Biology 612 Freshwater Ecology Exam 1 2010 ... 1) Match the terms with the letters (1 point...
advertisement
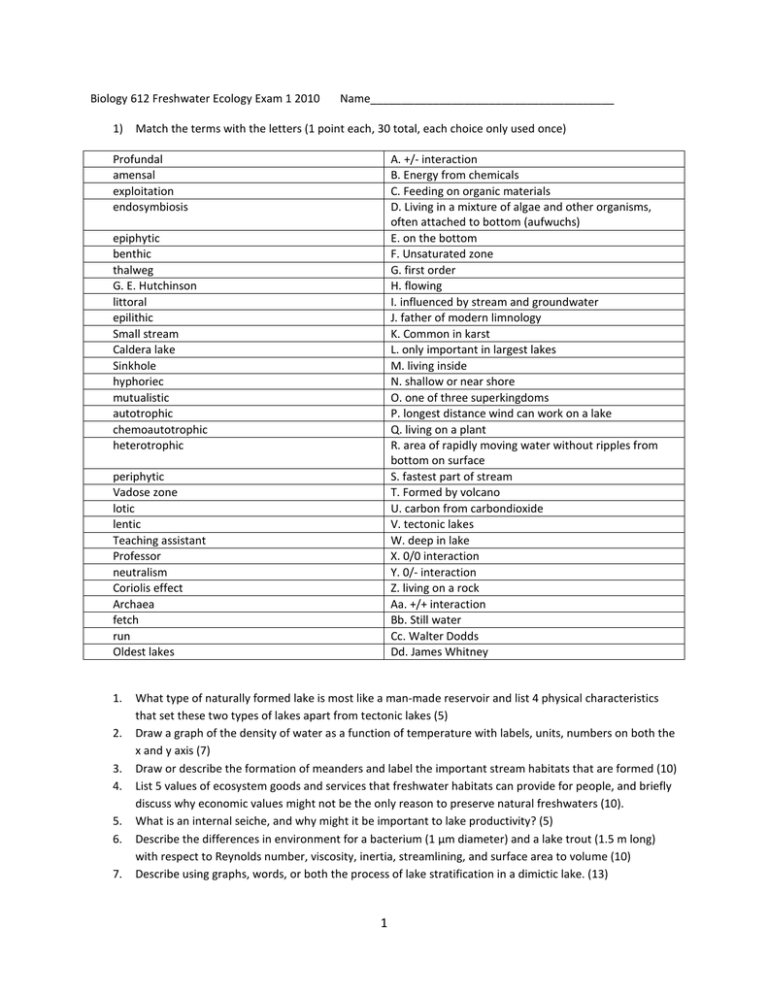
Biology 612 Freshwater Ecology Exam 1 2010 Name_______________________________________ 1) Match the terms with the letters (1 point each, 30 total, each choice only used once) Profundal amensal exploitation endosymbiosis A. +/- interaction B. Energy from chemicals C. Feeding on organic materials D. Living in a mixture of algae and other organisms, often attached to bottom (aufwuchs) E. on the bottom F. Unsaturated zone G. first order H. flowing I. influenced by stream and groundwater J. father of modern limnology K. Common in karst L. only important in largest lakes M. living inside N. shallow or near shore O. one of three superkingdoms P. longest distance wind can work on a lake Q. living on a plant R. area of rapidly moving water without ripples from bottom on surface S. fastest part of stream T. Formed by volcano U. carbon from carbondioxide V. tectonic lakes W. deep in lake X. 0/0 interaction Y. 0/- interaction Z. living on a rock Aa. +/+ interaction Bb. Still water Cc. Walter Dodds Dd. James Whitney epiphytic benthic thalweg G. E. Hutchinson littoral epilithic Small stream Caldera lake Sinkhole hyphoriec mutualistic autotrophic chemoautotrophic heterotrophic periphytic Vadose zone lotic lentic Teaching assistant Professor neutralism Coriolis effect Archaea fetch run Oldest lakes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What type of naturally formed lake is most like a man-made reservoir and list 4 physical characteristics that set these two types of lakes apart from tectonic lakes (5) Draw a graph of the density of water as a function of temperature with labels, units, numbers on both the x and y axis (7) Draw or describe the formation of meanders and label the important stream habitats that are formed (10) List 5 values of ecosystem goods and services that freshwater habitats can provide for people, and briefly discuss why economic values might not be the only reason to preserve natural freshwaters (10). What is an internal seiche, and why might it be important to lake productivity? (5) Describe the differences in environment for a bacterium (1 µm diameter) and a lake trout (1.5 m long) with respect to Reynolds number, viscosity, inertia, streamlining, and surface area to volume (10) Describe using graphs, words, or both the process of lake stratification in a dimictic lake. (13) 1 8. What is the relationship between the diffusion boundary layer and the flow boundary layer, where do we expect these to occur and how are they related to molecular and transport diffusion (10). Biology 612 Freshwater Ecology Exam 2 Fall 2010 1. Name___________________ st Please match the following, write the letter after the text in the 1 column (26 points, 1 each) Rhodophyceae Bacillariophyceae Dinophyceae Cyanobacteria Chlorophyceae Porfira Mollusca Cnidaria Plecoptera Trichoptera Ephemeroptera Arachnida Hemiptera Coleoptera Cladocera Isopoda Amphipoda Alpha diversity Beta diversity Evenness Endemic Amphibian extinction Nile Perch Extinction vortex Unionid mussels Diptera A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. R. S. T. U. V. W. X. Y. Z. 2. 3. 4. 