Drawing courtesy of Dr Eric Robinson, UCL Draw an area of granite yourself, identifying and labelling all three minerals and any features about them that you feel are important. Use the example sketch given to you for help in identification. GRANITE SKETCH Don’t forget to add a scale! Grain size The granite you are examining is EQUIGRANULAR, i.e. all the crystals are roughly the same size. Rocks can have different grain sizes depending on how they formed. There are three main types, termed simply as: COARSE GRAINED – crystal diameters >5mm MEDIUM GRAINED – crystal diameters = 1–5mm FINE GRAINED – crystal diameters <1mm Let’s find out the grain size for this granite… Using a ruler, measure the lengths of 5 feldspar crystals (use feldspar crystals because they have the most regular shape and distinct long axes that can be easily compared): Length of feldspar crystal: 1 ___________ Average: 2 ___________ _____ + _____ + _____ + _____ + _____ 5 3 ___________ 4 ___________ 5 ___________ = _____mm From your average feldspar crystal length, do you think this is a coarse, medium or fine grained rock? Why? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Xenoliths Can you see any patches within the granite that look different from the surrounding rock? (If you are at the Rhodes Family Grave you may not, so try one of the other granite stones marked on your map). What distinguishes them from the rest of the granite? ______________________________________________________________ What shape are they? ______________________________________________________________ (Check that it is not dirt or lichen that you are looking at!) These are XENOLITHS (Greek word for “strange rock”). Xenoliths are blocks of country rock (the rock into which the granite would have been intruded when molten) that were dislodged by the intrusion and “fell” into the hot magma. Originally the blocks would have been angular in shape but became more rounded as they were eroded by the hot magma (i.e. the edges melted). Draw an example of a xenolith, noting its size and its rounded edges. Try to point out how it is different from the surrounding granite, but don’t worry about its mineral content! XENOLITH SKETCH Don’t forget to add a scale! 4 SANDSTONE Sandstone is formed by the cementing together of grains of sand. Does this make it sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic? ________________________ Would you say that this sandstone is coarse grained, medium grained or fine grained? (use the same criteria that you did for granite) ____________________ Make your way to William Jones’ gravestone (see map). This gravestone has very well defined bedding planes. (Bedding = a series of visible layers in a rock that reflect the original surfaces of deposition) Has the gravestone been cut parallel or perpendicular to these bedding planes? ___________________________ Weathering tends to concentrate along the planes of weakness between sandstone layers (bedding planes). As a result, large flakes of sandstone are detached from the surface, leaving it very uneven. Make a sketch of the whole gravestone, marking on the bedding planes and eroded surfaces: GRAVESTONE SKETCH Don’t forget to add a scale! And finally… Using your map, make your way to the Burdett-Coutts Memorial Sundial. Then complete the diagram using terms from the list below: PINK GRANITE MANSFIELD SANDSTONE MARBLE PORTLAND LIMESTONE GREY GRANITE CAST IRON FOSSIL GROUP ONE Portland Limestone FOSSIL GROUP TWO Carboniferous Limestone KEY Portland Limestone Carboniferous Limestone St Pancras Hospital Railway William Jones’ Grave (SANDSTONE) Soane Mausoleum (LIMESTONE & MARBLE) Flaxman Family Vault (LIMESTONE) Jane Grundy Memorial (PINK GRANITE) Burdett Coutts Sundial Tate Family Grave (MARBLE) St Pancras Hospital The Hardy Tree Drinking fountain Limestone 2 Ann & William Birch’s Grave (GREY GRANITE) St Limestone 1 Pancras Ann Abbey Old Memorial Church (LIMESTONE) Limestone 3 Limestone 4 Rhodes Family Grave (PINK & GREY GRANITE)