Bluetooth Secure Simple Pairing Personal Area Network Countermeasure DOS Middle Attack Yashpal
advertisement
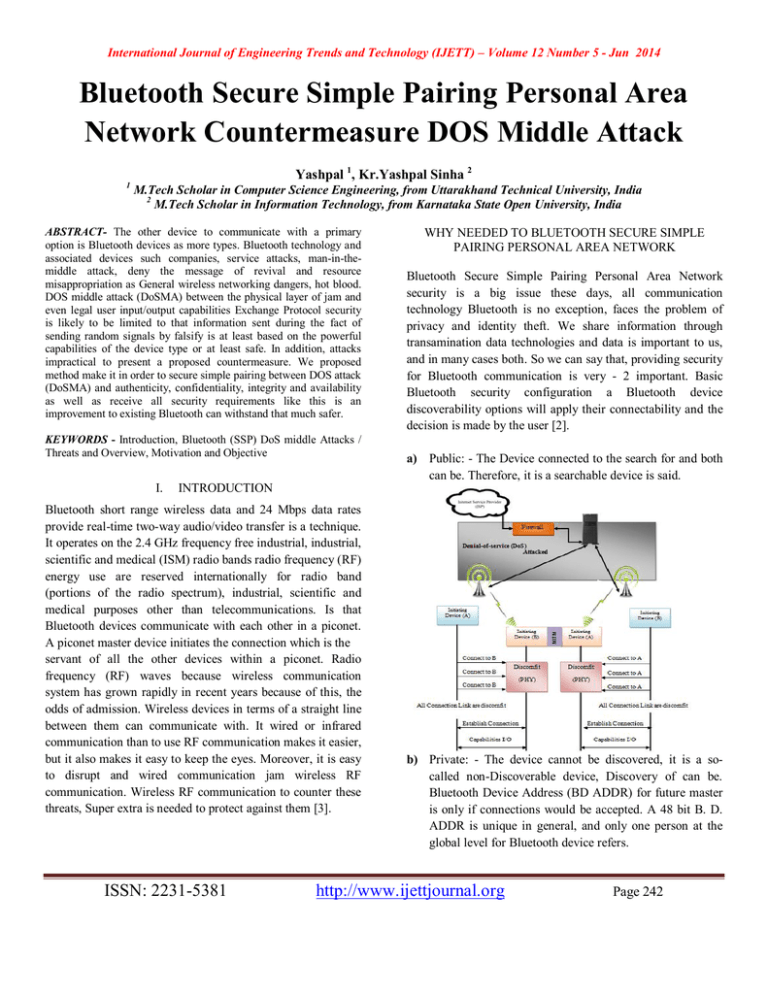
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 12 Number 5 - Jun 2014 Bluetooth Secure Simple Pairing Personal Area Network Countermeasure DOS Middle Attack Yashpal 1, Kr.Yashpal Sinha 2 1 M.Tech Scholar in Computer Science Engineering, from Uttarakhand Technical University, India 2 M.Tech Scholar in Information Technology, from Karnataka State Open University, India ABSTRACT- The other device to communicate with a primary option is Bluetooth devices as more types. Bluetooth technology and associated devices such companies, service attacks, man-in-themiddle attack, deny the message of revival and resource misappropriation as General wireless networking dangers, hot blood. DOS middle attack (DoSMA) between the physical layer of jam and even legal user input/output capabilities Exchange Protocol security is likely to be limited to that information sent during the fact of sending random signals by falsify is at least based on the powerful capabilities of the device type or at least safe. In addition, attacks impractical to present a proposed countermeasure. We proposed method make it in order to secure simple pairing between DOS attack (DoSMA) and authenticity, confidentiality, integrity and availability as well as receive all security requirements like this is an improvement to existing Bluetooth can withstand that much safer. KEYWORDS - Introduction, Bluetooth (SSP) DoS middle Attacks / Threats and Overview, Motivation and Objective I. WHY NEEDED TO BLUETOOTH SECURE SIMPLE PAIRING PERSONAL AREA NETWORK Bluetooth Secure Simple Pairing Personal Area Network security is a big issue these days, all communication technology Bluetooth is no exception, faces the problem of privacy and identity theft. We share information through transamination data technologies and data is important to us, and in many cases both. So we can say that, providing security for Bluetooth communication is very - 2 important. Basic Bluetooth security configuration a Bluetooth device discoverability options will apply their connectability and the decision is made by the user [2]. a) Public: - The Device connected to the search for and both can be. Therefore, it is a searchable device is said. INTRODUCTION Bluetooth short range wireless data and 24 Mbps data rates provide real-time two-way audio/video transfer is a technique. It operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency free industrial, industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio bands radio frequency (RF) energy use are reserved internationally for radio band (portions of the radio spectrum), industrial, scientific and medical purposes other than telecommunications. Is that Bluetooth devices communicate with each other in a piconet. A piconet master device initiates the connection which is the servant of all the other devices within a piconet. Radio frequency (RF) waves because wireless communication system has grown rapidly in recent years because of this, the odds of admission. Wireless devices in terms of a straight line between them can communicate with. It wired or infrared communication than to use RF communication makes it easier, but it also makes it easy to keep the eyes. Moreover, it is easy to disrupt and wired communication jam wireless RF communication. Wireless RF communication to counter these threats, Super extra is needed to protect against them [3]. ISSN: 2231-5381 b) Private: - The device cannot be discovered, it is a socalled non-Discoverable device, Discovery of can be. Bluetooth Device Address (BD ADDR) for future master is only if connections would be accepted. A 48 bit B. D. ADDR is unique in general, and only one person at the global level for Bluetooth device refers. http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 242 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 12 Number 5 - Jun 2014 c) Silent: - The device will never accept any connection. It's just the Bluetooth traffic monitors. BLUETOOTH (SSP) DoS MIDDLE ATTACKS AND THREATS Classification of severity of threat risks, precautions, and can assist in finding your counter. The risk classification (subjects) a Bluetooth a roadmap to satisfying all threats. There are nine different classes in the subject. In particular, concerning classification monitoring, range extension, nervousness, fuzzing, sniffing, denial of service (DOS), malware, unauthorized direct data access (UDDA), and MITM. The same attack can fall under several classification, however the key feature of every attack, its only one classification [1]. a) Surveillance Attacks: - Monitoring Bluetooth devices used to gather information from which an attack. These monitoring tools to cause adverse effects. Monitoring visits, audit risks under Blueprinting, red Fang, nibbling, bluefish, Canner, depressed and Sdptool BT scanner. b) Range Extension Attacks: - The range of any wireless device will be somewhat limited. Extend the range of a device the used. