Conductors and Insulators
advertisement
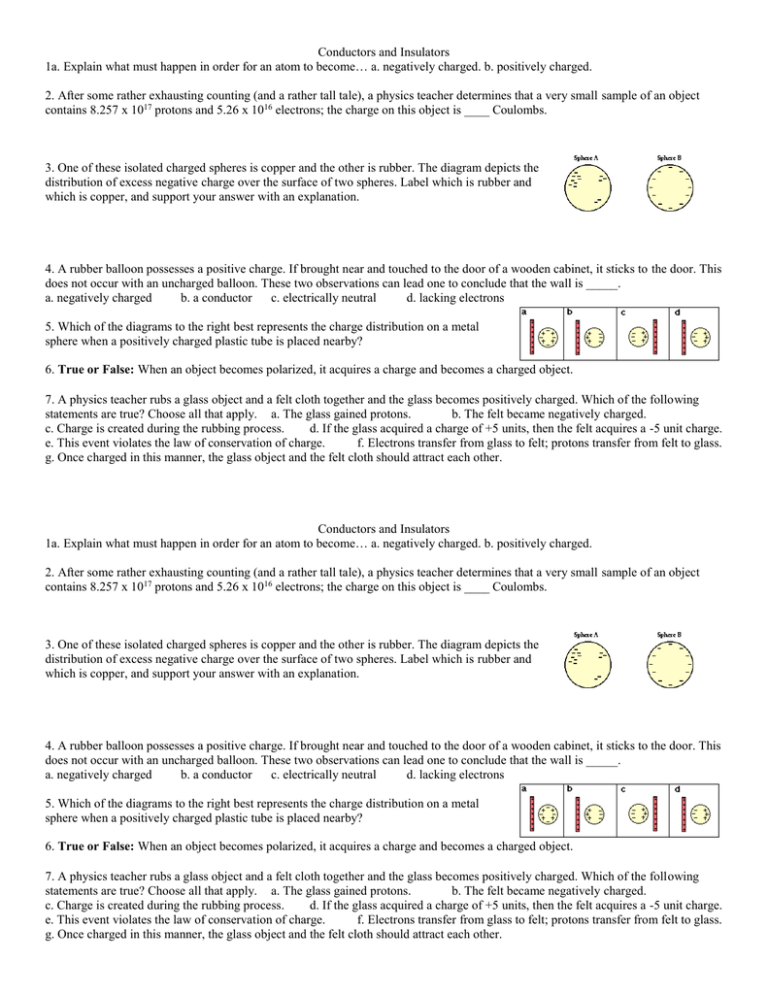
Conductors and Insulators 1a. Explain what must happen in order for an atom to become… a. negatively charged. b. positively charged. 2. After some rather exhausting counting (and a rather tall tale), a physics teacher determines that a very small sample of an object contains 8.257 x 1017 protons and 5.26 x 1016 electrons; the charge on this object is ____ Coulombs. 3. One of these isolated charged spheres is copper and the other is rubber. The diagram depicts the distribution of excess negative charge over the surface of two spheres. Label which is rubber and which is copper, and support your answer with an explanation. 4. A rubber balloon possesses a positive charge. If brought near and touched to the door of a wooden cabinet, it sticks to the door. This does not occur with an uncharged balloon. These two observations can lead one to conclude that the wall is _____. a. negatively charged b. a conductor c. electrically neutral d. lacking electrons 5. Which of the diagrams to the right best represents the charge distribution on a metal sphere when a positively charged plastic tube is placed nearby? 6. True or False: When an object becomes polarized, it acquires a charge and becomes a charged object. 7. A physics teacher rubs a glass object and a felt cloth together and the glass becomes positively charged. Which of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. a. The glass gained protons. b. The felt became negatively charged. c. Charge is created during the rubbing process. d. If the glass acquired a charge of +5 units, then the felt acquires a -5 unit charge. e. This event violates the law of conservation of charge. f. Electrons transfer from glass to felt; protons transfer from felt to glass. g. Once charged in this manner, the glass object and the felt cloth should attract each other. Conductors and Insulators 1a. Explain what must happen in order for an atom to become… a. negatively charged. b. positively charged. 2. After some rather exhausting counting (and a rather tall tale), a physics teacher determines that a very small sample of an object contains 8.257 x 1017 protons and 5.26 x 1016 electrons; the charge on this object is ____ Coulombs. 3. One of these isolated charged spheres is copper and the other is rubber. The diagram depicts the distribution of excess negative charge over the surface of two spheres. Label which is rubber and which is copper, and support your answer with an explanation. 4. A rubber balloon possesses a positive charge. If brought near and touched to the door of a wooden cabinet, it sticks to the door. This does not occur with an uncharged balloon. These two observations can lead one to conclude that the wall is _____. a. negatively charged b. a conductor c. electrically neutral d. lacking electrons 5. Which of the diagrams to the right best represents the charge distribution on a metal sphere when a positively charged plastic tube is placed nearby? 6. True or False: When an object becomes polarized, it acquires a charge and becomes a charged object. 7. A physics teacher rubs a glass object and a felt cloth together and the glass becomes positively charged. Which of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. a. The glass gained protons. b. The felt became negatively charged. c. Charge is created during the rubbing process. d. If the glass acquired a charge of +5 units, then the felt acquires a -5 unit charge. e. This event violates the law of conservation of charge. f. Electrons transfer from glass to felt; protons transfer from felt to glass. g. Once charged in this manner, the glass object and the felt cloth should attract each other. 8. A positively charged soda can is touched by a person standing on the ground. The can subsequently becomes neutral because____. a. electrons pass from the soda can to the person (ground) b. electrons pass from the person (ground) to the soda can c. protons pass from the soda can to the person (ground) d. protons pass from the person (ground) to the soda can 9. A negatively charged balloon is brought near a neutral conducting sphere as shown below. As it approaches, charge within the sphere will distribute itself in a very specific manner. Which one of the diagrams properly depicts the distribution of charge in the sphere? Answer #10 -12 on a SEPARATE piece of paper. 10. How are conductors different from insulators? 11. Using words and pictures (like the picures in #9 of a conducting sphere sitting on top of an insulator), describe how to charge a conducting sphere by induction, with a negatively charged balloon. What charge will the sphere have afterward? 12a. Explain the process of how a charged object attracts a neutral conductor. b. Explain the process of how a charged object attracts a neutral insulator. 8. A positively charged soda can is touched by a person standing on the ground. The can subsequently becomes neutral because____. a. electrons pass from the soda can to the person (ground) b. electrons pass from the person (ground) to the soda can c. protons pass from the soda can to the person (ground) d. protons pass from the person (ground) to the soda can 9. A negatively charged balloon is brought near a neutral conducting sphere as shown below. As it approaches, charge within the sphere will distribute itself in a very specific manner. Which one of the diagrams properly depicts the distribution of charge in the sphere? Answer #10 -12 on a SEPARATE piece of paper. 10. How are conductors different from insulators? 11. Using words and pictures (like the picures in #9 of a conducting sphere sitting on top of an insulator), describe how to charge a conducting sphere by induction, with a negatively charged balloon. What charge will the sphere have afterward? 12a. Explain the process of how a charged object attracts a neutral conductor. b. Explain the process of how a charged object attracts a neutral insulator.