5. Green algae sponges hydra caddisflies water mites Silicon frustules (cell walls) True bugs beetles Blue-green algae Dorsal-ventral flattened crustacean Laterally-flattened crutacean Red algae Degree of equal numbers of different species Dinoflagellates Between habitat diversity Fungal disease (chytridiomycosis) Snails and clams Extinction of fishes in Lake Victoria Stoneflies Persistence problem with too small population Fish lures and old fashioned buttons Flies and midges Species only found in limited area Within habitat diversity Daphnia mayflies Please draw and label the carbon cycle as in class (15) Please draw and label the nitrogen cycle as in class (15) Write the equations for photosynthesis and respiration (4) Why are zones between oxic and anoxic habitats “hot spots” of biogeochemical processes (rapid rates of many types of nutrient cycling? (5) 6. Please draw the relationship between light and photosynthesis with labels of both axes and the respiration rate, compensation point, alpha, maximum photosynthesis (Pmax), and photoinhibition labeled specifically (7). 7. Why do Lake Baikal and Lake Tanganyika both have many endemic species (3)? 8. How is adaptation to high temperature reflected in the molecular structure of proteins, DNA, RNA and lipids (8)? 9. How was the CO2 problem solved in Lake Nyos (4)? 10. Why is it not likely to have high concentrations of both iron and phosphate together, nor high concentrations of iron alone in oxygenated water (5)? 2 11. List 3 adaptations to temporary habitats (3) 12. What is extreme about the following habitats (5) Neuston Deep groundwater High altitude lakes Ultra oligotrophic lakes Saline lakes Biology 612 Freshwater Ecology Exam 3 1. 2. 3. Name _______________________________ What are some potential endocrine disruption compounds (e.g. ecoestrogens), why are they active at low concentrations, and what effects could they have on wildlife and even potentially people ? (5) When describing the effect of nutrients on organisms, what is the difference between Michaelis-Menten uptake, Droop equation, and the Monod equations (6)? Fill in the following table with the limitation if the phytoplankton have the following Redfield ratios (C carbon, N nitrogen, P phosphorus, no limitation, or any combination of these) 8 C:N:P 1006:16:1 106:4:1 106:33:1 25:16:1 4. 5. limitation What is the key threshold in lakes take can keep them in eutrophic state, and what are three ways to avoid crossing that threshold? (5) Order the following steps in managing eutrophication (number from 1-8, 8 points) 3 Step order in process Characterize system, morphometry, nutrient inputs Identify feasible nutrient control strategies identify problem lake Predict relationship between in lake total P and algal biomass Predict effect of nutrient management on nutrient loading and expected in lake total P Post control monitoring to assess results of actions Assess if costs of nutrient control is justified on basis of improvements Project effect on lake clarity 6. Contrast the energy flow in planktonic lake systems as described by the traditional food web model and that described by the microbial loop (5) 7. Describe the relationship between food concentration and Daphnia filtering rate and ingestion rate of food (graphs or words are ok) 6 8. How are stable isotopes used to assess position in food web (e.g. 15N and 13C) (8) 9. Describe the trophic cascade and how it may control algal biomass (5) 10. Match the letter with the number (20) Statement Rita Colwell Rachel Carson Lake Washington Lake Trummen Everglades Magnetosomes random walk allelchemical phototaxis 11. 