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) may be against the rules, but to conduct the attack from a distance of attackers can use it. Range expansion of Bluetooone and Vera blue sniping, the threats under NG. c) Obfuscation / Confusedness Attacks: - Attackers to launch an attack to achieve anonymity level of trepidation. Under threats of intimidation Bdaddr obfuscation, Hciconfig and Spooftooph. Network security, network security systems of inspection by panic attack payload to methods obscure. d) Fuzzer Attacks: - Dealing with application Fuzzing input used to test the technology. An application for obtaining malicious results Fuzzers nonstandard input by submitting work. Under threats of intimidation Fuzzer blue pass, Bluetooth stack Smasher, blue smack, Tanya and blue knives. e) Sniffing Attacks: - The Keep eyes on just one phone line, sniffing in transit traffic to capture process. Bluetooth, wirelessly broadcast traffic RF it is vulnerable to outside monitoring at specific frequencies. f) Malware Attacks:- The Malware such as data mining, accessing individual files, passwords, file corruption, and system punarvinyasan as carries out various activities that malicious software is often a self-replicating. A small subset of commonly known malware detections saw more ISSN: 2231-5381 Android Android malware threats 140,000 reporting viruses, worms, and Trojan horses and top 10 countries. Reported detections of almost 42% came from Saudi Arabia and 33% from India. European countries are responsible for 15%, and 5% in the US came along [1]. g) Man in the Middle Attacks:- MITM attacks a relay (the attacker to hide the device flurry attack) to act as an attack between two connected devices device. Paired devices before the attack to his scheduled destination relay which can send your information to the device [5]. h) Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: - To make the service unavailable. These attacks often target communications channels, but the device's processor, memory, disk space, battery life, and the system uses, including the availability of any service related. Tools Firewall rules cannot be defined that provides many security options. This "denial of service attacks" includes many types of protection. To thwart these attacks and computer security. Service (DOS) attacks to serve legitimate users Daniel hackers use a prevent or refuse that is used for a method. DOS attacks usually make the system unusable, the targeted server flood resources of the server (usually the Web, FTP, or mail servers), many requests are executed by sending packets. Your goal is to prevent information theft but passive or users now have access to network services/resources, so as to deprive a device or network [2]. All servers they become idle, forward, to a maximum. There are two types of DoS attacks:1. Computer Attack 2. Network Attack http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 243 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 12 Number 5 - Jun 2014 OVERVIEW OF DENIAL-OF-SERVICE (DoS) ATTACKS a) Synchronize (SYN) Flood: - Source and destination of the packet rate (packets/second) burst rate (packets/min) and configuration. Number of packets allowed applying SYN flood definition and control ‘apply’ checkbox, clicking on the flag. Source displays the number of packets the source traffic source packet rate control is applied in the case of the drop. Displays the number of packets to destination traffic packet rate control is applied in the case of the drop. To see real-time updates on flooding SYN flood. b) ICMP Flood: - An Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packet header is 8 bytes long. The first four bytes always have the same meaning, and the remaining four ICMP packets, depending on the type of content. Configure the source and destination of the packet rate (packets/min) and burst rate (packets/second). Number of ICMP packets is allowed to apply the definitions and control flooding ' apply ' checkbox, click on the flag. To see real-time updates on flooding ICMP/ICMPv6 flood. The flood was targeted and which IP address was used to that-this source IP address. Host/victim computers could not handle the Protocol implementation, so that ICMP/ICMPv6 packets/attack sends massive amounts of traffic [2]. c) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Flood:- An attacker due to this type of attack, many UDP ports on a remote host with random packet flood victims now can handle legitimate connection to talk to the victim containing IP datagram UDP aimed to slow sends packets when UDP flood happens time and time again that check for application listen on port, And (no application found) an ICMP destination unreachable packet with the host. This process may eventually reach saps, and host resources. d) Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) Flood: - TCP attack sends huge amount of TCP packet so that the host/victim computer cannot handle. II. MOTIVATION AND OBJECTIVE Internet running on multiple hardware and software platforms around the world hundreds