Cybersecurity Security activities in Japan towards the future standardization
advertisement

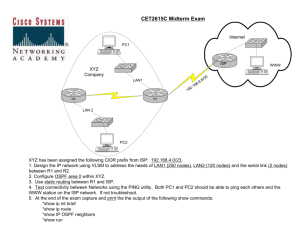
Security activities in Japan towards the future standardization Side Event Cybersecurity Koji NAKAO KDDI, Japan Content Current threats - Internet User in Japan - However, observation of many scans (by using Darknet monitoring) - Botnets threats Security Activities against threats in Japan - Bot countermeasure : CCC project - Trace-back project Conclusion WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 2 Number of Internet Users in Japan WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 3 However, Monitor data through Dark-Net Dark-Net: Unassigned IP addresses space and they are not connected to the Real Servers/PCs. Types of Packets arrived to the Dark-Net: – Scans by means of Malwares; – Malwares infection behaviors; – DDoS attacks by Backscatter; – Miss configurations/mistakes sc a n Darknet It is very useful to Observe the serious attacks behavior over the Internet. ck ba tte a sc r WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 4 Malware infection behavior by means of Dark-Net monitor End-LAN ISP IX Back-Bone ISP ISP Resp. ping TCP Observe the scan behaviors Resp. Hacked! Dark-Net senser WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 5 How large packets can we get from the Dark-Net? (Example: nicter /16 addresses block) 3.5 Million Packets from 150 Thousands Hosts per a day WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 6 Basic concept of Botnets According to analysis of Agobot source code. Owner of Botnets (HERDER) ) IRC SV Sometimes, many IRC Servers are used. It is configured at the site which Herder has hacked. DDoS! HERDER Internet Malicious orders are transmitted via IRC TARGET PCs at home and company DDoS, SPAM, any Infected PCs WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 7 Workflow for Countermeasures against Bot-infected Users in Japan (Cyber Clean Center) [Reference 2] ISP ・・ ・・ ④Requesting identification of infected PCs ⑥Sending e-mail for alerting about infection and urging removal of bots ⑤Identifying infected PCs Cyber Clean Center Bot-infected PCs (Users of participating ISPs) !! ・・ Analysis Internet Internet Honeypots ①Infection activities ②Detection of infection activities Capture of bot analytes ⑦Accessing the countermeasures website ⑧Downloading the botremoval tools Bot-infected PCs (General users) Accessing the disclosure website Countermeasures website [Reference 3] Disclosure website [Reference 1] ・・ Analytes and related information ③Preparation of bot removal tools Downloading the WTSA-08, bot-removal tools Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 8 8 Effect of CCC Activities Changes in Number of New Infections by ISP Linear approximation ISP A ISP B ISP C 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 2007/02/09 2007/03/09 2007/04/09 ISP A 2007/05/09 ISP B 2007/06/09 2007/07/09 2007/08/09 2007/09/09 2007/10/09 2007/11/09 ISP C There There is is aa trend trend of of aa decline decline in in the the number number of of new new users users infected infected by by malware malware 9 WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 9 Outline of Traceback system studied in Japan 1. Store suspicious information. Whenever IDS notify suspicious attacks, TB manager calculate the attack PKT’s HASH, and automatically generate it’s AS map recursively contacting with neighbor AS’s TB manager, and the generated AS map is stored to TB-DB. TB Contral Center 2. Detect the real attack path After an incident be recognized, TBOperator analyze TB-DB by attack PKT’s HASH, and detect the real attack path. TB-DB Real attack path (AS map) TB Manager IDS Prove Incident ISP(a) ISP(b) Real attack ISP(c) Attack from spoofed IP addresses 0. Store HASH data temporary. Each probe convert PKT to HASH, and store own cache automatically. WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 10 Activities related to ITU-T standardizations Since security issues are getting broad, diverse and complex, methodologies of standardization on security should also adapt to its diversification. Standardization of Bot countermeasures, information sharing and traceback technologies are recognized as new topics for ITU-T which apparently need COLLABORATION. Security standards are not only focused on high level requirements, but also focused on frameworks which jointly and actively work together (collaboratively) for Cybersecurity. WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 11 Implement & use Security* Monitor & review Security* Design Security* Maintain & improve Security* WTSA-08, Johannesburg, South Africa, 21-30 October 2008 12