12. 13. 14. Match A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. midge in Nostoc Spirit Lake Greater area shredders resource ratio theory J. K. L. M. N. grass carp vertical migration, diurnal sexual dimorphism keystone species viruses remineralization O. P. Q. R. S. T. Sugar cane production increases P pollution geotaxis mutualism primary succession more species eat leaves zooplankton avoid predation species with strong effect on others in community chemical that influences growth or behavior of another organism Silent Spring Research on cholera Eutrophication stopped by diverting P P control did not work, sediment dredged different competive abilities for different nutrients can lead to co-exisitence interspecific competition for mates major cause of microbial mortality supplies inorganic nutrients to primary producers can control macrophytes movement toward light strategy of chemotaxis What happens in primary, secondary and tertiary stage of modern sewage treatment? (6) Describe the seasonal succession in lakes (8) What did James Whitney talk about in class ? (5) What did Davi Cunha talk about in class? (5) Biology 612 Freshwater Ecology Final Name_____________________________ 4 1. Fill in the following table according to the expanded predictions of the river continuum concept with respect stream order in a deciduous stream in the summer (28) Attribute Discharge Flooding P/R ratio Relative abundance of grazers relative abundance of shredders types of predatory fish light reaching stream bottom zooplankton abundance temperature fish diversity substrata mid order (4-7) medium low order (1-3) small high order >7 large regular/ predictable mud sand silt 2. 3. Draw the nitrogen cycle as presented in class (10) Fill in the following table with ecosystem characteristics of the listed habitats (20) 4. Attribute Stream Peat bog Large Lake water replacement short time Hydrologic variance high Benthic primary productivity Allochthonous high, leaves carbon input Terrestrial influence Seasonal variance Fill in the following table with respect to a fish and a bacterium (10) Attribute Reynolds number Inertia Viscosity Type of flow Type of diffusion 5. 6. 7. 8. Fish Deep groundwater none Bacterium List 5 values of ecosystem goods and services of freshwater ecosystems (5) What do you think are the biggest threats (list 3) to freshwater ecosystems (6)? Why is a “two story” fishery with salmonids in the upper Midwest US not possible in a very eutrophic lake? (4) Explain the process of stratification including wind and heating of a dimictic lake in a temperate climate. You can do this in words or using a series of graphs. (5) 5 9. Match the terms (12) Term 1 Mayfly Cyanobacteria Caddis fly Daphnia matching A. Blue Green Algae B. Cladocera C. both eveness and richness D. a measure of the relative number of free electrons E. Ephemeroptera F. concentration of compound up the food web G. live in hotsprings H. makes reversing eutrophication difficult I. carried in ballast water from Europe J. uptake as a function of concentration K. recolonization of disturbed habitat L. Trichoptera Shannon diversity Zebra mussel Redox potential Biomagnification thermophilic internal loading of phosphorus Michaelis-Menten Primary succession 6