of millions of computers connected. It's personal and professional needs of people and corporations. However, attackers’ abuse resources and arbitrary denial of service (DOS) against sites to mount attacks computer use this difference between connectivity. A malicious user with many requests a victim fooding, a victim services offered by the site to take advantage of Internet ISSN: 2231-5381 connectivity. To launch the attack and compromise the host process to automate the sophisticated attack tools are readily available on the Internet, and detailed instructions, even an amateur to use them effectively [1]. Denying service attacks must detect and respond quickly to attacks makes framing technique, which each year cause substantial financial loss. Development of effective feedback techniques requires intimate knowledge of the dynamics of the attack; yet in the wild attacks less information is published in the research community. Moore et al dominated activity on the Internet provides insight into DOS, but their analysis is based on backscatter packets and studying or DOS attack dynamics research to generate high fidelity required for the level of detail required for the model lacks. Today's attack detection and monitoring devices such as traffic rates and packet type can identify basic properties [5]. For example: - FTP data packets and acknowledgement packets of 1500 bytes 40 bytes. Visit and Abe this fact and to detect DOS attacks proposed IP packet size entropy. Here the concept of IP packet was commonality and packet size entropy as. Check packet size entropy time series observed any changes by time slot a few spikes serve as a refusal to attack will be to indent. Both long-term and short-term attacks this method is able to detect. Real time data analysis organizations many of their geographical position vectors and maps the requests to analyze the use of our Web application that helps an Analytics interface. Server load balancing and content-based routing, application increases the speed of use of server resources and static applications Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption co-processing, offloads encryption functions accelerates transaction times, and reduces Web server processing requirements During the different hours and days of the week to rate the application identifies. For example, some applications quite apart from their traffic and other hours other days of http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 244 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 12 Number 5 - Jun 2014 the week on Monday morning rush hour traffic can draw level. Application and network based Denial of Server (DoS) policies IV. REFERENCES [1]. [2]. [3]. [4]. [5]. [6]. [7]. An Improved Packet size Entropy Based DoS Attack Detection Scheme (ASWANI KUMAR ) May 2013 "Cyber Security Tip ST04-015 - Understanding Denial-of-Service Attacks". United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team. Archived from the original on 2013-11-04. Retrieved December 11, 2013. Man-in-the-Middle Attack and its Countermeasure in Bluetooth Secure Simple Pairing (M Thrinatha Reddy) 2011 K. Haataja and P. Toivanen. Two practical man-in-the-middle attacks on Bluetooth secure simple pairing and countermeasures. Wireless Communications, IEEE Transactions on, 9(1):384-392, Jan. 2010. RobotSkirts. Bluetooth keyboard attacks, Feb 2010. http://www.robotskirts.com/2010/02/06/bluetooth-keyboardattacks/. Timothy K. Buennemeyer and Randy C. Marchany Michael A. Gora. Battery polling and trace determination for bluetooth attack detection in mobile devices. IEEE Leyden, John "US credit card firm fights DDoS attack". The Register. Retrieved 2011-12-02 III. CONCLUSION The thesis introduction explore the denial of service attack packet size distribution using and distributing this research are an alternative introduction to the technique and it was disclosed that the MITM attack research, Bluetooth range is very damaging. We Internet Protocol services to protect against MITM attacks ID and also support them has never been the has been used in Bluetooth range till today. Know the research packet size distribution and distribution by using denial of service attacks an alternative technology. IPSE-based denial of service detection of new plan's major strengths that come with changing packet size denial of service attacks can hit. We have real time traffic by using the data to prove it. Our method is better than all other methods that are not claimed. Yet we deny our plan packet size distribution feature can deliver service attacks. The main obstacle comes with different source addresses and change comes with the packet that is a distributed denial of service attack. Still a lot of research opportunities are available in this area IV. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We would like to thank Asst.Prof. Nikhil Ranjan, MCA Department IMS Dehradun for his immense support and guidance. We would also like to thank CSE department JBIT Dehradun. ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 245






